HashMap、ConcurrentHashMap数据结构、底层原理、源码分析
- HashMap
数据结构
JDK1.7
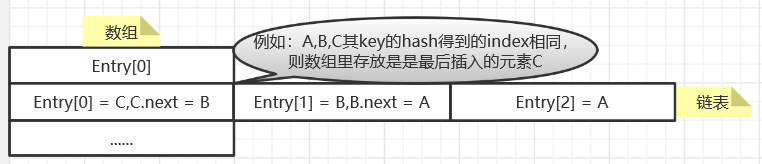
HashMap由数组+单向链表组成,数组是HashMap的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的。
什么是哈希冲突?由于哈希算法被计算的数据是无限的,而计算后的结果范围有限,因此总会存在不同的数据经过计算后得到的值相同,这就是哈希冲突。
如果发生hash冲突,HashMap会将同一个桶中的数据以链表的形式存储,但是如果发生hash冲突的概率比较高,就会导致同一个桶中的链表长度过长,遍历效率降低。
JDK1.8
HashMap由数组+单向链表/红黑树组成,当链表长度大于阈值(默认为8)时,将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间。
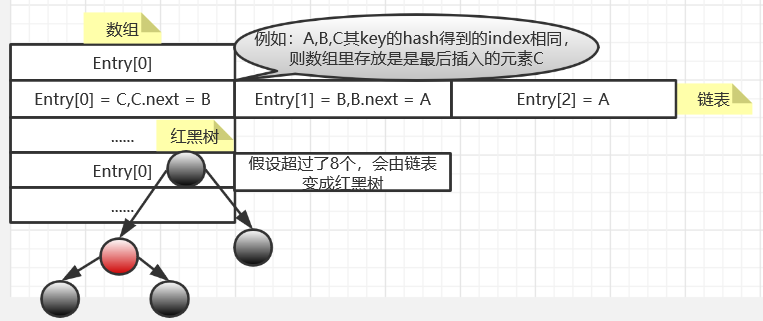
转为红黑树后,链表的结构仍然会存在,通过next属性维持,红黑树节点在进行操作时都会维护链表的结构。
底层原理
怎么实现扩容?(JDK1.7)
hashMap默认的初始容量是16,加载因子是0.75;我们也可以通过构造器 HashMap(int initialCapacity) 来指定初始容量,但需要为2的n次幂,每次扩容都为原来的两倍。
当达到其容量的3/4时,会自动进行扩容,如初始为16,存储第12个元素时,这时候会扩容为32,同时,这时需要创建一张新表,将原表的数据移到新表,可以看resize()和transfer()方法。

void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
在扩容时,JDK1.8不需要像JDK1.7的实现那样重新计算hash,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变,是1的话索引变成“原索引+oldCap”。
怎么实现存取?
key可以存放null,null key总是存放在Entry[]数组的第一个元素,可以看putForNullKey()方法。
HashMap存取时,都需要计算当前key应该对应Entry[]数组哪个元素,通过调用hash()方法,得到hash值,再调用indexFor()得到Entry[]数组下标。

final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } /** * Returns index for hash code h. */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; return h & (length-1); }
如果有两个相同的结果,如果hash相同且key对象为同一个,则为同一个对象,直接在该位置替换原对象;否则为不同对象,这时候发生碰撞了,我们通过链表来存储,可以分析createEntry()方法。

void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; } static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; /** * Creates new entry. */ Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } }
源码分析(JDK1.7)
- put

/** * JDK 1.7 */ public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } /** nullkey */ private V putForNullKey(V value) { for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(0, null, value, 0); return null; }
- get

/** * JDK 1.7 */ public V get(Object key) { if (key == null) return getForNullKey(); Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); } final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } return null; } private V getForNullKey() { if (size == 0) { return null; } for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) return e.value; } return null; }
- ConcurrentHashMap(JDK1.7)
数据结构
JDK1.7仍然是数组+单向链表
底层原理
ConcurrentHashMap怎么实现同步的?和HashMap不同之处,ConcurrentHashMap最外层是多个Segment,每个Segment数据结构和HashMap类似,数组+链表组成。每个Segment 都有一个ReentrantLock锁,之间互不影响。
1、HashEntry内部类里的value ,以及链表next都是volatile 修饰的,能保证获取时的可见性。

static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; } static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; transient int count; transient int modCount; transient int threshold; final float loadFactor; }
2、采用了分段锁技术,具体可以看Segment内部类 ,继承于 ReentrantLock。每当一个线程占用锁访问一个 Segment 时,不会影响到其他的 Segment。
可以看下面的put()方法,put里面第一次尝试加锁,利用自旋获取锁,ReentrantLock提供的tryLock() 方法。
如果如果重试的次数达到了 MAX_SCAN_RETRIES 则改为阻塞锁获取,ReentrantLock提供的lock()方法,这种方式获取不到则一直休眠等待,直到能获取成功。

final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; }

private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) { HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash); HashEntry<K,V> e = first; HashEntry<K,V> node = null; int retries = -1; // negative while locating node while (!tryLock()) { HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below if (retries < 0) { if (e == null) { if (node == null) // speculatively create node node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); retries = 0; } else if (key.equals(e.key)) retries = 0; else e = e.next; } else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { lock(); break; } else if ((retries & 1) == 0 && (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) { e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed retries = -1; } } return node; }
JDK1.8改为了数组+单向链表+红黑树的数据结构,链表长度增加到8时,可能触发变为红黑树,加快查找速度;
在JDK1.7中Segment在初始化时默认为16,可以设置初始化但后续不能扩容修改,在JDK1.8中取消了Segment,直接用HashEntry<K,V>,在一些特定情况会扩容。




