读取数据中的时间
pd.read_csv('demo.csv'
,parse_dates = ['col1'] # 待转换为**datetime64[ns]**格式的列→col1
,infer_datetime_format=True # 将parse_dates指定的列转换为时间
)
data = pd.read_csv(workbook, parse_dates = ['start_time', 'con_over_time'],infer_datetime_format=True, low_memory=False)
计算相差秒数
两种不同时间格式的计算结果当然是一样的。
#datetime64[ns]格式计算相差秒数 df['ns时间秒差'] = df['A_ns'] - df['B_ns'] df['ns时间秒差'] = pd.to_timedelta(df['ns时间秒差']) df['ns时间秒差'] = df['ns时间秒差'].dt.total_seconds() #datetime64[ns, UTC]格式计算相差秒数 df['ns_utc时间秒差'] = df['A_ns_utc'] - df['B_ns_utc'] df['ns_utc时间秒差'] = pd.to_timedelta(df['ns_utc时间秒差']) df['ns_utc时间秒差'] = df['ns_utc时间秒差'].dt.total_seconds() df
计算相差天数
datetime_start = datetime.strptime(start_date, "%Y-%m-%d") datetime_end = datetime.strptime(end_date, "%Y-%m-%d") delta_days = (datetime_end - datetime_start).days
提取年和月份
import numpy as np # 创建一个datetime64对象 dt = np.datetime64('2022-07-15 12:30') # 提取年份 year = np.datetime_as_string(dt, unit='Y') # 提取月份 month = np.datetime_as_string(dt, unit='M') print("Year:", year) print("Month:", month)
dataframe
data['入住日期'].dt.year #获取年份 data['入住日期'].dt.month #获取月份 data['入住日期'].dt.quarter #获取季度
data['入住日期'].dt.weekday
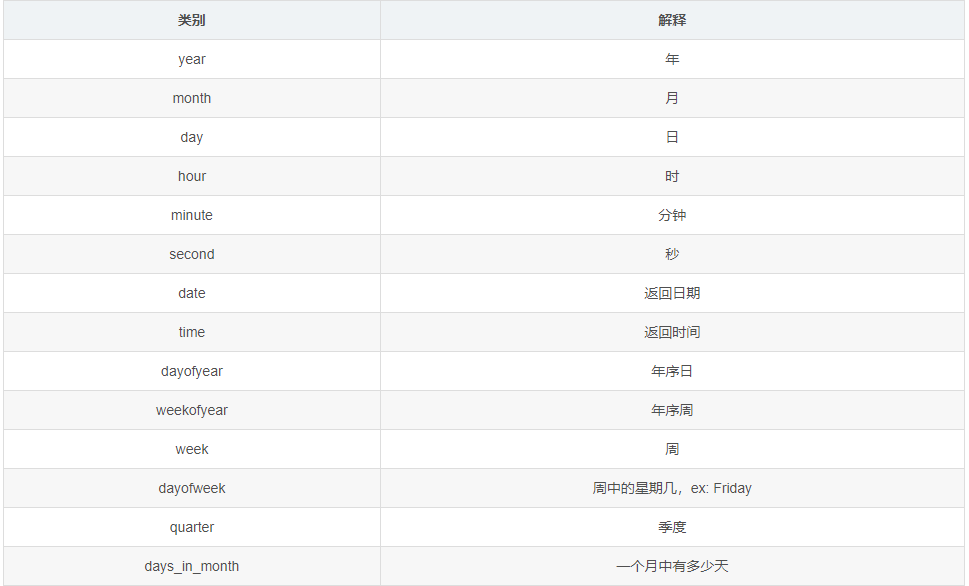
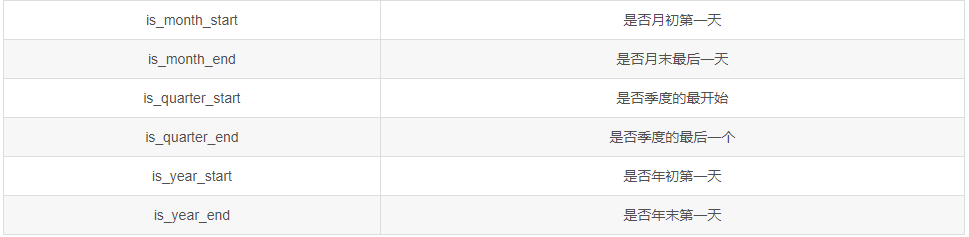
pandas.Series.dt对象能够返回的信息有:
strftime函数格式化日期
strftime函数实际上是datetime模块中的函数,并不是pandas中的成员,在实际工作中我们常用这种方式对日期进行格式化
api:datetime.strftime(date,format_str)
date:需要格式化的日期
format_str:格式化字符串
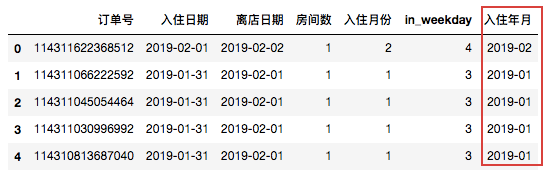
例如:我们需要提取’入住日期’的年份和月份组成一个新的列:
#首先需要引入datetime模块 from datetime import datetime #配合apply函数 data.loc[:,'入住年月']=data['入住日期'].apply(lambda x:datetime.strftime(x,"%Y-%m")) data.head()
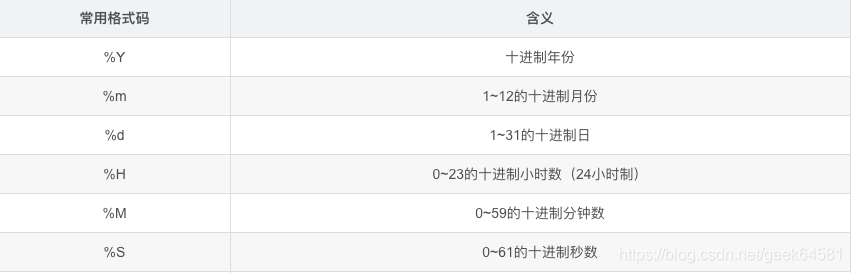
常用格式字符串介绍:
Series.dt.to_period 另一种方法
data.loc[:,'入住年月2']= data['入住日期'].dt.to_period('M') data.head()
第二种方法使用起来更加简单,参数 M 表示月份,Q 表示季度,A 表示年度,D 表示按天,这几个参数比较常用。
Jupyter中打印进度条
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm with tqdm(total=len(df['imei'].unique())) as pbar: pbar.set_description('Processing:') for imei, group in df.groupby(['imei']): mean_current = group['con_avg_current_no_charging'].mean() imei_current_dic[imei] = mean_current # print('imei: ', imei, ', mean_avg_current: ', mean_current) pbar.update(1)
DataFrame中常见的其他方法
df.count() #非空元素计算 df.min() #最小值 df.max() #最大值 df.idxmin() #最小值的位置,类似于R中的which.min函数 df.idxmax() #最大值的位置,类似于R中的which.max函数 df.quantile(0.1) #10%分位数 df.sum() #求和 df.mean() #均值 df.median() #中位数 df.mode() #众数 df.var() #方差 df.std() #标准差 df.mad() #平均绝对偏差 df.skew() #偏度 df.kurt() #峰度 df.describe() #一次性输出多个描述性统计指标
字符串转datetime obj
from datetime import datetime # 输入的字符串日期时间 date_string = "2023-08-04 15:30:00" # 按照特定的格式将字符串转换为 datetime format_string = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" datetime_obj = datetime.strptime(date_string, format_string) print("转换后的 datetime 对象:", datetime_obj)
datetime obj 转字符串
datetime_str = datetime_obj.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
获取特定日期
import datetime cur_date = (datetime.date.today() - datetime.timedelta(days=1)).strftime("%Y%m%d")




