django基础 -- 7.Ajax
一.ajax 的特点
1.异步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,需要等待服务器响应结束后,
才能发出第二个请求
2.局部刷新:给用户的感受是在不知不觉中完成请求和响应过程.
二.ajax 模板示例 ($.ajax({}) )

1.urls.py文件中
from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views #引入views.py 文件
urlpatterns = [ # url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^login/', views.login,name='login'), url(r'^home/', views.home,name='home'), ]
2.views.py 文件中
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect #响应模块 from django.http import JsonResponse #django自带的 json加工模块 from app01 import models #数据库加工模块 from django.urls import reverse # 反向解析模块 import json #引入 json 模块 # Create your views here. def home(request): return render(request,'home.html') def login(request): if request.method == 'GET': # get请求 响应方式 return render(request,'login.html') else: a = {'status': None, 'home_url': None} #一个开始的状态 username = request.POST.get('user') pwd = request.POST.get('password') ret=models.name_pwd.objects.filter(name=username,password=pwd)
#与数据库中的信息进行对比 if ret: # 数据库中是否存在数据 a['status'] = True #更改状态 a['home_url'] = reverse('home') a_json = json.dumps(a) 转换成 json 格式的字符串 return HttpResponse(a_json) else: a_json = json.dumps(a) return HttpResponse(a_json)
3.在 .html 中
{% load static %} #引入静态文件的路径
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
{% csrf_token %} #post 提交方式必须加的验证方式
<input type="text" class="d2">
<input type="password" class="d3">
<button class="d1">登录</button>
<span class="msg" style="color: red"></span> #预留添加字符串的地方
</body>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.js' %}"></script> #引入 js
<script>
$('.d1').click(function () { # 绑定点击事件
var name = $(".d2").val();
var pwd = $('.d3').val();
var csrf_token = $('input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]').val();
$.ajax({ #绑定 ajax 格式
url:"{% url 'login' %}", # 提交的路径
type:'post',
data:{'user':name,'password':pwd ,'csrfmiddlewaretoken':csrf_token},
# 给后端的数据
success:function (content) { 获得响应数据 (content是参数)
ret= JSON.parse(content); #将json格式的字符串 变为 前端格式的字符串
if (ret .status){
$('.msg').text('成功啦!'); #向预留的地方添加字符串
location.href = ret.home_url 跳转到相应路径
}
else {
$('.msg').text('失败了,检查一下自己输入的内容');
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
4.通过 json 转换格式的 三种方式
① 引入 json模块
1). 在后端文件 views.py中

2)将python类型的数据转换成 json 类型的数据
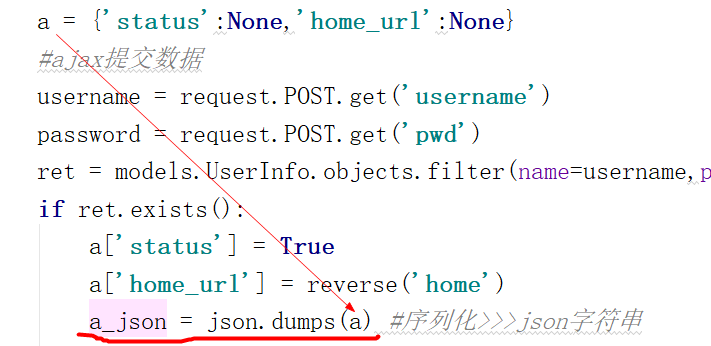
3).在前端文件 .html 中 将 json类型的数据转换成前端js类型

② 引入 django 自带的 json处理模块
1)在 views.py 文件中 引入模块
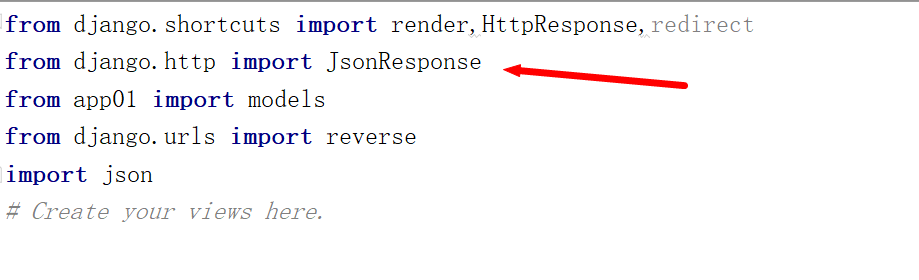
2).

3).在前端.html 文件中直接调用

③ 响应信息是 加消息头
1) 在 后端views.py文件中

2).在前端.html 文件中, 直接调用传过去的数据

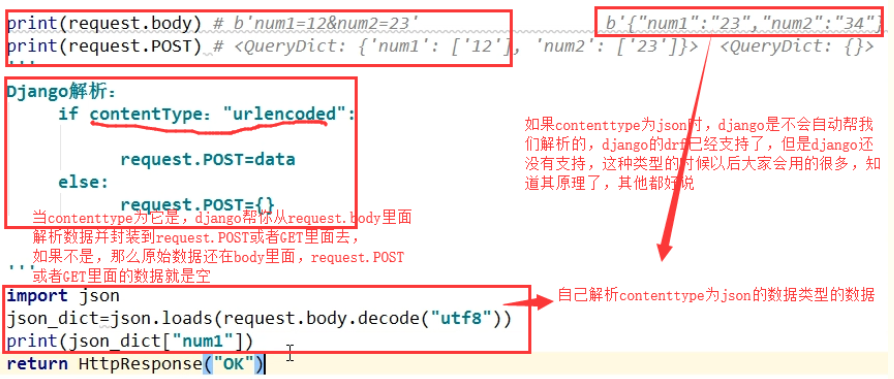
三.请求头 (content_type)

1. application/x-www-form-urlencoded (默认)
请求信息用 "&" 连接
这应该是最常见的 POST 提交数据的方式了。浏览器的原生 <form> 表单,如果不设置 enctype 属性,
那么最终就会以 默认格式application/x-www-form-urlencoded 方式提交数据,ajax默认也是这个。
POST http://www.example.com HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8 user=yuan&age=22 #这就是上面这种contenttype规定的数据格式,后端对应这个格式来解析获取数据,
不管是get方法还是post方法,都是这样拼接数据,大家公认的一种数据格式,但是如果你contenttype
指定的是urlencoded类型,但是post请求体里面的数据是下面那种json的格式,那么就出错了,
服务端没法解开数据。
2.multipart/form-data (传输文件)
将文件分成一段一段的传输
3. application/json (json格式)
①请求信息与响应信息
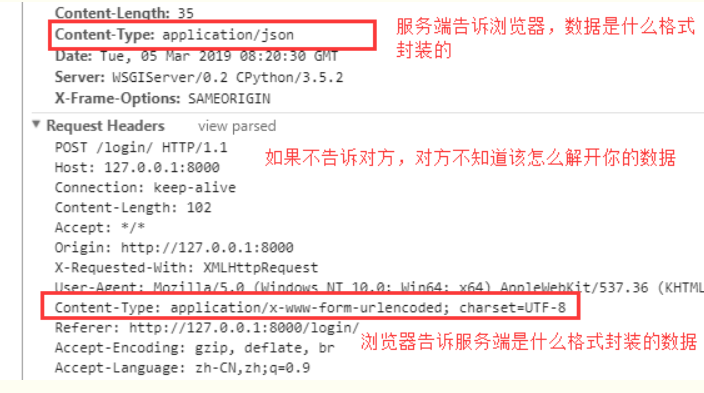
②服务端指定为json 格式
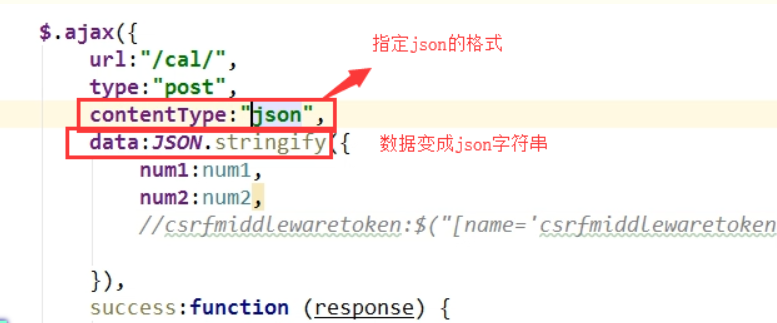
③
四. 文件上传
1.基于表单的文件上传
①在 .html 文件中
{% load static %} #导入静态文件路径 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Title</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}">
#导入bootstrap </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3"> <form class="form-horizontal" method="post" action="{% url 'upload' %}"
enctype="multipart/form-data"> #插入发送文件的 请求头 {% csrf_token %} #POST请求的验证 <div class="form-group"> <label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">用户名</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="text" class="form-control" id="inputEmail3"
placeholder="用户名" name="username"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 control-label">头像</label> <div class="col-sm-10"> <input type="file" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="文件" name="file_obj"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"> <div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">提交</button> </div> </div> </form> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
②在view.py文件中
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse import os from 文件上传 import settings #导入 setting.py 文件中的路径 def upload(request): if request.method == 'GET': return render(request,'upload.html') else: username = request.POST.get('username') file_obj = request.FILES.get('file_obj') #获取文件 file_name = file_obj.name #获取文件名 path = os.path.join(settings.BASE_DIR, 'statics', 'img', file_name) #拼接保存路径 with open(path,'wb')as f: #要保存到的文件位置 #for i in file_obj: #读取上传的文件 #f.write(i) #写入新文件
for chunk in file_obj.chunks(): #常使用的读取方式,数据大小可控
f.write(chunk)
return HttpResponse('ok')
2.基于 Ajax 的上传文件
① view.py 文件中获取方法 相同
② 在 前端.html 文件中
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">
{% csrf_token %}
<div>
用户名:
<input type="text" name ='username'>
</div>
<div>
<input type="file" name="file_obj">
</div>
<button id="sub">提交</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.js' %}"></script>
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.cookie.js' %}"></script>
<script>
$("#sub").click(function () {
var name = $("input[name=username]").val();
var file = $('input[type=file]')[0].files[0]; #获取上传的文件
var csrf = $('input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]').val();
var formdata = new FormData(); #上传文件时需要的类型
formdata.append('username',name); #将请求的数据加入新类型中
formdata.append('file_obj',file);
formdata.append('csrfmiddlewaretoken',csrf);
$.ajax({
url:'{% url 'upload' %}',
type:'post',
data:formdata,
processData: false , // 不处理数据(必写)
contentType: false, // 不设置内容类型(必写)
success:function (response) {
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
五. Ajax请求设置csrf_token
1.通过获取隐藏的input标签中的csrfmiddlewaretoken值,
放置在data中发送。
$.ajax({ url: "/cookie_ajax/", type: "POST", data: { "username": "chao", "password": 123456, "csrfmiddlewaretoken": $("[name = 'csrfmiddlewaretoken']").val()
// 使用jQuery取出csrfmiddlewaretoken的值,拼接到data中 }, success: function (data) { console.log(data); } })
2.
$.ajaxSetup({ data: {csrfmiddlewaretoken: '{{ csrf_token }}' }, });
3.通过获取返回的cookie中的字符串 放置在请求头中发送。
(在发送 json格式的时候只能通过这种方式)
注意:需要引入一个jquery.cookie.js插件。
<script src="{% static 'js/jquery.cookie.js' %}"></script> $.ajax({ headers:{"X-CSRFToken":$.cookie('csrftoken')},
#其实在ajax里面还有一个参数是headers,自定制请求头,可以将csrf_token加在这里,
我们发contenttype类型数据的时候,csrf_token就可以这样加 })
$.ajax({ url: "/cookie_ajax/", type: "POST", headers: {"X-CSRFToken": $.cookie('csrftoken')}, // 从Cookie取csrftoken,并设置到请求头中 data: {"username": "chao", "password": 123456}, success: function (data) { console.log(data); } })
六. json


七. sweetAlert 插件
1.插件下载 点击

2.引入插件

3.示例:
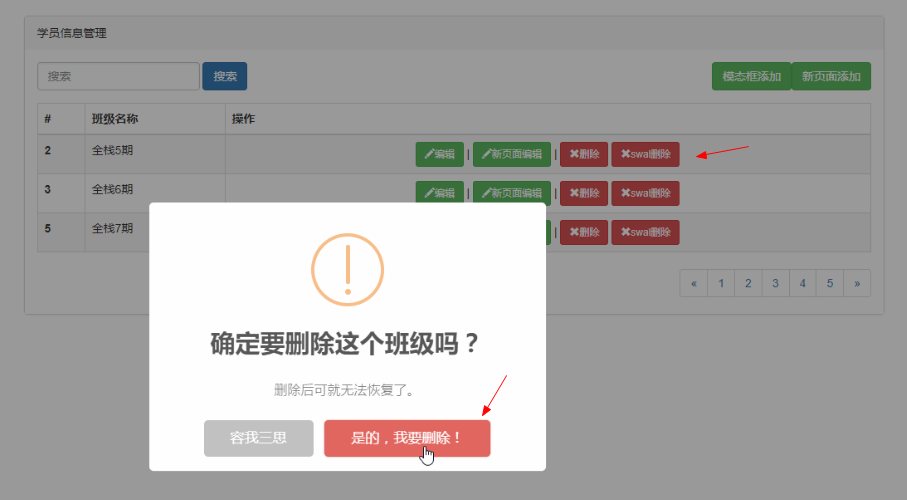
{% load static %} <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <!-- 上述3个meta标签*必须*放在最前面,任何其他内容都*必须*跟随其后! --> <title>Bootstrap 101 Template</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css
/bootstrap.min.css' %}"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'plugins/bootstrap-sweetalert-master
/dist/sweetalert.css' %}"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'plugins/bootstrap-sweetalert-master/
lib/sweet-alert.less' %}"> </head> <body> <button class="btn-danger">删除</button> <script src="{% static 'js/jquery.js' %}"></script> <script src="{% static 'plugins/bootstrap-sweetalert-master/dist
/sweetalert.js' %}"></script> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script> <script> $(".btn-danger").on("click", function () { swal({ title: "你确定要删除吗?", text: "删除可就找不回来了哦!", type: "warning", showCancelButton: true, confirmButtonClass: "btn-danger", confirmButtonText: "删除", cancelButtonText: "取消", closeOnConfirm: false }, function () { var deleteId = $(this).parent().parent().attr("data_id"); $.ajax({ url: "/delete_book/", type: "post", data: {"id": deleteId}, success: function (data) { if (data.status === 1) { swal("删除成功!", "你可以准备跑路了!", "success"); } else { swal("删除失败", "你可以再尝试一下!", "error") } } }) }); }) </script> </body> </html>
八. 对json序列化日期时间 的插件
import json from datetime import datetime from datetime import date #对含有日期格式数据的json数据进行转换 class JsonCustomEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, field): if isinstance(field,datetime): return field.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') elif isinstance(field,date): return field.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') else: return json.JSONEncoder.default(self,field) d1 = datetime.now() dd = json.dumps(d1,cls=JsonCustomEncoder) print(dd)
补充:
1.在 setting.py 文件中设置上 以下代码
可显示操作数据库时执行的mysql 语句
LOGGING = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'handlers': { 'console':{ 'level':'DEBUG', 'class':'logging.StreamHandler', }, }, 'loggers': { 'django.db.backends': { 'handlers': ['console'], 'propagate': True, 'level':'DEBUG', }, } }


