引用:https://www.cnblogs.com/kingos/p/4498224.html
方法一:将链表数据全部读到数组中,然后在倒序输出。
方法二:从第二个结点开始,记录它的下个结点,把它挪到第一个结点之前,成为新表头,然后下个结点继续这个过程。
方法三:从第二个结点开始,把之后的每个结点都插入到第一个结点之后,最后在把第一个结点挪到表尾。
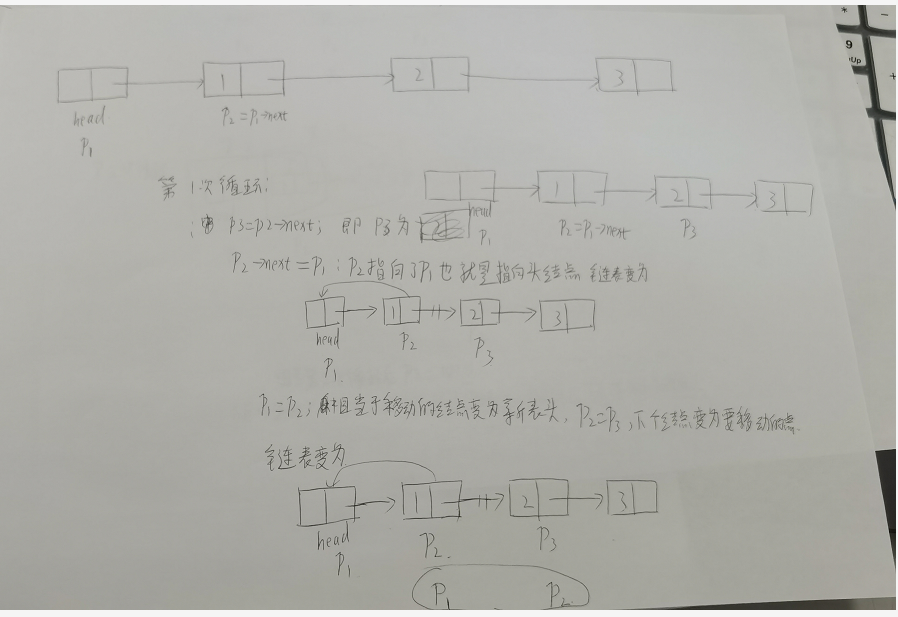
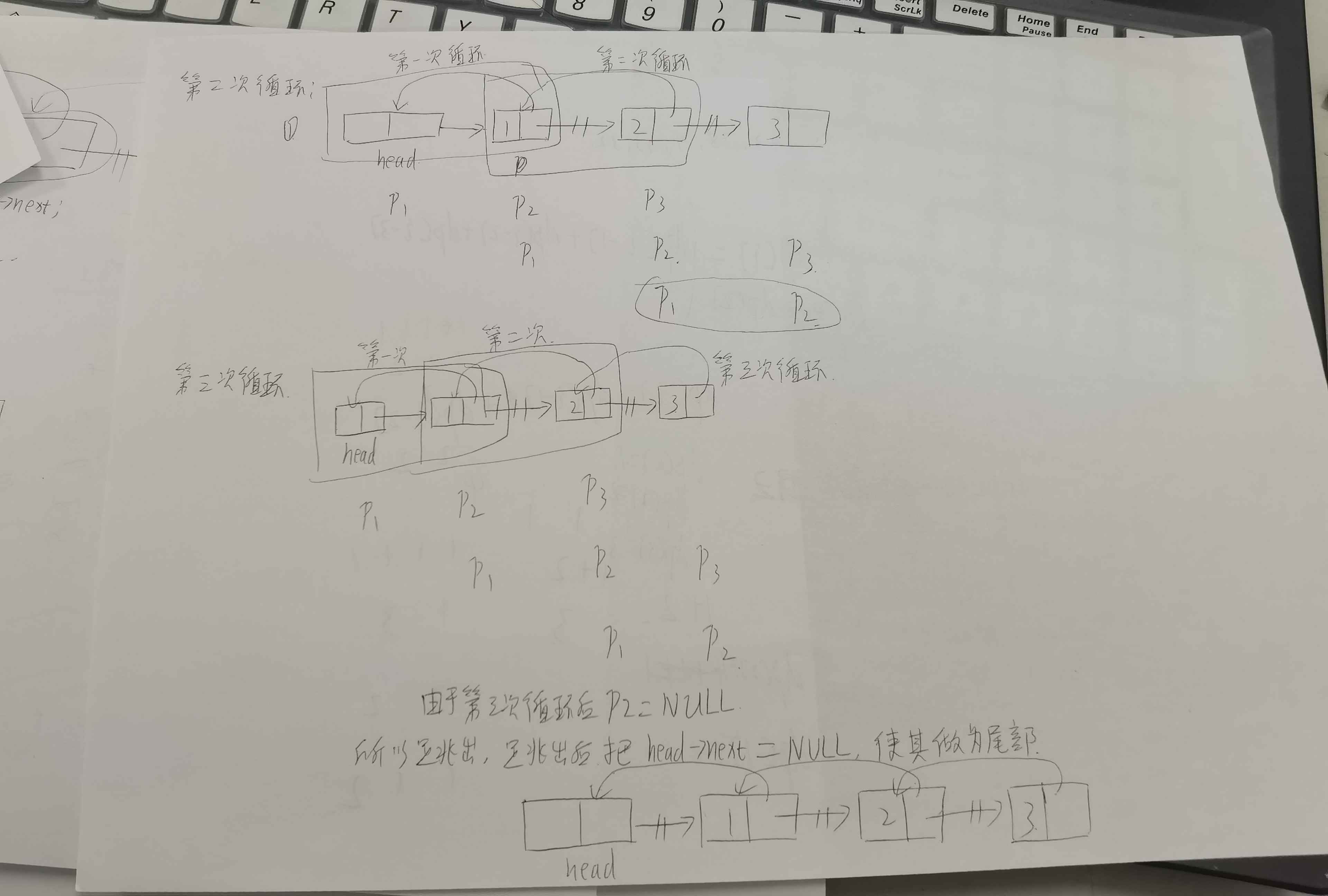
第二种方法:
1 struct stu *reserve(struct stu *head) 2 { 3 struct stu *p1,*p2,*p3; 4 p1=head; 5 p2=p1->next; // 这个结点为要移动的结点 6 while(p2) 7 { 8 p3=p2->next; //记录的为要移动的结点的下一个结点 9 p2->next=p1; //移动结点到最前 10 p1=p2; //移动的结点变为新表头 11 p2=p3; //下个结点变为要移动的结点 12 } 13 head->next=NULL; //移动完毕后head变为表尾,让它指向为空 14 head=p1; 15 return head; 16 }
方法三的贴下原作者的代码加上自己的思路:
1 struct stu *reserve(struct stu *head) 2 { 3 struct stu *p,*q; 4 p=head->next; //记录第二个结点 5 while(p->next!=NULL) 6 { 7 q=p->next; //记录要移动的结点 8 p->next=q->next; //把该结点从原链表中移除 9 q->next=head->next; //把该结点连接到head之后 10 head->next=q; 11 } 12 p->next=head; //把head移动到新表尾,此时链表成环 13 head=p->next->next; //找到移动完之后的新head 14 p->next->next=NULL; //断开环 15 return head; 16 17 }



