Java 设计模式--策略模式,枚举+工厂方法实现
如果项目中的一个页面跳转功能存在10个以上的if else判断,想要做一下整改
一、什么是策略模式
策略模式是对算法的包装,是把使用算法的责任和算法本身分割开来,委派给不同的对象管理,最终可以实现解决多重If判断问题。
1.环境(Context)角色:持有一个Strategy的引用。
2.抽象策略(Strategy)角色:这是一个抽象角色,通常由一个接口或抽象类实现。此角色给出所有的具体策略类所需的接口。
3.具体策略(ConcreteStrategy)角色:包装了相关的算法或行为。
(定义策略接口→实现不同的策略类→利用多态或其他方式调用策略。)
二、策略模式优缺点
优点:
算法可以自由切换(高层屏蔽算法,角色自由切换)
避免使用多重条件判断(如果算法过多就会出现很多相同的判断,很难维护)
扩展性好(可自由添加取消算法,而不影响整个功能)
缺点:
策略数量增多(每一个策略类复用性小,如果需要增加算法,就只能新增类)
所有的策略类都需要对外暴露(使用的人必须了解使用策略,这个就需要其他模式来补充,比如工厂模式、代理模式)
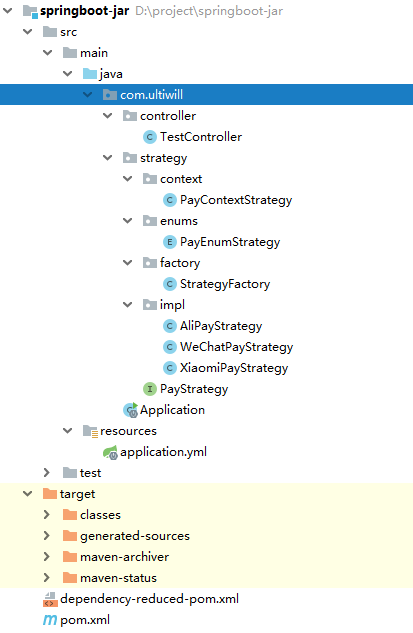
三、代码示例
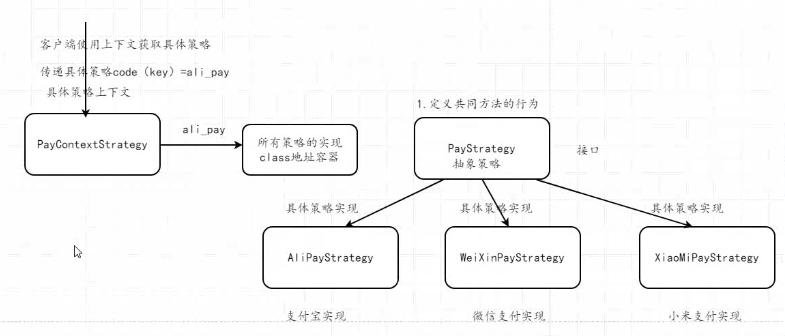
1.定义共同的方法和行为
package com.ultiwill.strategy;
public interface PayStrategy {
/**
* 共同的行为方法
* @return
*/
String toPayHtml();
}
2. 三种具体策略的实现 (阿里支付, 微信支付, 小米支付)
package com.ultiwill.strategy.impl;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.PayStrategy;
/**
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 15:21
*/
public class AliPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
@Override
public String toPayHtml() {
return "调用阿里支付...AliPayStrategy";
}
}
package com.ultiwill.strategy.impl;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.PayStrategy;
/**
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 15:29
*/
public class WeChatPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
@Override
public String toPayHtml() {
return "调用微信支付...WeChatPayStrategy";
}
}
package com.ultiwill.strategy.impl;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.PayStrategy;
/**
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 15:34
*/
public class XiaomiPayStrategy implements PayStrategy {
@Override
public String toPayHtml() {
return "调用小米支付...XiaomiPayStrategy";
}
}
3. 枚举类定义映射地址
package com.ultiwill.strategy.enums;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
/**
* 枚举
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 15:45
*/
public enum PayEnumStrategy {
/**
* 阿里支付
*/
ALI_PAY("1","com.ultiwill.strategy.impl.AliPayStrategy"),
/**
* 微信支付
*/
WECHAT_PAY("2","com.ultiwill.strategy.impl.WeChatPayStrategy"),
/**
* 小米支付
*/
XIAOMI_PAY("3","com.ultiwill.strategy.impl.XiaomiPayStrategy");
private String code;
private String className;
PayEnumStrategy() {
}
PayEnumStrategy(String code, String className) {
this.code = code;
this.className = className;
}
public static String getClassNameByCode(String code) {
String className = "";
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(code)) {
return className;
}
for (PayEnumStrategy e : PayEnumStrategy.values()) {
if (e.code.equalsIgnoreCase(code)) {
className = e.className;
break;
}
}
return className;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
}
4.工厂类反射执行
package com.ultiwill.strategy.factory;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.PayStrategy;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.enums.PayEnumStrategy;
/**
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 16:10
*/
public class StrategyFactory {
/**
* 使用策略工厂获取具体策略实现
* @param code
* @return
*/
public static PayStrategy getPayStrategy(String code) {
try {
return (PayStrategy) Class.forName(PayEnumStrategy.getClassNameByCode(code)).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
5.上下文获取具体策略
package com.ultiwill.strategy.context;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.PayStrategy;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.enums.PayEnumStrategy;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.factory.StrategyFactory;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
/**
* 上下文
*
* @author chong.zuo
* @date 2020/9/24 15:41
*/
public class PayContextStrategy {
/**
* 获取具体的策略实现
*
* @param code
* @return
*/
public static String toPayHtml(String code) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(code)) {
return "code不能为空...";
}
PayStrategy payStrategy = StrategyFactory.getPayStrategy(code);
if (payStrategy == null) {
return "没有找到具体的策略...";
}
return payStrategy.toPayHtml();
}
}
四、测试
controller:
package com.ultiwill.controller;
import com.ultiwill.strategy.context.PayContextStrategy;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author c
* @date 2020/5/14 9:59
*/
@RestController
public class TestController {
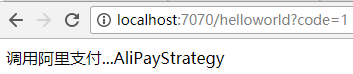
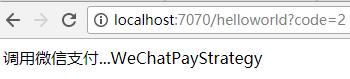
@RequestMapping("/helloworld")
public String hello(String code) {
return PayContextStrategy.toPayHtml(code);
/*if ("0".equals(code)) {
return "调用阿里支付...AliPayStrategy";
} else if ("1".equals(code)) {
return "调用微信支付...AliPayStrategy";
} else if ("2".equals(code)) {
return "调用小米支付...AliPayStrategy";
}
return "调用接口不存在";
*/
}
}
pom:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ultiwill</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-jar</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
<configuration>
<includeSystemScope>true</includeSystemScope>
<mainClass>com.ultiwill.Application</mainClass>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
五、结果
六、在spring中通过Autowired注解实现策略模式
使用AutowireCapableBeanFactory手动注入
使用.newInstance();创建对象的话,如果其他对象都使用Spring Autowired,还需要手动创建所有依赖的Bean:
private @Autowired AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public void process() {
MyBean obj = new MyBean();
beanFactory.autowireBean(obj);
// obj will now have its dependencies autowired.
}
本例中可以使用
private @Autowired AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory;
/**
* 使用策略工厂获取具体策略实现
* @param code
* @return
*/
public PayStrategy getPayStrategy(String code) {
String className = PayEnumStrategy.getClassNameByCode(code);
try {
PayStrategy str = (PayStrategy) Class.forName(className).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
beanFactory.autowireBean(str);
return str;
} catch (InstantiationException |
NoSuchMethodException |
ClassNotFoundException |
IllegalAccessException |
InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
使用Map<String,?> 自动注入
先附上如下的代码:
public interface TalkService {
void talk(String content);
}
@Service(value = "withSisterTalkService")
public class WithSisterTalkService implements TalkService {
@Override
public void talk(String content) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + ":" + content);
}
}
@Service(value = "withGirlFriendTalkService")
public class WithGirlFriendTalkService implements TalkService {
@Override
public void talk(String content) {
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName() + ":" + content);
}
}
@Service
public class TalkServiceStrategyContext implements TalkService {
private Map<String, TalkService> strategyMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Autowired
public TalkServiceStrategyContext(Map<String, TalkService> strategyMap) {
this.strategyMap.clear();
this.strategyMap.putAll(strategyMap);
}
@Override
public void talk(String content) {
}
}
注意,这里必须是Map<String, TalkService>类型!
@Autowired
private Map<String, TalkService> talkServiceMap;
@GetMapping(value = "doTest")
public String doTest() {
Set<String> strings = talkServiceMap.keySet();
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string + ":" + talkServiceMap.get(string).toString());
}
return this.getClass().getName();
}
其访问测试controller后,打印的信息如下:
talkServiceStrategyContext:com.haiyang.onlinejava.complier.service.impl.TalkServiceStrategyContext@2f0b1419
withGirlFriendTalkService:com.haiyang.onlinejava.complier.service.impl.WithGirlFriendTalkService@1cf19a02
withSisterTalkService:com.haiyang.onlinejava.complier.service.impl.WithSisterTalkService@1ef3c76d
看了后感觉很奇怪,在上方只定义了一个map<String,TalkService>的map,居然它就能自动找到实现了TalkService的所有bean,并将service的beanName作为了key,感觉还是牛逼啊,spring的注解居然还能这样用。
然后简单看了下Autowired的源码,其javaDoc文档里也有说明:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Marks a constructor, field, setter method or config method as to be
* autowired by Spring's dependency injection facilities.
*
* <p>Only one constructor (at max) of any given bean class may carry this
* annotation, indicating the constructor to autowire when used as a Spring
* bean. Such a constructor does not have to be public.
*
* <p>Fields are injected right after construction of a bean, before any
* config methods are invoked. Such a config field does not have to be public.
*
* <p>Config methods may have an arbitrary name and any number of arguments;
* each of those arguments will be autowired with a matching bean in the
* Spring container. Bean property setter methods are effectively just
* a special case of such a general config method. Such config methods
* do not have to be public.
*
* <p>In the case of multiple argument methods, the 'required' parameter is
* applicable for all arguments.
*
* <p>In case of a {@link java.util.Collection} or {@link java.util.Map}
* dependency type, the container will autowire all beans matching the
* declared value type. In case of a Map, the keys must be declared as
* type String and will be resolved to the corresponding bean names.
*
* <p>Note that actual injection is performed through a
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor
* BeanPostProcessor} which in turn means that you <em>cannot</em>
* use {@code @Autowired} to inject references into
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor
* BeanPostProcessor} or
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor BeanFactoryPostProcessor}
* types. Please consult the javadoc for the {@link AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* class (which, by default, checks for the presence of this annotation).
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Mark Fisher
* @since 2.5
* @see AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* @see Qualifier
* @see Value
*/
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
/**
* Declares whether the annotated dependency is required.
* <p>Defaults to {@code true}.
*/
boolean required() default true;
}
关注这句:
In case of a java.util.Collection or java.util.Map dependency type, the container will autowire all beans matching the declared value type. In case of a Map, the keys must be declared as type String and will be resolved to the corresponding bean names.
它大致是说Autowired当使用在Collection里时,会将所申明类的所有实现类都放在那个指定的Collection里;
如果Autowired和map使用的话呢,它将它bean的名称作为key,所有的bean作为value.
使用Set<?>自动注入
如果不想使用bean的名字作为map的Key的话,我们可以自定义寻址方式,自动注入时候使用Set<?>:
public interface Strategy {
void doStuff();
StrategyName getStrategyName();
}
public enum StrategyName {
StrategyA,
StrategyB,
StrategyC
}
@Component
public class StrategyA implements Strategy{
@Override
public void doStuff() {
//implement algorithm A here
}
@Override
public StrategyName getStrategyName() {
return StrategyName.StrategyA;
}
}
@Component
public class StrategyB implements Strategy{
@Override
public void doStuff() {
//implement algorithm B here
}
@Override
public StrategyName getStrategyName() {
return StrategyName.StrategyB;
}
}
@Component
public class StrategyC implements Strategy{
@Override
public void doStuff() {
}
@Override
public StrategyName getStrategyName() {
return StrategyName.StrategyC;
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class StrategyFactory {
private Map<StrategyName, Strategy> strategies;
@Autowired
public StrategyFactory(Set<Strategy> strategySet) {
createStrategy(strategySet);
}
public Strategy findStrategy(StrategyName strategyName) {
return strategies.get(strategyName);
}
private void createStrategy(Set<Strategy> strategySet) {
strategies = new HashMap<StrategyName, Strategy>();
strategySet.forEach(
strategy ->strategies.put(strategy.getStrategyName(), strategy));
}
}
Now we can inject StrategyFactory using @Autowired annotation. Here is the sample code using our StrategyFactory.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SomeService {
@Autowired
private StrategyFactory strategyFactory;
public void findSome(){
// Now get the strategy by passing the name
Strategy strategy = strategyFactory.findStrategy(StrategyName.StrategyA);
// you can now call the methods defined in strategy.
strategy.doStuff();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号