手动搭建:SpringBoot环境、项目结构、数据库模型
手动搭建:SpringBoot环境、项目结构、数据库模型
如果插件Spring Assistant与我们的电脑有冲突,那我们就不要选择此插件,
自己来搭建环境创建项目
1、创建一个项目
(1)选择Maven项目创建
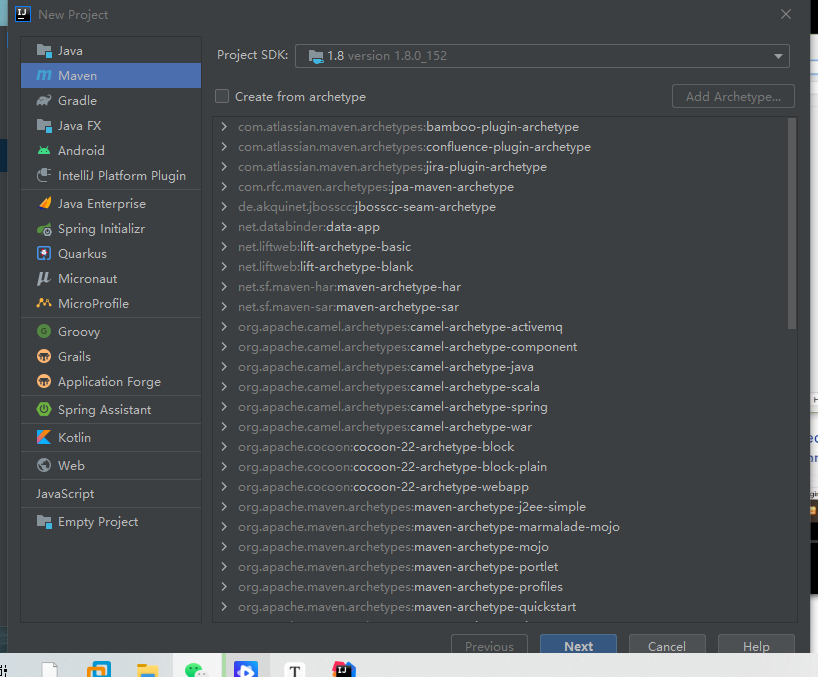
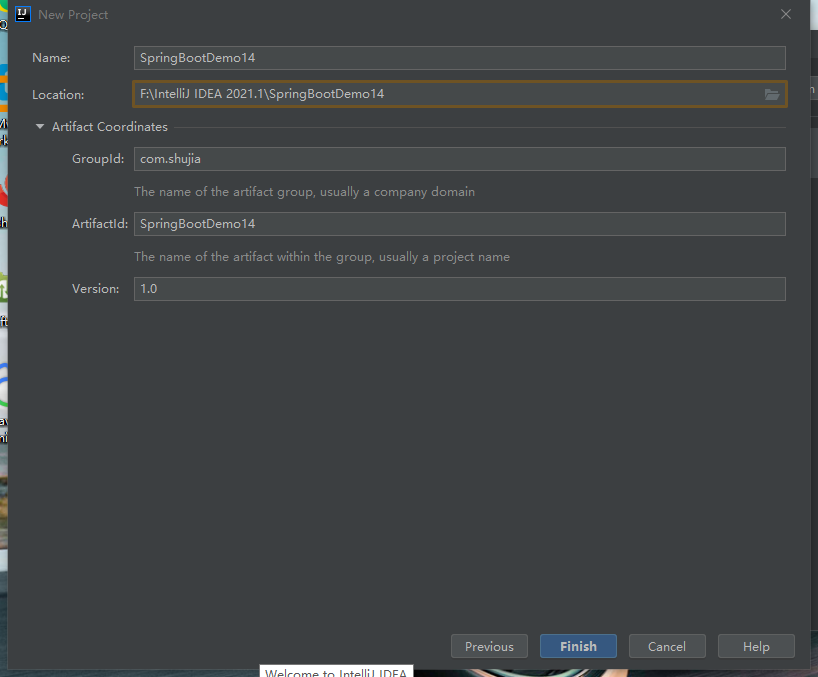
(2)自定义名称
(3)创建完成的样子
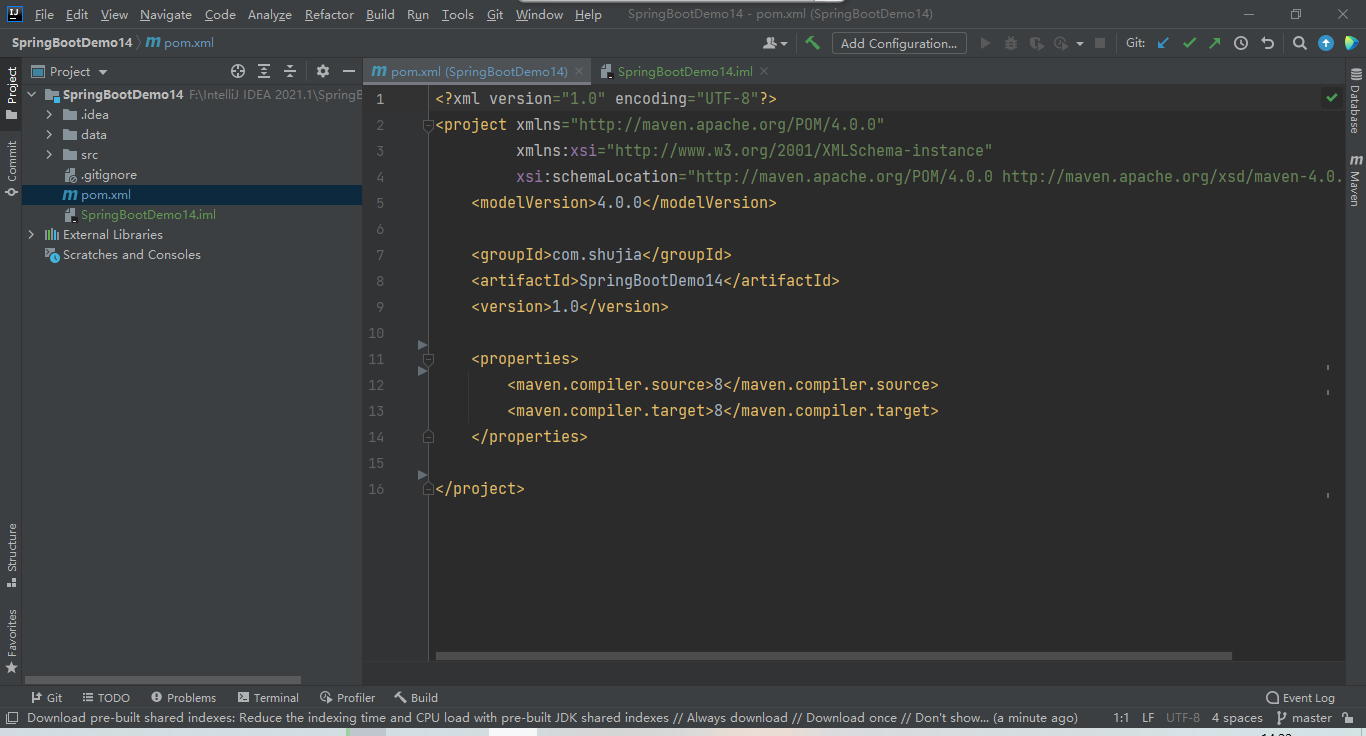
2、手动搭建SpringBoot环境
(1)将SpringBoot需要的依赖添加到pom.xml中
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
(2)将SpringBoot项目的编码添加到pom.xml中的<properties>中
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
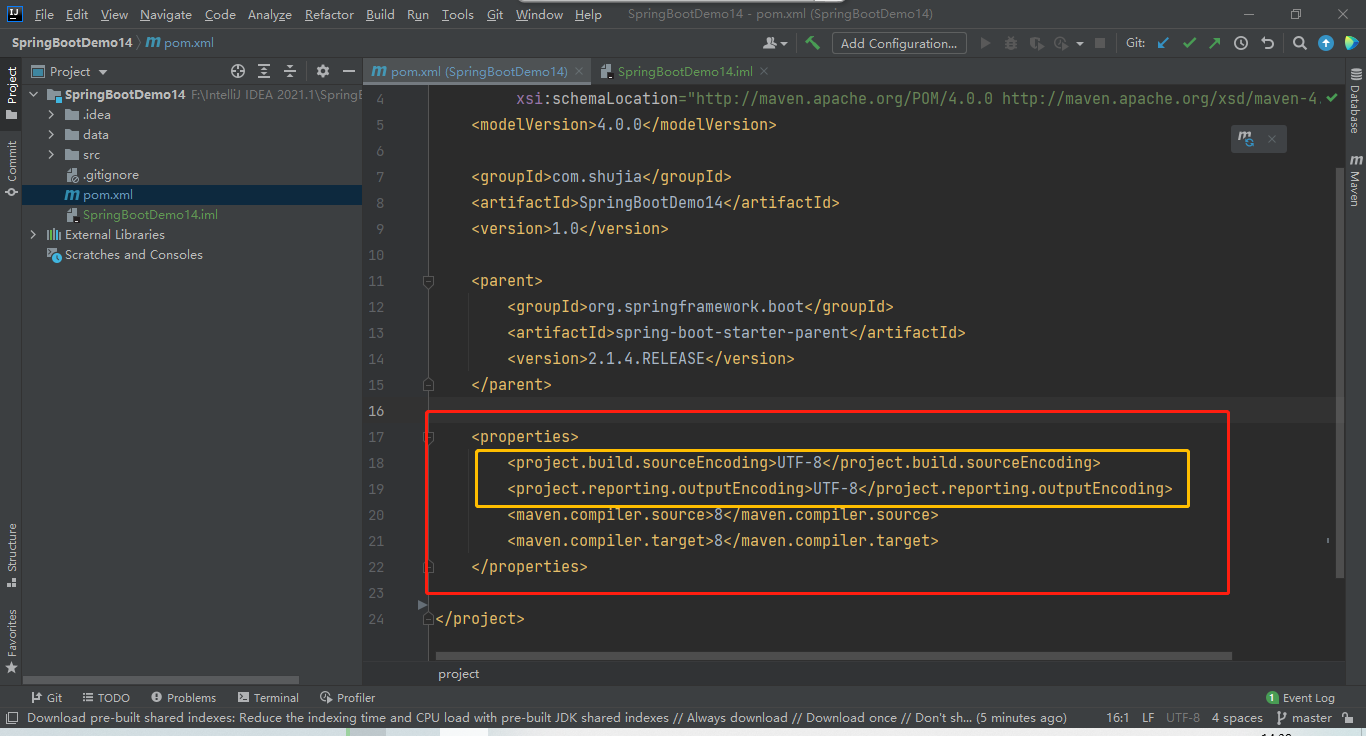
(3)将SpringBoot项目所需要的依赖添加到pom.xml中
<!--添加本项目所能用到的依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!--添加Springmvc依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springBoot JPA的起步依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--因为此项目需要mysql的库,那么此次添加mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
(4)SpringBoot项目需要的特定插件添加pom.xml中
因为SpringBoot项目打包的方式和其他东西打包有一定的差别,需要特定的插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
(5)刷新一下Maven:鼠标右击----选择Maven----选择Reload project
(6)所需要的东西都配置好了,那么这个SpringBoot项目就创建好了
3、添加配置文件
因为SpringBoot项目最终的数据要放到某一个数据库里面的,需要配置数据库的地址
本次使用mysql数据库,所以需要配置mysql数据库的地址
配置mysql数据库的地址之前,在mysql中先建一个表
(1)在mysql中新建一个数据库,命名为 springbootdemo
(2)在 springbootdemo库中,自定义设计一个表
create table student88(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(255) not null,
age int not null default 0,
gender varchar(255),
clazz varchar(255),
sum_score int
);
-- 对name做索引
create index stu_name_index on student88(name);
(2)返回IDEA,右击项目名称,选择new---->Directory新建一个目录,命名为 data
(3)右击data目录,选择 new---->File 新建一个文件,命名为 student88.sql
(4)将我们自定义学生表的代码粘贴到 student88.sql 文件中
添加数据库的配置
配置文件以及资源等,放在
resources目录内
(1)在 resources 目录中新建一个File文件,命名统一为:application.properties
(2)将mysql配置的代码粘贴到 application.properties 文件中
主机名
master:3306、数据库名称springbootdemo,权限root、密码123456mysql驱动名称
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver上面所述根据个人情况的不同,进行修改
# 对MySQL连接进行配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://master:3306/springbootdemo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2b8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
# mysql驱动
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
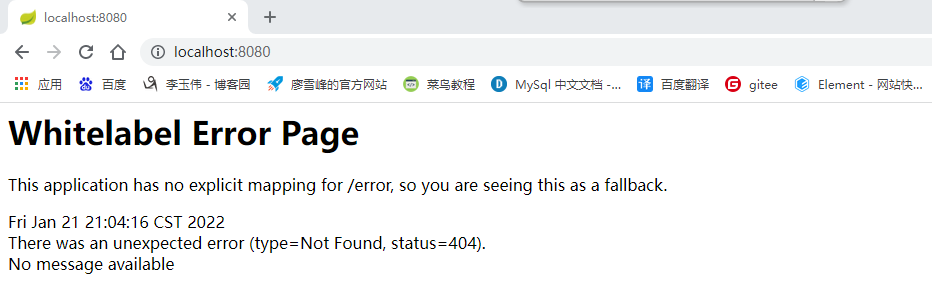
(3)配置完成后,运行一下,然后在浏览器中搜索localhost:8080
会出现如下图所示,说明访问是通的
4、创建SpringBoot的项目入口(该入口用来启动SpringBoot的项目)
Application:应用
(1)在 scr---->main---->java 中先新建一个包,例:com.shujia
(2)在新建的包内,新建一个class文件,例:SpringBootDemoApplication
(3)在类上方艾特一下SpringBootApplication(表示这个类是作为SpringBoot的应用)
(4)添加main方法
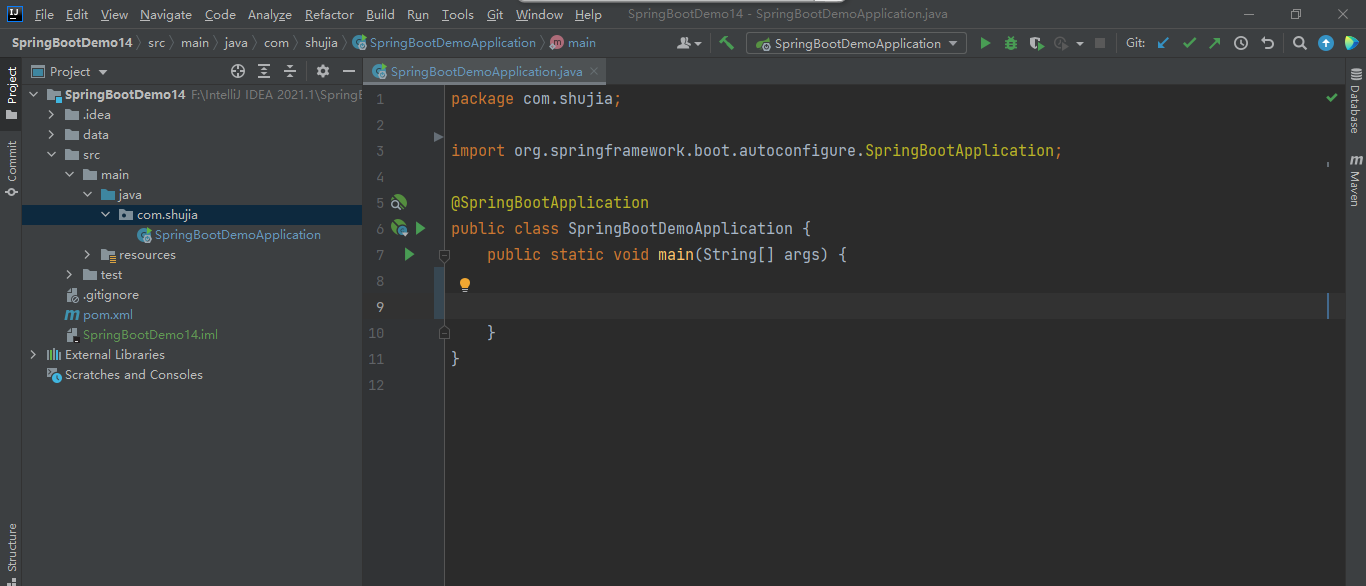
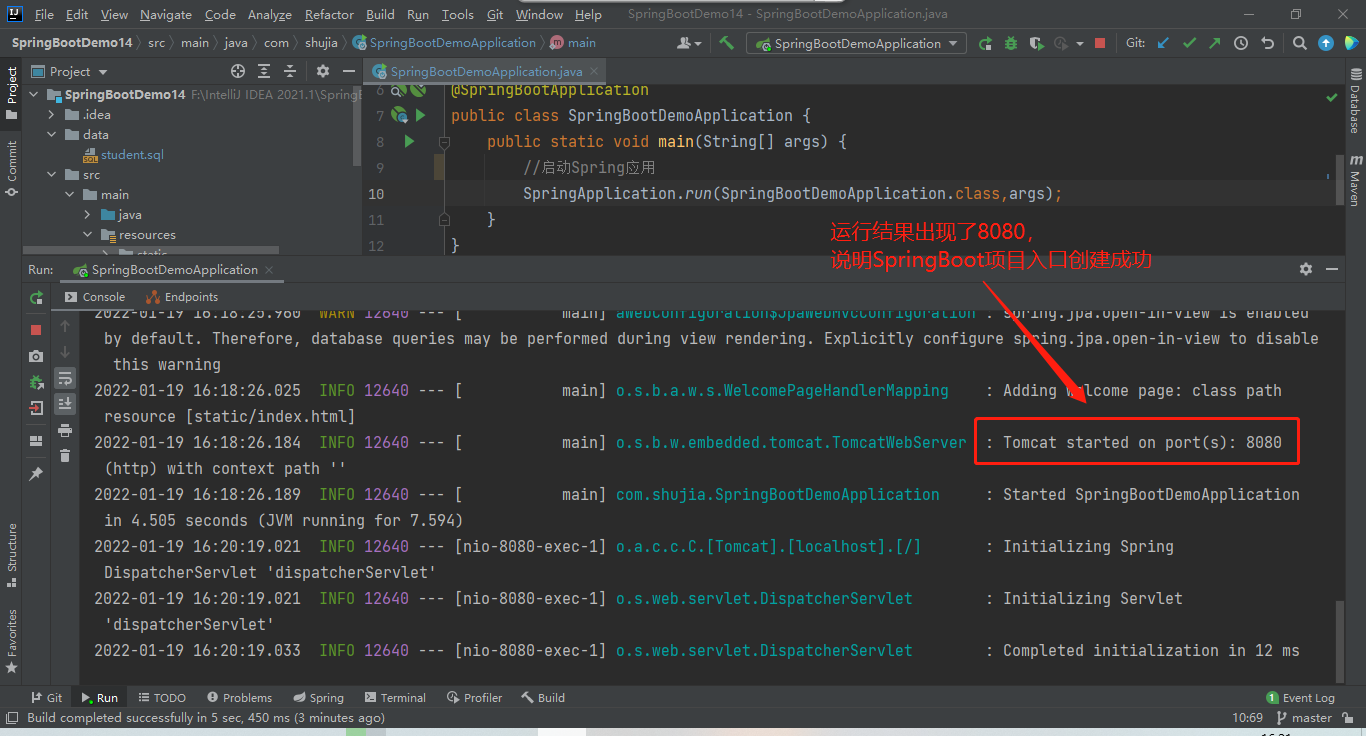
(5)添加启动Spring应用的代码:引用 SpringApplication,调取run方法
SpringApplication.run(类名.class,args);
//启动Spring应用
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class,args);
(6)运行程序
5、编写SpringBoot项目结构
首先用户请求页面先会到达Controller控制层,然后Controller控制层来调Service层;
Service层用来写复杂的业务逻辑,Service层调Dao层;
Dao层对数据的进行持久化,实现了很多方法,如查找、删除、筛选...,与MySQL数据库进行交互;
Entity/Model层用一个Java的类去描述MySQL的表
在编写代码的时候,先从Entity层开始写,由下往上
(1)创建项目结构层的目录,在 scr---->main---->java---->com.shujia 中创建目录
目录1:Entity-------数据库的模型,在Java里面定义一个类,去描述MySQL数据库中的表
目录2:Dao----------数据持久层
目录3:Service------数据服务层
目录4:Controller---数据控制层
目录5:common-------存放我们通用的东西
(2)编辑 Entity 层,在目录 Entity中新建一个class文件,类名与自定义的表名保持一致:Student88
在MySQ中,取列名的时候,是 sum_score ,而且忽略大小写;
在Java中,定义属性的时候则命名 sumScore ,而且严格区分大小写
当Java中命名 sumScore的时候,和MySQL中的列名对不上,这时候就需要在上方加个@Column注解
①在类上面加个注解:@Entity
②在类上面加个注解:@Table(),指定一下它是哪张表;
指定它的name="表名",当作参数加入括号内,按照表里面的列来定义属性
package com.shujia.Entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student88")
public class Student88 {
//定义属性
@Id //通过注解来设定主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //通过注解来设定Id自增
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String clazz;
//属性名一般同数据库中表的列名一致,不一致时可以使用 @Column 注解
@Column(name = "sum_score")
private Integer sumScore;
//因为属性都用private修饰,需要定义公共的SetXxx()和GetXxx()来进行增删改查
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(String clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public Integer getSumScore() {
return sumScore;
}
public void setSumScore(Integer sumScore) {
this.sumScore = sumScore;
}
}
(3)编辑 Dao 层,在目录Dao中新建一个接口,命名为 Student88Repository
repository:仓库
除了Dao层是接口,其他层都是类
接口会定义很多种方法,可能没有具体的实现;
实际上它继承的父类,对一些方法基本上都实现了,就不需要在接口中添加方法了;
如果需要我们自定义的方法,那么再到该接口中来定义
在接口的上方需要添加注解`@Repository`
Dao层的接口需要继承`JpaRepository`类,指定泛型为`Student88`,指定主键为`Integer`
package com.shujia.Dao;
import com.shujia.Entity.Student88;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface Student88Repository extends JpaRepository<Student88,Integer> {
}
(4)编辑 Service 层,在目录Service 中新建一个class文件,命名为:Student88Service
Resource:资源,谋略;
在
Service层内,可以进行增删改查、分页、保存等功能,是写业务具体的一个逻辑;由于
Dao层是最终和数据库交互的一层,那么Service层调的是Dao层;
在类的上方需要添加注解@Service;
在类中添加注解@Resource;
引用Dao层资源;
引用Dao层之后,就可以添加操作:例如:
findAll()------把所有的学生信息拿出来
findById()-----通过Id去找学生
deleteById()---通过Id去删除学生
save()---------保存
...
根据操作需求来定义方法;
package com.shujia.Service;
import com.shujia.Dao.Student88Repository;
import com.shujia.Entity.Student88;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class Student88Service {
@Resource //添加资源注解
private Student88Repository student88Repository;//引用Dao层资源
//引用Dao层资源后,就可以在此层进行业务操作了(定义方法)
//定义findAll()方法,返回的是一个集合,参数是在Entity定义的类
public List<Student88> findAll(){
return student88Repository.findAll();
}
}
(5)编辑 Controller 层,在目录Controller新建一个class文件,
命名为:Student88Controller
用户通过
url来请求获得数据,url会发到Controller去处理
添加注解@RestController,表示一个规范,将数据以json的格式返回
添加注解@RequestMapping(),括号里加个参数,确保用户想要请求的是什么
例:@RequestMapping("/user")-------请求user中的数据
@RequestMapping("/student")----请求student表中的数据
@RestController //将数据以json的格式返回
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@RequestMapping("/all")
public List<Student> findAll(){
}
@RequestMapping("/all2")
public List<Student> findAll2(){
}
}
(6)编辑 common 层,在目录common新建一个class文件,命名为:Result
用户向服务器发送请求(Req)--->服务器处理请求--->服务器返回给用户响应(Res)
返回给用户的一般有:
404,notfound:表示访问的页面不存在
505:服务器内部错误
200:访问页面成功
404、505、200表示http的状态码,紧跟着返回给用户的还有消息、数据
返回给用户的一般有:状态码、消息、数据
基于状态码、消息、数据,我们可以在Java中定义一个类来描述它们
根据类返回一个对象给用户,用户根据对象提取状态码、消息、数据
package com.shujia.common;
public class Result<T> {
//定义返回给用户的状态码、消息、数据
private String code;
private String msg;
//返回的数据有可能是user,有可能是student,有可能是集合,类型不确定,所有使用泛型类型
//同时类名后面要加上泛型
private T data;
//添加数据的构造方法
public Result() { //无参构造,有些请求是不需要返回数据的,比如删除了某个东西
}
public Result(T data) { //想要返回数据,就调用有参构造方法
this.data = data;
}
//添加三个属性的公共方法
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
//访问要么成功,要么失败,可以添加两个静态方法
//不管成功与否,都会返回一个Result对象
//请求成功,不返回数据(只返回状态码和消息)
public static <T> Result<T> success() {
//返回一个对象给用户
Result rs = new Result<>();
rs.setCode("200");
rs.setMsg("OK");
return rs;
}
//请求成功,返回数据(T data作为参数,会调用有参构造方法)
public static <T> Result<T> success(T data) {
//返回一个对象给用户
Result<T> rs = new Result<T>(data);
rs.setCode("200");
rs.setMsg("OK");
return rs;
}
//请求失败
public static <T> Result<T> error(String code,String msg) {
Result rs = new Result<>();
rs.setCode(code);
rs.setMsg(msg);
return rs;
}
}
(7)因为在common层设置了静态方法,这时候还需要返回 Controller 层修改一下代码
package com.shujia.Controller;
import com.shujia.Entity.Student88;
import com.shujia.Service.Student88Service;
import com.shujia.common.Result;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@RestController //控制将数据以JSON形式返回
@RequestMapping("/student88") //确认用户想要请求的数据
public class Student88Controller {
//因为本层需要调用Service,所有引用资源
@Resource
private Student88Service student88Service;
@GetMapping("/all")
public Result<List<Student88>> findAll(){
//返回值类型 List<Student88> 改成Result<List<Student88>>
//引用Service资源后,可以调取Service的方法了
List<Student88> list = student88Service.findAll();
//本方法需要返回数据,直接类名调取Result中的静态方法
return Result.success(list);
}
}
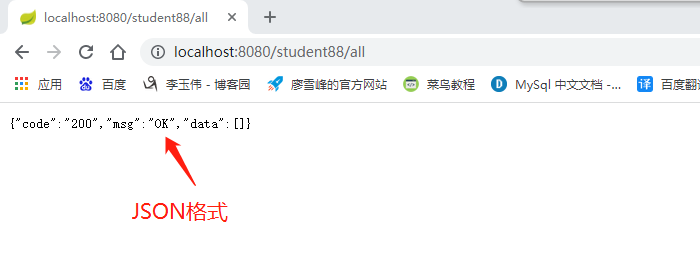
(9)开始运行,查看是否有错误
(8)若无错误,想要访问Controller层,8080后面要加上路径/student88
想要调取Controller层的findAll方法,/student88加上/aa


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号