数据结构系列(1)之 二叉搜索树
本文将主要以动图方式展示二叉搜索树的结构,以及动态操作;但是对于基本的概念和性质则不会有过多的提及,如果想系统了解建议查看邓俊辉老师的《数据结构》课程;
一、结构概述
二叉树:融合了向量的静态操作(二分查找)和列表的动态操作(插入和删除)的优点;使得树成了应用广泛的数据结构;
二叉搜索树:即顺序排列,可以搜索的树就是二叉搜索树;如下图所示;
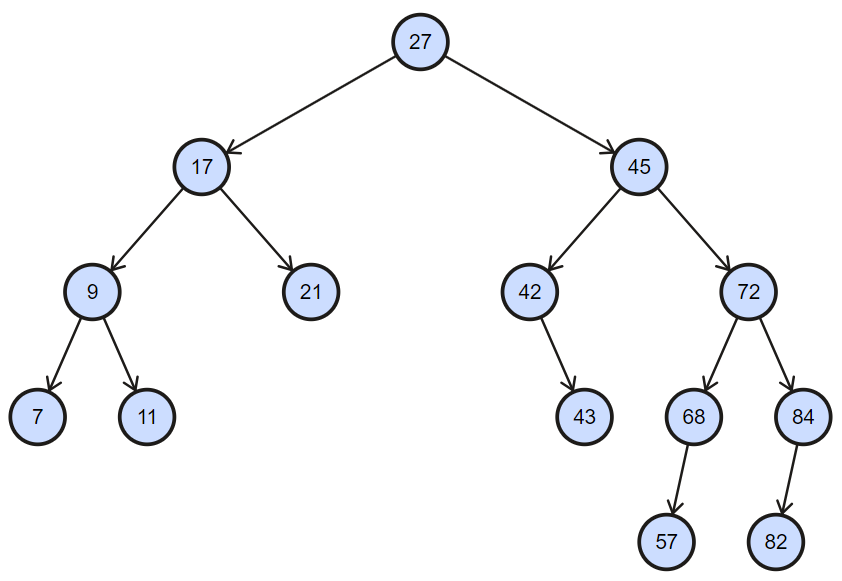
忽略二叉树的大小,高度等信息的简版结构如下:
public class BST<T extends Comparable<? super T>> {
private BSTNode<T> root;
public BST() {root = null;}
...
class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<? super T>> {
T key;
BSTNode<T> parent;
BSTNode<T> left;
BSTNode<T> right;
BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
二、查找
根据二叉搜索树左孩子节点小于父节点,右孩子节点大于等于父节点,逐步深入查找;
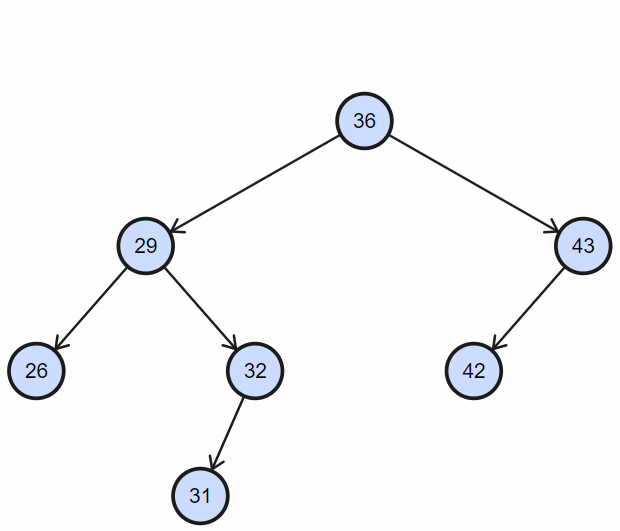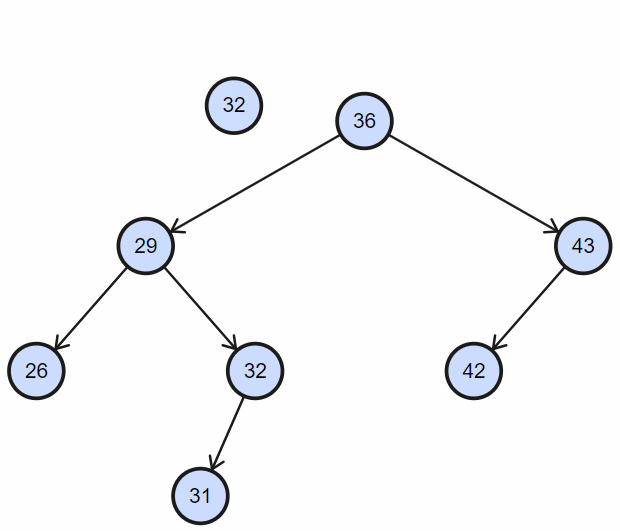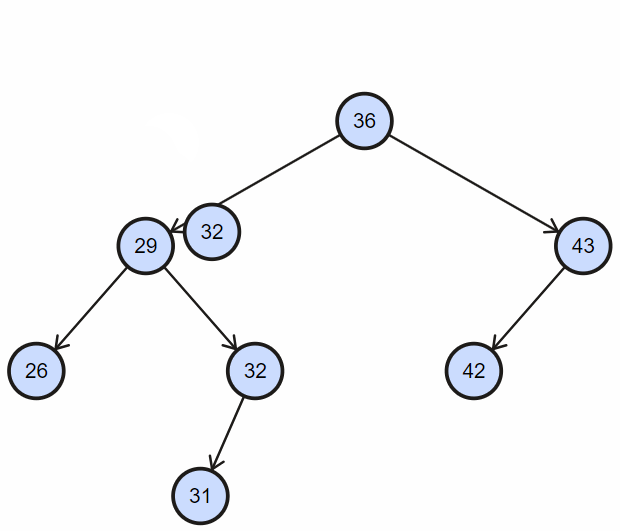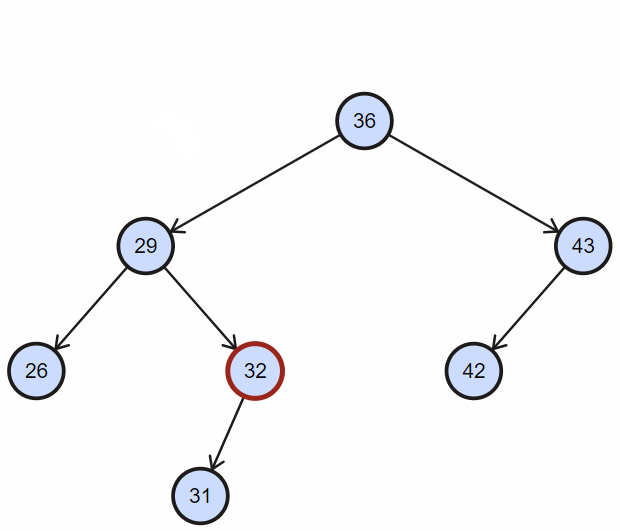
实现如下:
private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x == null) return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public BSTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(root, key);
}
更好的实现还应该记录查找失败的上一个节点,除此之外还可以实现查找最大值,最小值;
三、插入
插入,同样根据 BST 的排序规则,先查找插入位置,然后确定插入节点的引用关系;
1. 插入不重复节点
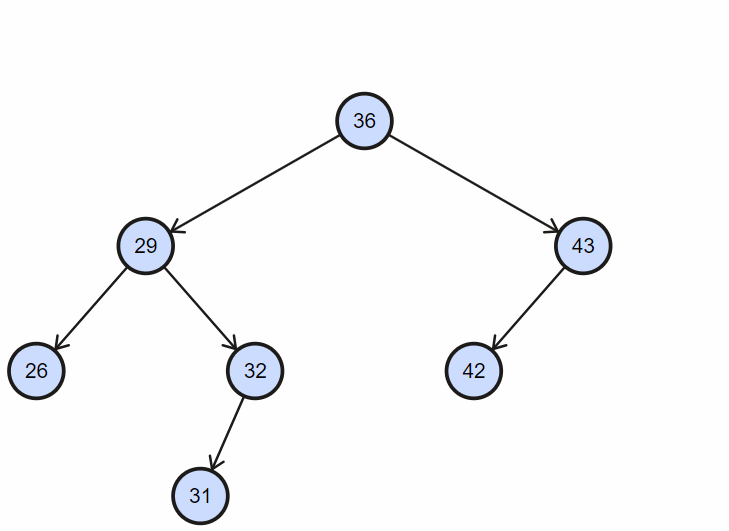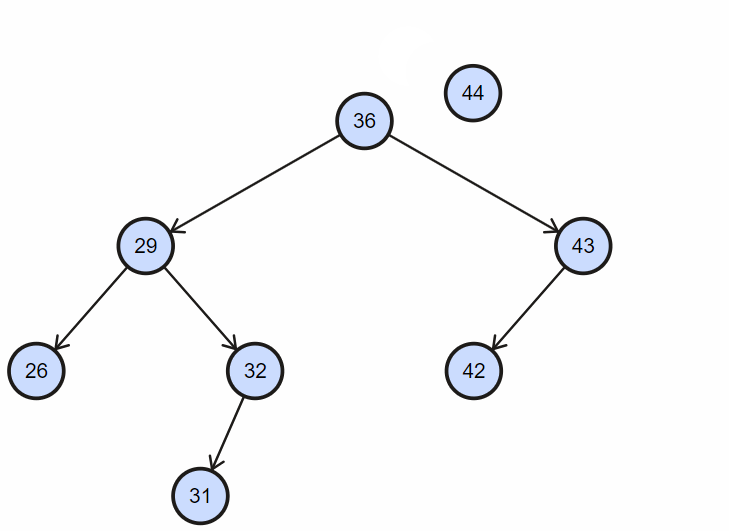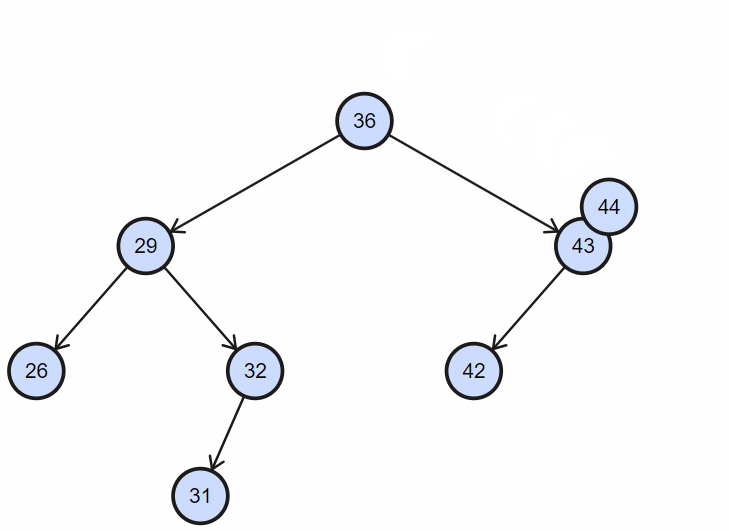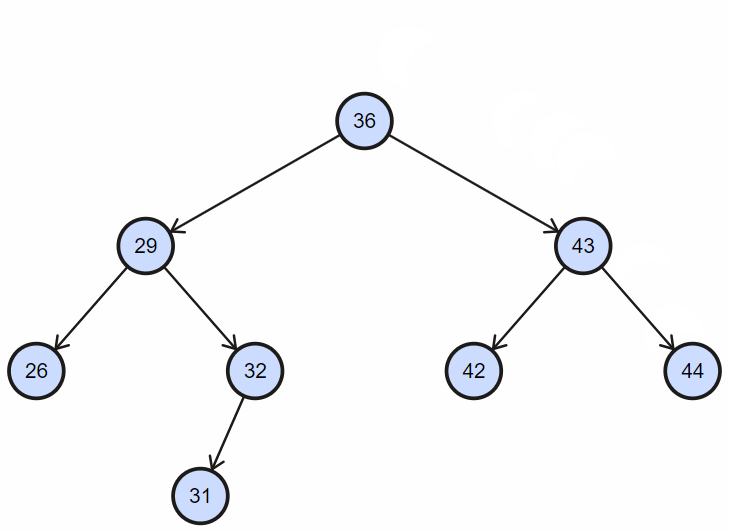
2. 插入重复节点
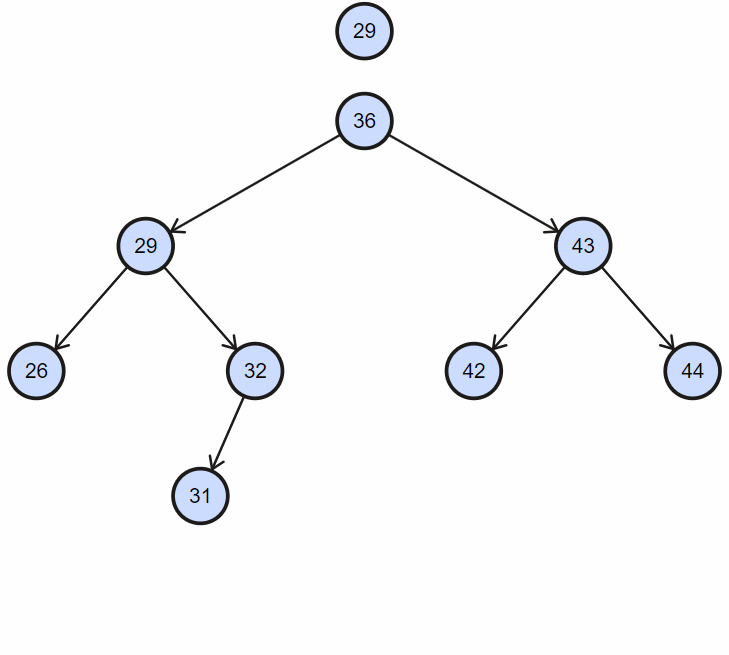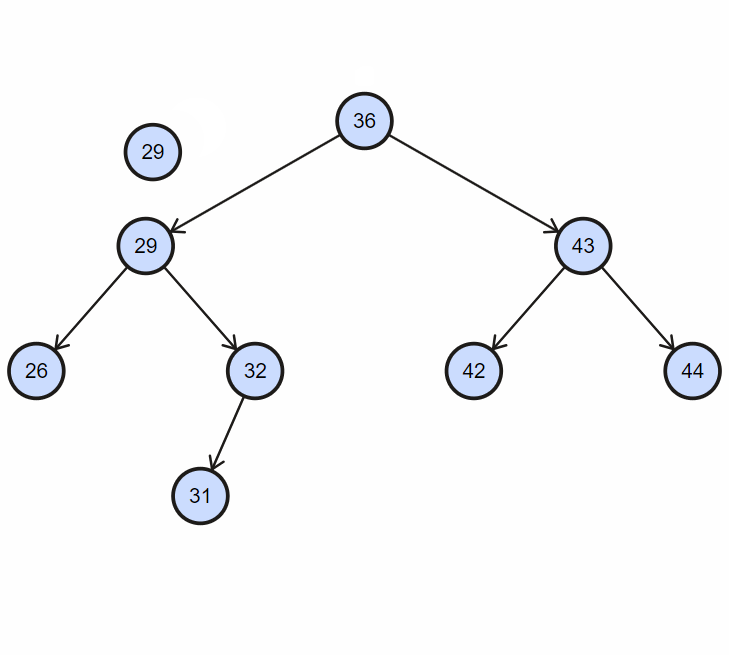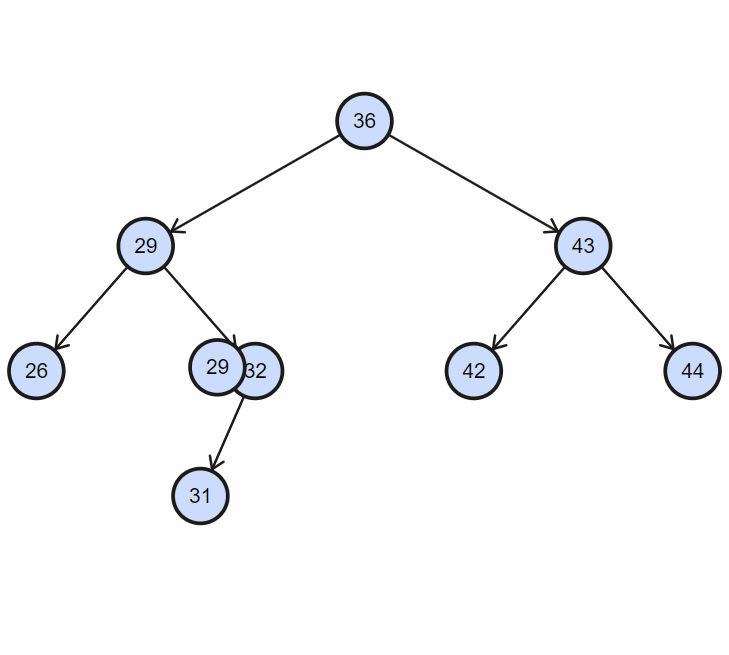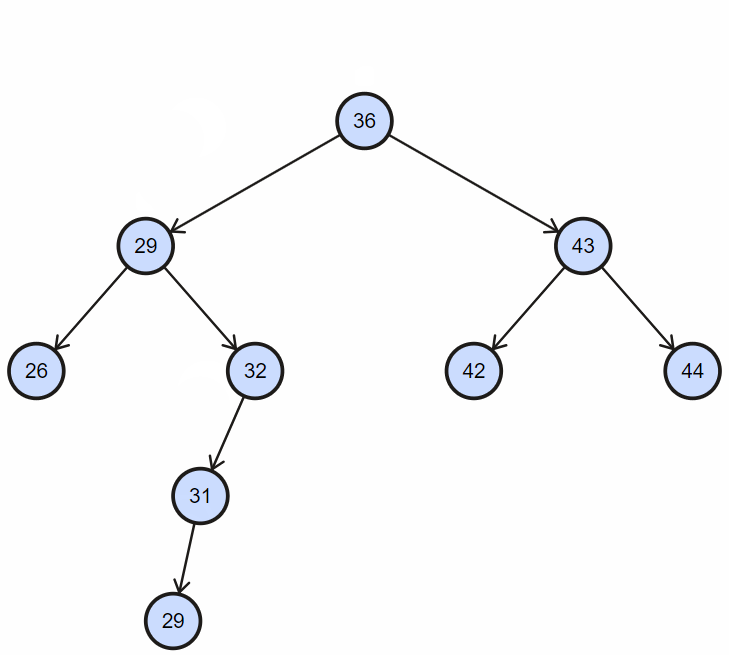
3. 实现
如果有 size 等信息,则需要从节点向上依次更新祖先节点
private void insert(T key) {
BSTNode<T> node = new BSTNode<T>(key, null, null, null);
BSTNode<T> r = this.root;
BSTNode<T> p = null;
int cmp;
// 查找插入位置
while (r != null) {
p = r;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(r.key);
if (cmp < 0)
r = r.left;
else
r = r.right;
}
if (p == null)
this.root = node;
else {
node.parent = p;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p.left = node;
else
p.right = node;
}
}
四、删除
删除,同样首先需要查找该节点,然后删除;
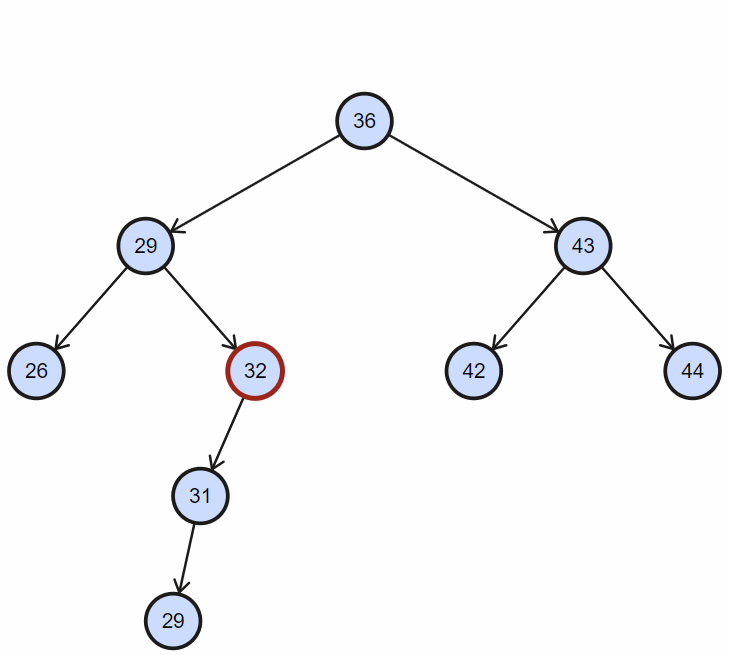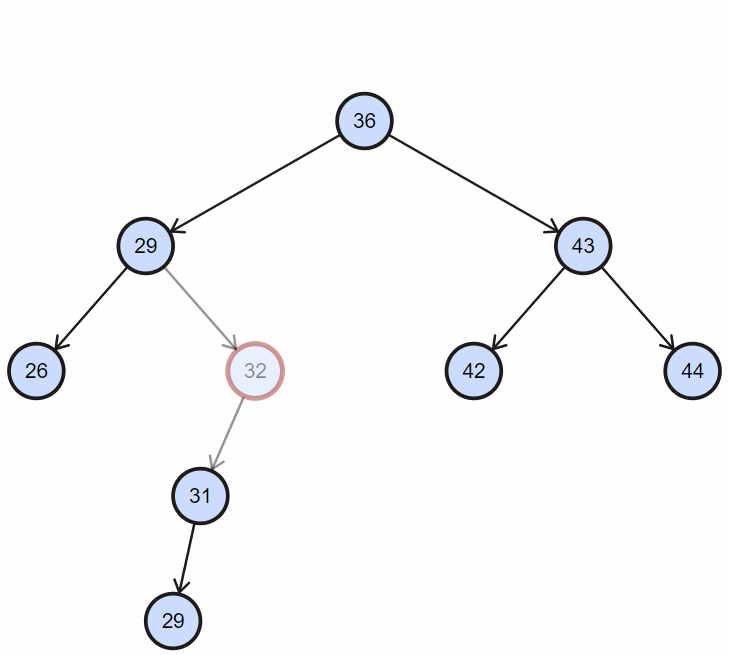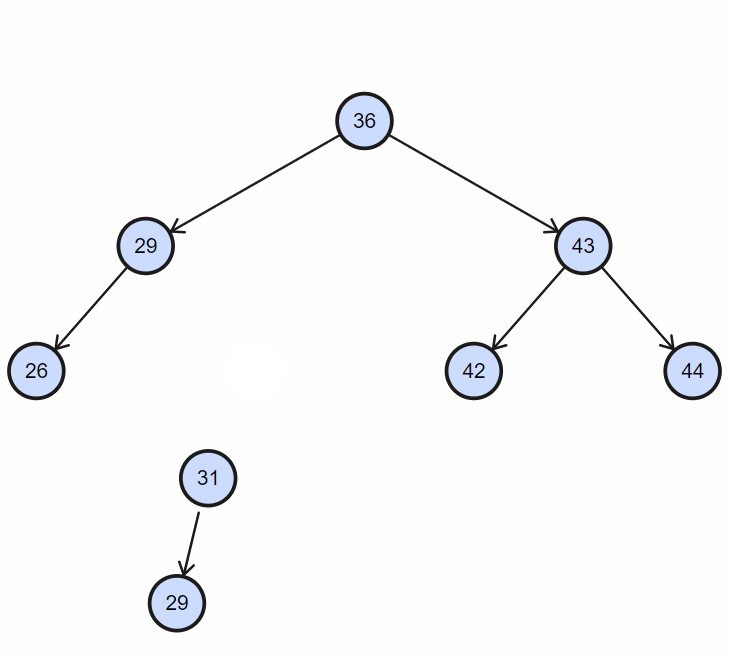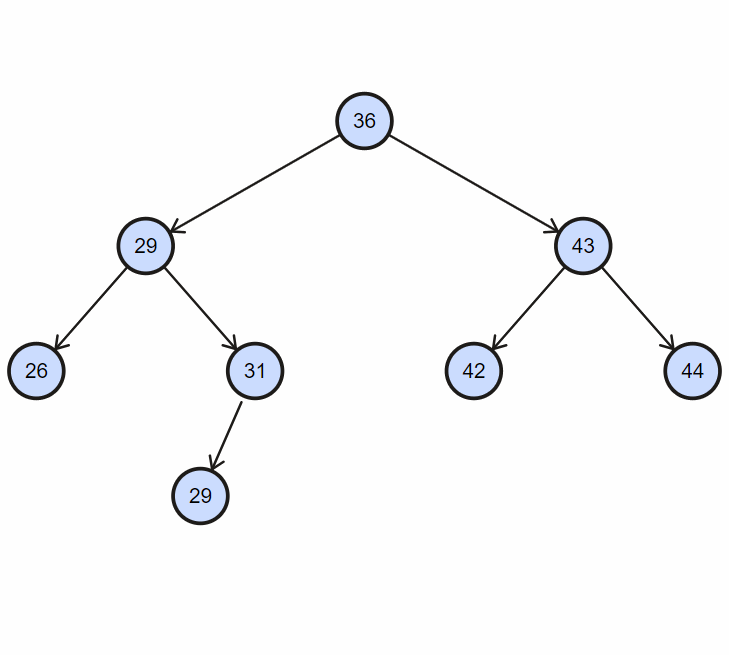
1. 删除不完全节点
目标节点没有左孩子或者右孩子时,直接删除节点,然后令其后代代替;
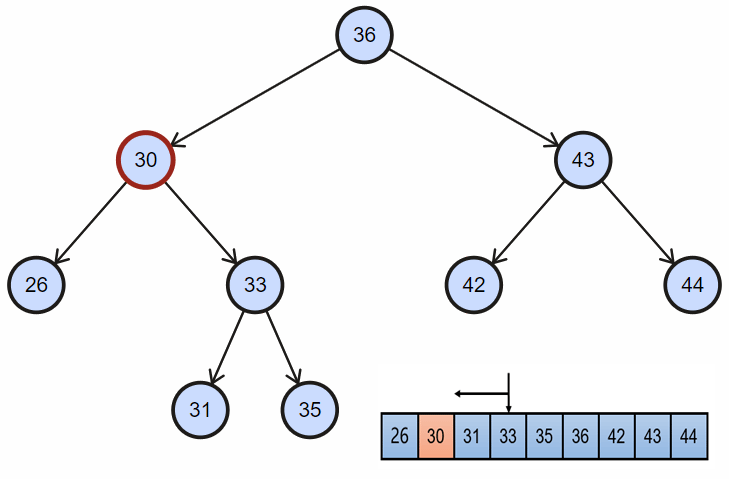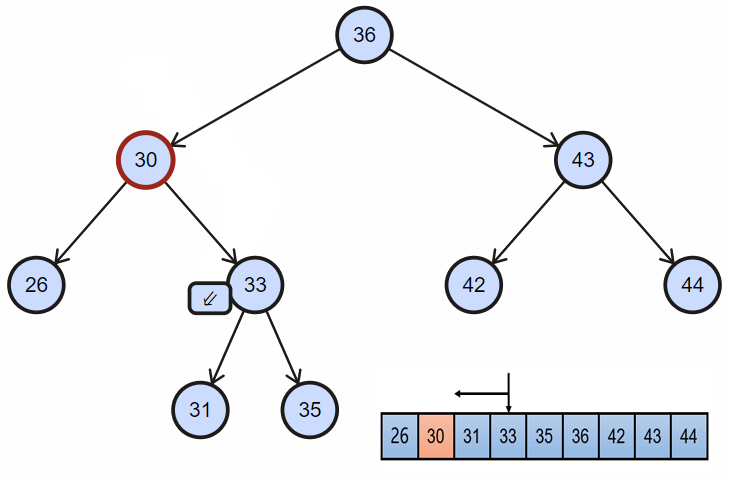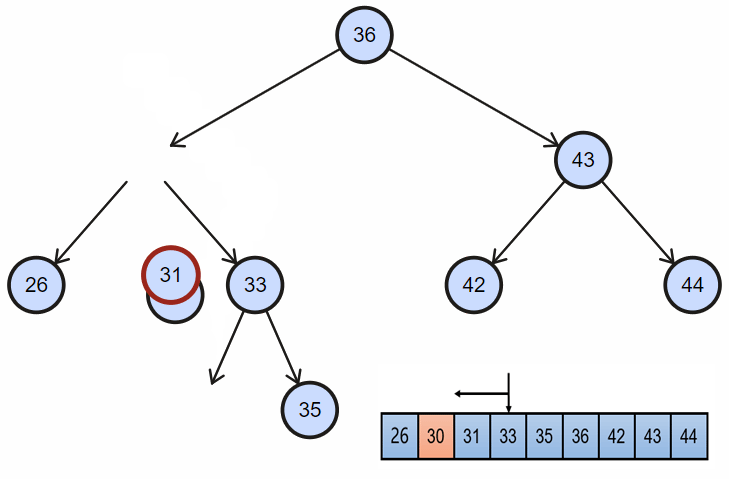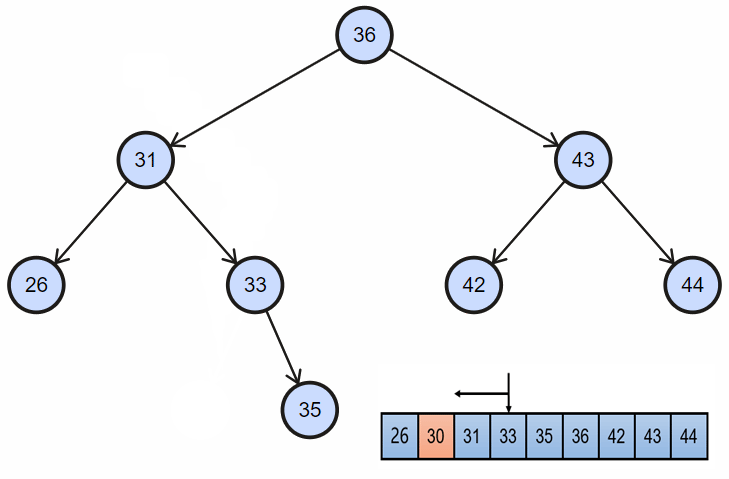
2. 删除完全节点
当目标节点同时拥有左孩子和右孩子时:
- 需要首先找到目标节点的直接后继(自然顺序或者中序遍历顺序的下一个节点),目标节点右孩子一直往左;当然这里同样可以找目标节点的前驱节点替换;
- 然后交换目标节点和后继节点的位置;
- 最后同上面的删除一样,直接删除节点;
3. 实现
注意这里只是实现的一种,还可以是可前驱进行交换
public void delete(T key) {
BSTNode<T> node = search(root, key);
if (node != null) delete(node);
node = null;
}
private BSTNode<T> delete(BSTNode<T> node) {
// 将完全节点和直接后继交换
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
BSTNode<T> succ = successor(node);
node.key = succ.key;
node = succ;
}
// 将孩子节点的父亲接到祖父上
BSTNode<T> child = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
if (child != null) child.parent = node.parent;
// 目标节点没有父节点则是根节点
if (node.parent == null) root = child;
// 目标节点是左孩子时
else if (node == node.parent.left) node.parent.left = child;
// 目标节点是右孩子时
else node.parent.right = child;
return node;
}
private BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> node) {
BSTNode<T> succ = node.right;
while (succ.left != null) succ = succ.left;
return succ;
}
// 这里只是右子树中的直接后继;整个中序遍历中直接后继还可能是其父节点或者祖先节点;
五、前序遍历
对于一个数据结构而言,了解他最直接的方式就是遍历操作,而对于二叉树则有前、中、后、层次遍历四种;
1. 描述
- 首先遍历根节点
- 再一次递归遍历左子树和右子树;
具体过程如下:
2. 实现
// 递归实现
private void travPre(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
travPre(tree.left);
travPre(tree.right);
}
// 迭代实现
public void travPre2(BSTNode<T> tree) {
Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack = new Stack<>();
while (true) {
visitAlongVine(tree, stack);
if (stack.isEmpty()) break;
tree = stack.pop();
}
}
private void visitAlongVine(BSTNode<T> tree, Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack) {
while (tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
stack.push(tree.right);
tree = tree.left;
}
}
六、中序遍历
1. 描述
- 对于中序遍历,则首先遍历左子树
- 再遍历根节点
- 最后遍历右子树
具体过程如下:
2. 实现
// 递归实现
private void travIn(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
travIn(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
travIn(tree.right);
}
// 迭代实现
public void travIn2(BSTNode<T> tree) {
Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack = new Stack<>();
while (true) {
goAlongVine(tree, stack);
if (stack.isEmpty()) break;
tree = stack.pop();
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
tree = tree.right;
}
}
private void goAlongVine(BSTNode<T> tree, Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack) {
while (tree != null) {
stack.push(tree);
tree = tree.left;
}
}
七、后序遍历
1. 描述
- 对于后序遍历,则首先遍历左子树
- 再遍历根右子树
- 最后遍历根节点
具体过程如下:
2. 实现
// 递归实现
private void travPost(BSTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null) return;
travPost(tree.left);
travPost(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
}
// 迭代实现
public void travPost2(BSTNode<T> tree) {
Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack = new Stack<>();
if (tree != null) stack.push(tree);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (stack.peek() != tree.parent)
gotoHLVFL(stack);
tree = stack.pop();
System.out.print(tree.key + " ");
}
}
private void gotoHLVFL(Stack<BSTNode<T>> stack) {
BSTNode<T> tree;
while ((tree = stack.peek()) != null)
if (tree.left != null) {
if (tree.right != null) stack.push(tree.right);
stack.push(tree.left);
} else
stack.push(tree.right);
stack.pop();
}
八、层次遍历
1. 描述
对于层次遍历而言就相对简单,即由上到下逐层遍历;
2. 实现
public void travLevel() {
Queue<BSTNode<T>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
BSTNode<T> x = queue.poll();
System.out.print(x.key + " ");
if (x.left != null) queue.offer(x.left);
if (x.right != null) queue.offer(x.right);
}
}
总结
- 正是因为二叉树同时具有向量和列表的特性,所以他的使用场景非常广泛,当然他还有很多的变种,这些我们后续会继续讲到;
- 对于文中的动图大家可以在这个网站自行实验;http://btv.melezinek.cz/binary-search-tree.html

