centos8-x86_64安装kylinv10-arrch64
1. vmware esxi安装centos8,开启内核虚拟化
2. 安装qemu-system-arrch64
操作:
wget https://download.qemu.org/qemu-2.11.0.tar.xz tar xvJf qemu-2.11.0.tar.xz cd qemu-2.11.0 ./configure –-target-list=aarch64-softmmu make make install
报错1:Python not found. Use --python=/path/to/python
# ./configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu ERROR: Python not found. Use --python=/path/to/python #解决1,指定python路径,提示当前python版本过高: # ./configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu --python=/usr/bin/python3.6 ERROR: Cannot use '/usr/bin/python3.6', Python 2.6 or later is required. Note that Python 3 or later is not yet supported. Use --python=/path/to/python to specify a supported Python. #解决2,下载python2,再次尝试遇到新的报错 # ./configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu --python=/usr/bin/python2 ERROR: "cc" either does not exist or does not work
报错2:ERROR: "cc" either does not exist or does not work
下载gcc解决该报错,然后提示依然是缺包
# ./configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu --python=/usr/bin/python2
ERROR: zlib check failed
Make sure to have the zlib libs and headers installed.
报错3:ERROR: zlib check failed Make sure to have the zlib libs and headers installed.
下载zlib zlib-devel,然后再次提示缺包
# ./configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu --python=/usr/bin/python2 ERROR: glib-2.22 gthread-2.0 is required to compile QEMU
下载glib2 glib2-devel,提示还是缺包
下载pixman pixman-devel
./config成功
make告警:缺少命令:flex bison
下载flex,bison
然后还是失败:
util/memfd.c:40:12: error: static declaration of ‘memfd_create’ follows non-static declaration static int memfd_create(const char *name, unsigned int flags) ^~~~~~~~~~~~ In file included from /usr/include/bits/mman-linux.h:117, from /usr/include/bits/mman.h:49, from /usr/include/sys/mman.h:41, from /root/qemu-2.11.0/include/sysemu/os-posix.h:29, from /root/qemu-2.11.0/include/qemu/osdep.h:104, from util/memfd.c:28: /usr/include/bits/mman-shared.h:46:5: note: previous declaration of ‘memfd_create’ was here int memfd_create (const char *__name, unsigned int __flags) __THROW; ^~~~~~~~~~~~ make: *** [/root/qemu-2.11.0/rules.mak:66: util/memfd.o] Error 1
看百度上各种解决办法,懒得去一个一个验证,直接换最新的包
wget https://download.qemu.org/qemu-7.2.0.tar.xz
查看README文件,根据提示操作
mkdir build cd build ../configure make
提示缺包ninjia
yum --enablerepo=powertools install ninja-build
这次提示python版本过低
Found ninja-1.8.2 at /usr/bin/ninja Running postconf script '/usr/bin/python3 /root/qemu-7.2.0/scripts/symlink-install-tree.py' NOTICE: You are using Python 3.6 which is EOL. Starting with v0.62.0, Meson will require Python 3.7 or newer
安装一个python3.9 然后把/usr/bin/python3指向python3.9
然后再次执行
mkdir build cd build ../configure --target-list=aarch64-softmmu make
无报错
make install
缺包就装包:perl
然后make install成功
# which qemu-system-aarch64 /usr/local/bin/qemu-system-aarch64
#理论上一切OK,除非包有问题 qemu-img create -f raw -o size=30G test.img qemu-system-aarch64 -m 2048 -cpu cortex-a57 -smp 2 -M virt -bios QEMU_EFI.fd -nographic -drive if=none,file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/Kylin-Server-10-SP1-Release-Build04-20200711-arm64.iso,id=cdrom,media=cdrom -device virtio-scsi-device -device scsi-cd,drive=cdrom -drive if=none,file=test.img,id=hd0 -device virtio-blk-device,drive=hd0
果然还是报错了
#报错:EFI stub: Exiting boot services and installing virtual address map
查了一下,是EFI固件包的问题,重新下载UEFI固件
wget https://www.kraxel.org/repos/firmware.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/firmware.repo yum install edk2.git-aarch64
或者
rpm -ivh http://mirror.centos.org/centos/8-stream/AppStream/aarch64/os/Packages/edk2-aarch64-20220126gitbb1bba3d77-5.el8.noarch.rpm
然后再试一次
qemu-img create -f qcow2 KylinV10sp2.qcow2 64G
qemu-system-aarch64 -m 8192 -cpu cortex-a57 -smp 2 -M virt -bios /usr/share/edk2.git/aarch64/QEMU_EFI-pflash.raw -nographic -drive if=none,file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/Kylin-Server-10-SP2-aarch64-Release-Build09-20210524.iso,id=cdrom,media=cdrom -device virtio-scsi-device -device scsi-cd,drive=cdrom -drive if=none,file=KylinV10sp2.qcow2,id=hd0 -device virtio-blk-device,drive=hd0 -net none
这次一切正常,直到。。。这。。。直接让打电话,再试了一次,还是卡在这里下不去了。。。
[ 325.623043][ 1] Authorization warning: Authorization binary is corrupted, Please call 400-089-1870 for help.
既然跑流程没问题,装系统卡iso镜像,那就试试直接从现成的arm虚拟机镜像文件起给虚机试试吧
qemu-system-aarch64 -m 8192 -cpu cortex-a57 -smp 2 -M virt -bios /usr/share/edk2.git/aarch64/QEMU_EFI.fd -nographic -device e1000e,netdev=dev0,mac='00:00:00:01:00:01' -netdev tap,ifname=tap-int,id=dev0,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=dev1,mac='00:00:00:01:00:02',vectors=32,mq=on -netdev tap,ifname=tap-0,id=dev1,script=no,downscript=no,vhost=on,queues=16 -drive format=raw,file=test-kylin10-2.raw
终于成功了,也就是说卡的是这一个iso镜像,换一家不那么"高贵"的iso应该也能行。
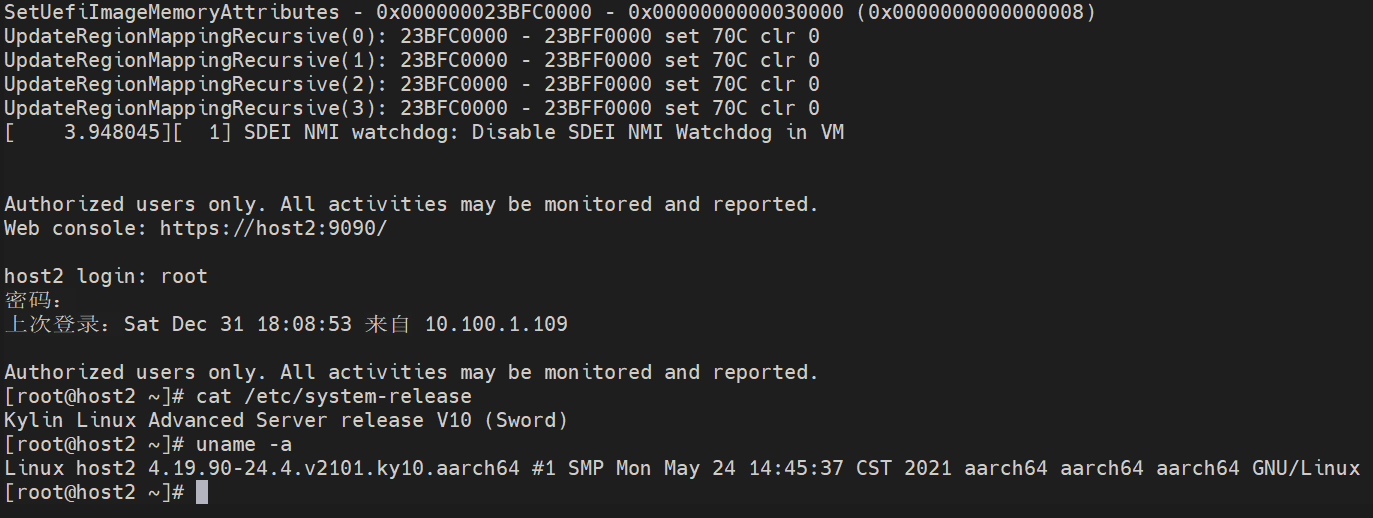
该走的流程先走完,记下后续笔记(虽然没什么用,我的virt-manager就默认了一个x64的qemu,arm64的qemu没对接上)
安装virt-manager组件,编辑/etc/libvirt/qemu.conf最后一行添加
nvram = [ "/usr/share/edk2.git/aarch64/QEMU_EFI-pflash.raw:/usr/share/edk2.git/aarch64/vars-template-pflash.raw" ]
然后开始尝试使用virt-manager管理服务。
操作记录:现安装virt-manager,再编译安装qemu,于是:
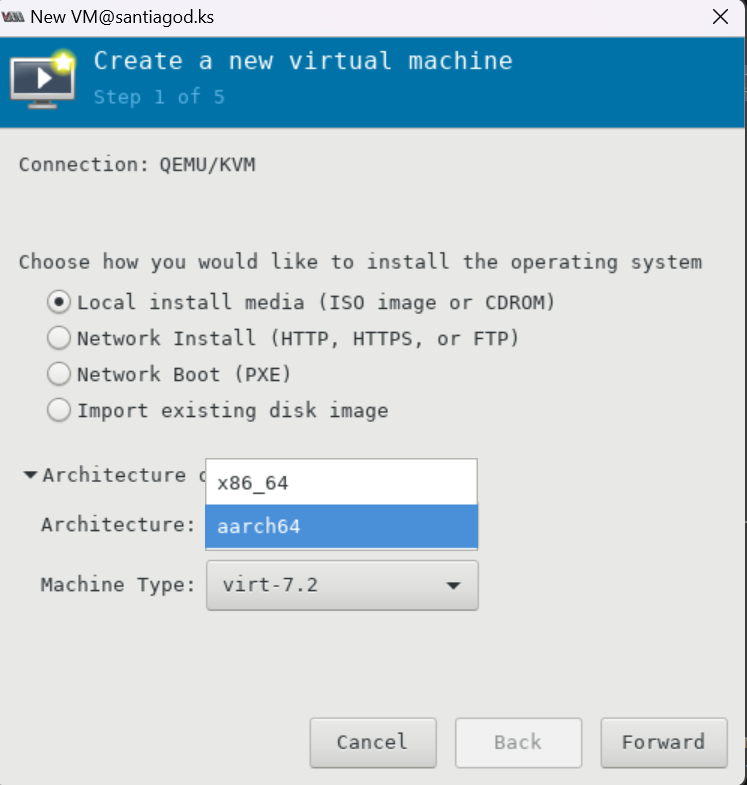
其他
qemu基础
1. ttyS0串口重定向
qemu启动一个Linux Guest,如果只需要这个Guest的终端,不需要图形用户界面,可将Linux Guest的输出重定向至虚拟串口(最终是重定向到终端)。下面以Fedora Guest为例说明用法。不同发行版和版本设置方法可能不同(如grub、grub2就不一样,debian这样的发行版需要配置/etc/inittab)。 重定向虚拟串口到console,有两种用法 内核不在虚拟机镜像文件里头 qemu -kernel arch/i386/boot/bzImage -hda root-2.4.20.img -append "root=/dev/hda console=ttyS0" -nographic 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/defeattroy/article/details/5257323 内核在虚拟机镜像文件里头 先畸形启动Guest,如果是grub2,编辑文件 /etc/default/grub GRUB_TIMEOUT=5 GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR="Fedora" GRUB_DEFAULT=saved GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="rd.md=0 rd.lvm=0 rd.dm=0 SYSFONT=True KEYTABLE=us rd.luks=0 LANG=en_US.UTF-8 rhgb quiet console=tty0 console=ttyS0,9600n8" GRUB_TERMINAL=serial GRUB_SERIAL_COMMAND="serial --speed=9600 --unit=0 --word=8 --parity=no --stop=1" 生成的/boot/grub2/grub.cfg文件应有如下配置 serial --speed=9600 --unit=0 --word=8 --parity=no --stop=1 terminal_input serial terminal_output serial ...... linux /vmlinuz-3.6.11-rt32 root=UUID=0ff1fb64-4e8d-44bf-87f7-8a2f111159d8 ro rd.md=0 rd.lvm=0 rd.dm=0 SYSFONT=True KEYTABLE=us rd.luks=0 LANG=en_US.UTF-8 rhgb quiet console=tty0 console=ttyS0,9600n8 然后用-nographic参数启动qemu qemu-kvm -enable-kvm -m 1024 -nographic -drive file=/mnt/sdb/vms/testfc/testfc.qcow2,if=virtio,index=0,format=qcow2
参考链接:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/UEFI/virt-install
https://www.txisfine.cn/archives/a0d5fa12
https://www.cnblogs.com/linuxxl/p/11658387.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353547345
https://jgsun.github.io/2018/12/17/qemu-virt-arm64/
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42001403/article/details/100532861
https://luomuxiaoxiao.com/?p=743
https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/Networking
https://blog.csdn.net/richardysteven/article/details/54807927 #关于vnc,kvm与网络
--enable-kvm ,-serial telent:localhost:4321,server,nowait,-vnc :port
https://www.cnblogs.com/schips/p/15489856.html #关于串口重定向与自动登录
https://fadeevab.com/build-android-kernel-and-run-on-qemu-minimal-step-by-step/ #qemu虚拟化安卓
以下转载自:https://fadeevab.com/how-to-setup-qemu-output-to-console-and-automate-using-shell-script/
1. Input/output to the host terminal
-serial stdio
qemu-system-x86_64 -serial stdio wheezy.qcow2
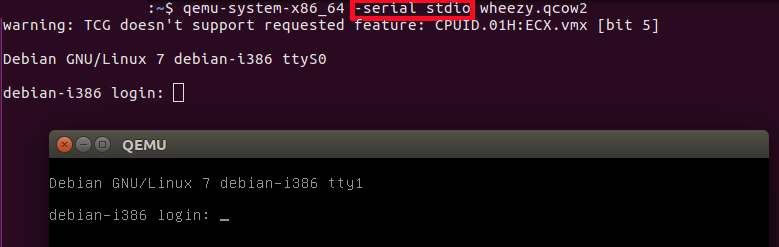
-serial stdio redirects the virtual serial port to the host's terminal input/output. You will see a welcome string after a successful boot.
-nographic
qemu-system-x86_64 -nographic wheezy.qcow2
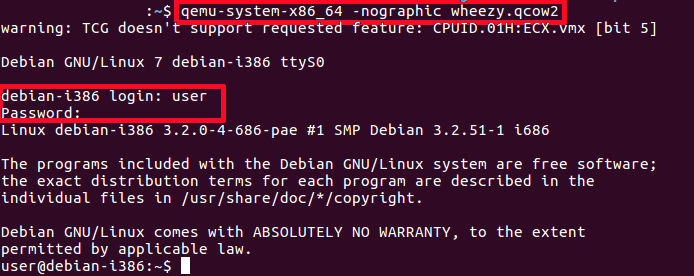
-nographic does the same as "-serial stdio" and also hides a QEMU's graphical window.
Cautions:
- You will not see any early boot logs in the host's console. To get them, see Early boot messages in the host terminal below.
- To exit the guest system without GUI, using stdio redirected to the terminal, login as a root (user: root, password: root) and shutdown the system (wait after that for a while):
# Guest shutdown -h now
2. Early boot messages in the host terminal
console=ttyS0
If you want to see early boot logs, you should pass console=ttyS0 parameter to a Linux kernel command line:
qemu-system-x86_64 -nographic -kernel vmlinuz -hda wheezy.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0"
or
qemu-system-x86_64 -serial stdio -kernel vmlinuz -hda wheezy.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0"
or
qemu-system-x86_64 -serial stdio wheezy.qcow2
# 1. Wait for a GRUB menu to show.
# 2. Press `e`.
# 3. Find the line starting with "linux".
# 4. Add "console=ttyS0".
qemu-system-x86_64 -serial stdio -kernel vmlinuz -hda wheezy.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0":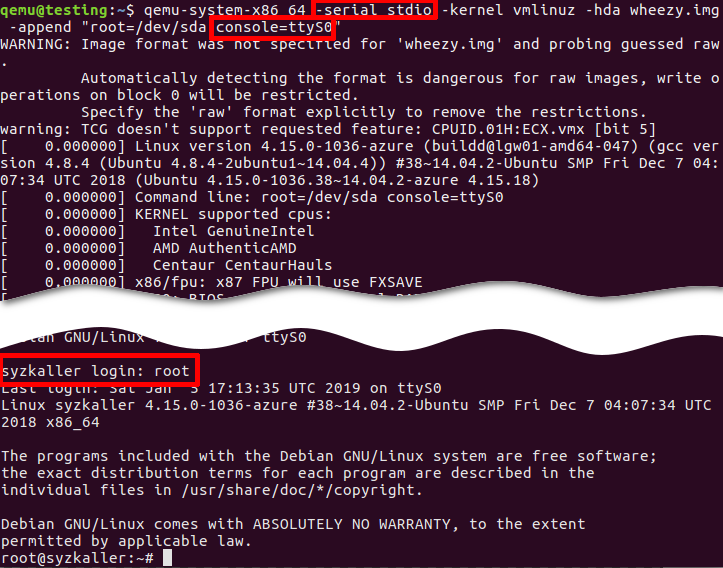
- -serial stdio or -nographic redirects input/output to the current terminal.
- -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0":
console=ttyS0forces the guest kernel to send output to the first UART serial port ttyS0, which is redirected to the host by the-serial stdiooption, androot=/dev/sdapoints the kernel to use a /dev/sda device to load the wheezy.img.
Other options:
- -kernel vmlinuz loads the kernel from the local "./vmlinuz" file.
- -hda wheezy.img is a raw image which is suitable for booting with vmlinuz binary (wheezy.qcow2 won't be recognized in the block device).
3. Input/output through a named pipe (file)
Create a named pipe
mkfifo /tmp/guest.in /tmp/guest.out
Start QEMU
qemu-system-x86_64 -serial pipe:/tmp/guest -kernel vmlinuz -hda wheezy.img -append "root=/dev/sda console=ttyS0"
-serial pipe:/tmp/guest redirects a guest's output to a /tmp/guest.out and allows to send input from host to guest via /tmp/guest.in.
Take an output from the guest
cat /tmp/guest.out
Send a command to the guest
When login screen appears, send a login string:
printf "root\n" > /tmp/guest.in
Wait until some string
Wait until SSH Daemon starts.
while read line; do
echo "${line}"
if [[ ${line} == *"Secure Shell server: sshd"* ]]; then
break;
fi
done < /tmp/quest.out
4. Automate QEMU guest using expect tool
Install "expect" tool
sudo apt install expect
Create an expect script
example.exp:
#!/usr/bin/expect -f
# Wait enough (forever) until a long-time boot
set timeout -1
# Start the guest VM
spawn qemu-system-x86_64 -serial stdio wheezy.qcow2
expect "login: "
send "root\n"
expect "Password: "
send "root\n"
expect "# "
send "shutdown -h now"
Original script is found there: https://stacoverflow.com/questions/314613/qemu-guest-automation, but be careful, symbol of quotes “ (which is not a ") in the original stackoverflow answer cannot be recognized by the expect utility (send "root\n").
Execute "expect" script
chmod +x example.exp
./example.exp
5. Automate QEMU guest using ssh
Set up port forwarding
qemu-system-x86_64 -netdev user,id=net0,hostfwd=tcp::10022-:22 -device e1000,netdev=net0 wheezy.qcow2
Connect via ssh
ssh root@localhost -p 10022 'uptime; ls; echo Test;'
- To apply server's public key automatically use
-o "StrictHostKeyChecking no":ssh root@localhost -p 10022 -o "StrictHostKeyChecking no" 'uptime; ls; echo Test;'
Troubleshooting
- QEMU guest has to be able to recognize a network card device (NIC, Network Interface Card):
-netdev user,id=net0 -device e1000,netdev=net0.# Without port forwarding qemu-system-x86_64 -netdev user,id=net0 -device e1000,netdev=net0 wheezy.qcow2 - Boot and check that the new interface has appeared on the guest system:
# Guest ifconfig -a - Check the
10022port on the host:# Host netstat -tanp | grep 10022 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10022 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 16589/qemu-system-x - Check the
22port on the guest:# Guest netstat -tanp | grep 22 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2430/sshd - You can forward telnet port
23and verify the connection:qemu-system-x86_64 -netdev user,id=net0,hostfwd=tcp::10023-:23 -device e1000,netdev=net0 wheezy.qcow2- Guest (server):
# Guest nc -v -l -p 23 Listening on [0.0.0.0] (family 0, port 23) - Host (client):
# Host echo asdf | nc localhost 10023
- Guest (server):
Establish passwordless login via ssh
- Generate host SSH keys:
# Host ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -q -N "" -f ./qemukey - Set up a public key to the guest as a trusted (authorized) key.
- Via
ssh-copy-id- You need a root with password. You the guest root is passwordless, go to the guest system and set up the password:
# Guest sudo passwd - Send the generated public key:
# Host ssh-copy-id -p 10022 -i ~/.ssh/qemukey root@localhost - Reset the password in the guest system:
# Guest sudo passwd -l root
- You need a root with password. You the guest root is passwordless, go to the guest system and set up the password:
- Manually
- Send a public key via
scp:# Host scp -P 10022 ./qemukey.pub root@localhost:/root/.ssh/ - Login to the guest and set up new authorized key:
# Guest cat /root/.ssh/qemukey.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys /etc/init.d/ssh restart - Or mount device locally, put the public key to the .ssh directory, and concatenate to authorized_keys.
- Send a public key via
- Via
- Fix the
/etc/ssh/sshd_configon the guest:PasswordAuthentication no PermitRootLogin without-password - Restart SSH daemon on the guest:
# Guest /etc/init.d/ssh restart - Connect via ssh:
# Host ssh root@localhost -p 10022 -i ./qemukey
Binaries used in the examples
- wheezy.qcow2 (i386): bootable Debian "Wheezy" image a QEMU copy-on-write format. Login/password: "root"/"root", and "user"/"user".
wget https://people.debian.org/~aurel32/qemu/i386/debian_wheezy_i386_standard.qcow2 -O wheezy.qcow2 - wheezy.img (i386): non-bootable Debian "Wheezy" image (without kernel) to use with own kernel (-kernel vmlinuz).
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/syzkaller/wheezy.img - vmlinuz (i386): compressed bootable Linux kernel. Options:
- Build from the scratch: Build Android Kernel and Run on QEMU with Minimal Environment: Step by Step.
- Download from Ubuntu repository (WARNING! Port forwarding will NOT work):
wget http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-signed-azure/linux-image-4.15.0-1036-azure_4.15.0-1036.38~14.04.2_amd64.deb ar x linux-image-4.15.0-1036-azure_4.15.0-1036.38~14.04.2_amd64.deb tar xf data.tar.xz ./boot/vmlinuz-4.15.0-1036-azure cp ./boot/vmlinuz-4.15.0-1036-azure ./vmlinuz - You can try your host's linux kernel passing one to the QEMU guest (WARNING! You could have problems either with port forwarding, or with a block device):
sudo cp /boot/vmlinuz-$(uname -r) ./





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构