redis 客户端库 之 spring data redis ----- 源码解析系列(一)之 jedis 库连接 redis 集群
一、背景
spring boot redis 接入 redis ,提供了两种库的方式,一是:lettuce,而是:jedis,被系列介绍接入 jedis时的源码
二、代码示例(包含maven依赖)
<!-- spring config -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- redis 客户端需要使用到 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Jedis 客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
package com.summer.demo.springboot.redis; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class RediesDemoController { @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate; @GetMapping("/jedis/hello") public Object testJedis() { Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); if (value == null) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "jedis"); value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); } return value; } @GetMapping("/lettuce/hello") public Object testLettuce() { Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); if (value == null) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "lettuce"); value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); } return value; } @GetMapping("/query/hello") public Object testSection(@RequestParam("key") String key) { Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); if (value == null) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, key); value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); } return value; } }
package com.summer.springboot.redis.config; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; @Configuration public class Redisconfig { /** * RedisTemplate配置 * @param connectionFactory * @return */ @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean(RedisTemplate.class) public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) { // 配置redisTemplate RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); RedisSerializer<String> redisKeySerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(redisKeySerializer); redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(redisKeySerializer); redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer()); redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet(); return redisTemplate; } }
package com.summer.demo.springboot.redis; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class RedisDemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args){ SpringApplication.run(RedisDemoApplication.class); } }
#Redis配置 spring: redis: password: 123456 # 密码(默认为空) timeout: 6000ms # 连接超时时长(毫秒) cluster: max-redirects: 3 # 获取失败 最大重定向次数 nodes: 192.168.149.128:6370,192.168.149.128:6371,192.168.149.129:6370,192.168.149.129:6371,192.168.149.130:6370,192.168.149.130:6371 jedis: pool: max-active: 1000 # 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) max-wait: -1ms # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) max-idle: 10 # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 min-idle: 5 # 连接池中的最小空闲连接
三、源码解析
1、 初始化

图一: jedis 初始化
步骤大致如下:
(1) 通过 spring-boot-autoconfigure 自动加载 RedisAutoConfiguration.
在该类中存在如下注解:
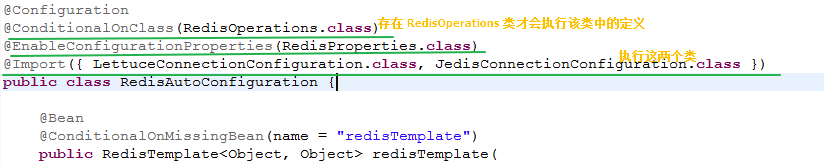
RedisAutoConfiguration 作为 redis 相关初始化的 引入类,其上会自动初始化 LettuceConnectionConfiguration 及 JedisConnectionConfiguration。
JedisConnectionConfiguration 负责所有 jedis 相关的初始化;
(2) JedisConnectionConfiguration 类中 完成的事件主要是初始化 JedisConnectionFactory 实例,在该类中可以看到为了初始化 JedisConnectionFactory 实例时所需要的所有配置来自 RedisProperties。RedisProperties 的配置项均可配置在 application.properties 文件中,目前 已有配置如下:

图二: spring boot redis 提供的相关配置项
从上图中可以看到,配置分为如下几类:
- 未引入高可用时,单个 redis 结点的相关配置 ----- RedisStandaloneConfiguration
- 高可用采用集群模式的配置 ---- RedisClusterConfiguration
- 高可用采用哨兵模式的配置 ---- RedisSentinelConfiguration
application.properties 可定义的关于 redis的配置表见下:
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 说明 |
| spring.redis.ssl | false | 是否开启SSL |
| spring.redis.database | 0 | |
| spring.redis.host | localhost | redis 节点连接 IP或域名 |
| spring.redis.password | redis 连接密码 | |
| spring.redis.port | 6379 | |
| spring.redis.timeout | 连接池读写超时时间、连接超时时间 | |
| spring.redis.url |
redis连接地址,若是 rediss:// 为前缀,则默认开启SSL, 格式为:redis://user:password@example.com:6379 可以覆盖 host\port\password;其中 user 忽略 |
|
| spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active | 8 | 连接池最大连接数,值为-1时,表示没有限制 |
| spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle | 8 | 连接池中最大空闲连接数,若值为-1表示不限制空闲连接数 |
| spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle | 0 | 连接池中最小空闲连接数,该值为正数时才有意义 |
| spring.redis.jedis.pool.time-between-eviction-runs | 清理过期连接的周期时间 | |
| spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait | -1 | 当从池子中阻塞性获取连接时阻塞的时间,若为-1,则表示一直阻塞知道成功从池子中获取到一个连接 |
| spring.redis.sentinel.master | 哨兵模式下的主节点 | |
| spring.redis.sentinel.nodes | 哨兵模式下的多个备节点,格式为:host:port,host:port | |
| spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects | 5 | 通过槽点查找到redis node 对应的 pool,获取连接失败可尝试的次数 |
| spring.redis.cluster.nodes | redis 集群所有的redis节点,格式为:host:port,host:port | |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active | 8 | 连接池最大连接数,值为-1时,表示没有限制 |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle | 8 | 连接池中最大空闲连接数,若值为-1表示不限制空闲连接数 |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle | 0 | 连接池中最小空闲连接数,该值为正数时才有意义 |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait | -1 | 当从池子中阻塞性获取连接时阻塞的时间,若为-1,则表示一直阻塞知道成功从池子中获取到一个连接 |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.time-between-eviction-runs | 清理过期连接的周期时间 | |
| spring.redis.lettuce.pool.shutdown-timeout | 100,单位毫秒 | 关闭池子的超时时间 |
初始化 JedisConnectionFactory 实例除了要使用 来在 RedisProperties 中的配置外,有些功能可能还需要些扩展,这个时候可以编写 ObjectProvider<JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer> builderCustomizers 来做这件事,详见下面。
(3) JedisConnectionFactory 类由于存在以下类继承,因此在初始化该bean的时候,会自动执行 该类中的 afterPropertiesSet ,而该方法,就是用来初始化 redis 结点,每个结点创建连接池,若 redis 结点 master 角色,则

public void afterPropertiesSet() { if (shardInfo == null && clientConfiguration instanceof MutableJedisClientConfiguration) { providedShardInfo = false; shardInfo = new JedisShardInfo(getHostName(), getPort(), isUseSsl(), // clientConfiguration.getSslSocketFactory().orElse(null), // clientConfiguration.getSslParameters().orElse(null), // clientConfiguration.getHostnameVerifier().orElse(null)); getRedisPassword().map(String::new).ifPresent(shardInfo::setPassword); int readTimeout = getReadTimeout(); if (readTimeout > 0) { shardInfo.setSoTimeout(readTimeout); } getMutableConfiguration().setShardInfo(shardInfo); } if (getUsePool() && !isRedisClusterAware()) { this.pool = createPool(); } if (isRedisClusterAware()) { this.cluster = createCluster(); } } private Pool<Jedis> createPool() { if (isRedisSentinelAware()) { return createRedisSentinelPool((RedisSentinelConfiguration) this.configuration); } return createRedisPool(); }
(4) createCluster 方法中 会去创建 一个 JedisCluster 实例,该实例中含有 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 属性;
(5) JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 类中存在 JedisClusterInfoCache 属性, JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 在构造函数中 不仅 初始化 JedisClusterInfoCache 实例,同时调用该实例的方法初始化集群节点信息、每个节点的pool池、槽点和 master 之间的映射关系。pool 池创建的时候会将 jedisCluster 中 poolConfig中所有配置给 pool 对象。

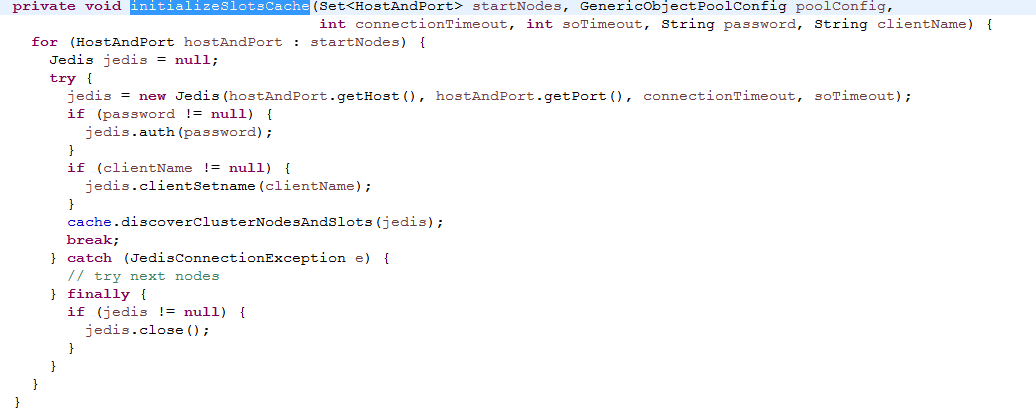
在 initializeSlotsCache 方法中可以看到,遍历 redis 结点,若有个结点可以连接上并通过该结点成功 初始化 每个节点的pool池、槽点和 master 之间的映射关系 ,则直接跳出。一次可见,连接上任意一个redis 结点就可以知道 集群全貌,这个和 通过 redis的工具 redis-cli 使用 cluster nodes 命令获取集群全貌是一样的。
(6) JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 类配合 JedisClusterInfoCache 实例 更新 这个 cache 信息。
JedisSlotBasedConnnectionHandler 类中存在以下方法:
public void renewSlotCache() { cache.renewClusterSlots(null); } public void renewSlotCache(Jedis jedis) { cache.renewClusterSlots(jedis); } @Override public void close() { cache.reset(); }
2、通过 redisTemplate 设置或查询 key 时的源码
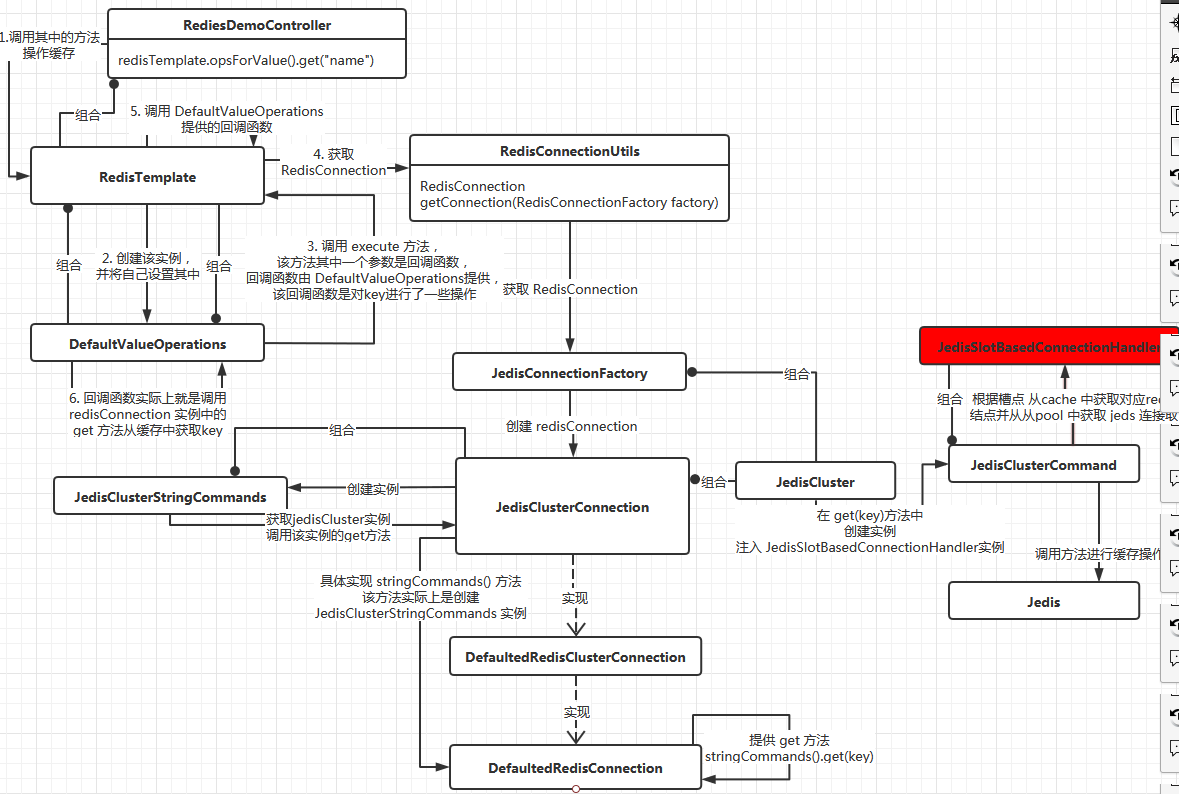
图三 操作缓存
(1) redisTemplate 可以自己重新定义,见第二章节
(2) redisTemplate 提供的直接面向用户操作缓存的方法中,都会定义一个类来进行额外的操作,如 DefaultValuesOperations.
controller:
@GetMapping("/jedis/hello") public Object testJedis() { Object value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); # redisTemplate.opsForValue() 实际上是生成 DefaultValueOperations 实例 if (value == null) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "jedis"); value = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name"); } return value;
public ValueOperations<K, V> opsForValue() { if (valueOps == null) { valueOps = new DefaultValueOperations<>(this); } return valueOps; }
DefaultValueOperations类
@Override public V get(Object key) { return execute(new ValueDeserializingRedisCallback(key) { @Override protected byte[] inRedis(byte[] rawKey, RedisConnection connection) { return connection.get(rawKey); } }, true); }
@Nullable <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> callback, boolean b) { return template.execute(callback, b); }
abstract class ValueDeserializingRedisCallback implements RedisCallback<V> { private Object key; public ValueDeserializingRedisCallback(Object key) { this.key = key; } public final V doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) { byte[] result = inRedis(rawKey(key), connection); return deserializeValue(result); } @Nullable protected abstract byte[] inRedis(byte[] rawKey, RedisConnection connection); }
所以 get 实际上还是执行 redisTemplate 中的 execute 方法,而 DefaultValueOperations 类实现了 execute 中的回调方法,从而类中也可以看到 回调方法类的具体实现类是 ValueDeserializingRedisCallback,该类 会对 key 以及从 缓存中查询到的内容 进行序列化或反序列化处理。
(3) 缓存操作核心代码还是在 redisTemplate 中 的execute 方法
@Nullable public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean pipeline) { Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it"); Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory(); RedisConnection conn = null; try { if (enableTransactionSupport) { // only bind resources in case of potential transaction synchronization conn = RedisConnectionUtils.bindConnection(factory, enableTransactionSupport); } else { conn = RedisConnectionUtils.getConnection(factory); //获取 redisConnection 实例 } boolean existingConnection = TransactionSynchronizationManager.hasResource(factory); RedisConnection connToUse = preProcessConnection(conn, existingConnection); boolean pipelineStatus = connToUse.isPipelined(); if (pipeline && !pipelineStatus) { connToUse.openPipeline(); } RedisConnection connToExpose = (exposeConnection ? connToUse : createRedisConnectionProxy(connToUse)); T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose); //执行回调函数 ValueDeserializingRedisCallback 中的方法,该方法直接调用 redisConnection.get(key)方法 // close pipeline if (pipeline && !pipelineStatus) { connToUse.closePipeline(); } // TODO: any other connection processing? return postProcessResult(result, connToUse, existingConnection); } finally { RedisConnectionUtils.releaseConnection(conn, factory, enableTransactionSupport); } }
这里有两个核心点:
- 获取 RedisConnection 实例;
- 通过 RedisConnection 操作缓存;
(4) 获取 RedisConnection 实例
从图三中可以看到,
- 这里的 redisConnection 实例它实际上是 RedisClusterConnection对象,它是由 JedisConnectionFactory 创建,该对象创建的时候 将关键 实例 jedisCluster 也注入到了该对象中;
- RedisClusterConnection 类中 对外提供的操作缓存的方法中(这里以 get(key)为例),会创建 JedisClusterStringCommands 实例,直接通过该 实例调用 jedisCluster 实例中的方法操作缓存;
- jedisCluster 实例在操作缓存的方法中,又 创建了 JedisClusterCommand 方法,调用 JedisClusterCommand 的 run 方法操作缓存
JedisCluster 类
@Override public String get(final String key) { return new JedisClusterCommand<String>(connectionHandler, maxAttempts) { @Override public String execute(Jedis connection) { return connection.get(key); } }.run(key); }
JedisClusterCommand类
public T run(String key) { if (key == null) { throw new JedisClusterException("No way to dispatch this command to Redis Cluster."); } return runWithRetries(JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key), this.maxAttempts, false, false); }
private T runWithRetries(final int slot, int attempts, boolean tryRandomNode, boolean asking) { if (attempts <= 0) { throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?"); } Jedis connection = null; try { if (asking) { // TODO: Pipeline asking with the original command to make it // faster.... connection = askConnection.get(); connection.asking(); // if asking success, reset asking flag asking = false; } else { if (tryRandomNode) { connection = connectionHandler.getConnection(); } else { connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(slot); // connectionHandler 为 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 实例,从该实例中获取 Jedis connection 连接 } } return execute(connection); } catch (JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException jnrcne) { throw jnrcne; } catch (JedisConnectionException jce) { // release current connection before recursion releaseConnection(connection); connection = null; if (attempts <= 1) { //We need this because if node is not reachable anymore - we need to finally initiate slots renewing, //or we can stuck with cluster state without one node in opposite case. //But now if maxAttempts = 1 or 2 we will do it too often. For each time-outed request. //TODO make tracking of successful/unsuccessful operations for node - do renewing only //if there were no successful responses from this node last few seconds this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(); } return runWithRetries(slot, attempts - 1, tryRandomNode, asking); } catch (JedisRedirectionException jre) { // if MOVED redirection occurred, if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) { // it rebuilds cluster's slot cache // recommended by Redis cluster specification this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(connection); } // release current connection before recursion or renewing releaseConnection(connection); connection = null; if (jre instanceof JedisAskDataException) { asking = true; askConnection.set(this.connectionHandler.getConnectionFromNode(jre.getTargetNode())); } else if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) { } else { throw new JedisClusterException(jre); } return runWithRetries(slot, attempts - 1, false, asking); } finally { releaseConnection(connection); } }
JedisClusterCommand 类中的 runWithRetries 是整个过程中最最最核心的代码
runWithRetries方法 从 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 中根据 key 计算出的 slot 获取对应结点的 jedis connection连接,在上述代码里面 明显显示:获取不到连接的时候,可以尝试 attemps次获取连接,在尝试最后一次机会的时候,若仍然失败了,会调用 JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 实例中的方法重新刷新 cache 上面的信息(重新和reids 结点连接并刷新集群信息)。
从这个逻辑看,这里存在一个问题:
cache 中的 slot 属性 里面存储的都是 slot 和 集群中master结点的应的池对象的关系。若某个slot 存在的master redis node结点挂掉,这个缓存数据都不到更新,也就是 slot 不会切换和新的master redis node 池建立关系(新的master redis node 是原来 master redis node 的 slave)。切换必须是一次请求尝试全部失败再刷新关系。这样的逻辑显然对 使用方是不友好的。
JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler 类中存在的代码:
@Override public Jedis getConnectionFromSlot(int slot) { JedisPool connectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot); if (connectionPool != null) { // It can't guaranteed to get valid connection because of node // assignment return connectionPool.getResource(); //这个是真正获取和redis开源软件建立的连接 } else { renewSlotCache(); //It's abnormal situation for cluster mode, that we have just nothing for slot, try to rediscover state connectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot); if (connectionPool != null) { return connectionPool.getResource(); } else { //no choice, fallback to new connection to random node return getConnection(); } } }
// 下面这 三个 方法在父类中 public void renewSlotCache() { cache.renewClusterSlots(null); } public void renewSlotCache(Jedis jedis) { cache.renewClusterSlots(jedis); } @Override public void close() { cache.reset(); }
(5) 从 redis node 的连接池中获取 jedis connection
从上面的代码中可以看到从 cache 中可以拿到 slot 存在 master redis node 对应的 pool ,然后再次 这个 pool 中获取redis 开源软件建立的真正连接。
JedisPool 类
public T getResource() { try { return internalPool.borrowObject(); } catch (NoSuchElementException nse) { throw new JedisException("Could not get a resource from the pool", nse); } catch (Exception e) { throw new JedisConnectionException("Could not get a resource from the pool", e); } }
internalPool 是 org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPool 对象,这个对象才是真正管理一个 redis node 的连接池对象。
GenericObjectPool类
public T borrowObject(final long borrowMaxWaitMillis) throws Exception { assertOpen(); final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig; if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnBorrow() && (getNumIdle() < 2) && (getNumActive() > getMaxTotal() - 3) ) { removeAbandoned(ac); } PooledObject<T> p = null; // Get local copy of current config so it is consistent for entire // method execution final boolean blockWhenExhausted = getBlockWhenExhausted(); boolean create; final long waitTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); while (p == null) { create = false; p = idleObjects.pollFirst(); if (p == null) { p = create(); if (p != null) { create = true; } } if (blockWhenExhausted) { if (p == null) { if (borrowMaxWaitMillis < 0) { p = idleObjects.takeFirst(); } else { p = idleObjects.pollFirst(borrowMaxWaitMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } if (p == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException( "Timeout waiting for idle object"); } } else { if (p == null) { throw new NoSuchElementException("Pool exhausted"); } } if (!p.allocate()) { p = null; } if (p != null) { try { factory.activateObject(p); } catch (final Exception e) { try { destroy(p); } catch (final Exception e1) { // Ignore - activation failure is more important } p = null; if (create) { final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException( "Unable to activate object"); nsee.initCause(e); throw nsee; } } if (p != null && (getTestOnBorrow() || create && getTestOnCreate())) { boolean validate = false; Throwable validationThrowable = null; try { validate = factory.validateObject(p); } catch (final Throwable t) { PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t); validationThrowable = t; } if (!validate) { try { destroy(p); destroyedByBorrowValidationCount.incrementAndGet(); } catch (final Exception e) { // Ignore - validation failure is more important } p = null; if (create) { final NoSuchElementException nsee = new NoSuchElementException( "Unable to validate object"); nsee.initCause(validationThrowable); throw nsee; } } } } } updateStatsBorrow(p, System.currentTimeMillis() - waitTime); return p.getObject(); }
上述代码中可以看到存在一些配置项用来限制相关功能如下:
- testOnBorrow:从池中获得一个连接是否校验该连接是否可用;
- testOnCreate:是否校验 新创建的连接是否可用;
该类中 LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>> idleObjects 中用来存放 池中空闲的所有的连接;Map<IdentityWrapper<T>, PooledObject<T>> allObjects 存放 池中所有连接;池中所有配置来自 BaseObjectPoolConfig<T> conf 类
由此通过该类的逻辑和 BaseObjectPoolConfig,可以得到存在如下配置项控制池或连接相关逻辑。
| 配置项 | 默认值 | 作用 |
| lifo | true | 为true,表示 idleObjects 为 后进先出队列(当作栈使用),否则为先进先出队列 |
| maxWaitMillis | -1L | 当从池子中阻塞性获取连接时阻塞的时间,若为-1,则表示一直阻塞知道成功从池子中获取到一个连接(该值可通过 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait 进行配置) |
| blockWhenExhausted | true |
阻塞性方式从 idleObjects 获取 连接对象,配合 borrowMaxWaitMillis使用: a) borrowMaxWaitMillis为-1时,直接阻塞性idleObjects中获取连接对象,没有获取的话,就一直阻塞在那里; b) borrowMaxWaitMillis 不为 -1 时,阻塞一段时间从 idleObjects中获取连接对象; |
| testOnCreate | false | 向池中请求连接时,获取不到空闲连接就创建一个连接,是否验证创建的连接有效性(ping redis结点);值为false,表示不验证,否则进行验证 |
| testOnBorrow | false | 向池中请求连接时,获取到的是空闲连接,是否验证空闲连接有效性(ping redis结点);值为false,表示不验证,否则进行验证 |
| testOnReturn | false | 将连接放到 idleObjects 队列中,是否校验连接的有效性;值为false,表示不验证,否则进行验证(ping redis结点) |
| testWhileIdle | true | 对空闲连接进行检测(ping redis结点) |
| timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis | 30000,单位毫秒 | 周期性检查池中空闲队列中的空闲连接有效性的间隔 (该值可通过spring.redis.jedis.pool.time-between-eviction-runs 进行配置) |
| numTestsPerEvictionRun | -1 | 表示每次周期性检测空闲连接有效性时可以检查的数量 |
| minEvictableIdleTimeMillis | 60000,单位毫秒 | 连接对象在被驱逐之前可以停留在池中的最短时间,若为负数,则不驱逐 (根据默认去追逐策略中的算法) |
| softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis | -1 | 连接对象在被驱逐之前可以停留在池中的最短时间,在停留了最短时间可驱逐的并列条件为空闲的连接数超出了minIdle |
| evictionPolicyClassName | DefaultEvictionPolicy.class.getName() | 判断空闲连接过期全类名,可以自定义 |
| evictorShutdownTimeoutMillis | 10L * 1000L : 10秒 | |
| maxTotal | 8 | 池中最大连接数 (该值可通过 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active 进行配置) |
| maxIdle | 8 | 池中空闲队列最大连接数 (该值可通过 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle 进行配置) |
| minIdle | 0 | 池中空闲队列最小连接数 (该值可通过 spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle 进行配置) |
| fairness | false |
在上述表格中若没有注明 配置项来自 spring.redis,则可通过以下方式进行配置:
package com.summer.demo.springboot.redis.jedis.config; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisClientConfiguration.DefaultJedisClientConfigurationBuilder; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisClientConfiguration.JedisClientConfigurationBuilder; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder; import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils; @Configuration public class JedisConfig { @Bean public JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer builderCustomizers(){ JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer customizer = new JedisClientConfigurationBuilderCustomizer(){ @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") @Override public void customize(JedisClientConfigurationBuilder clientConfigurationBuilder) { DefaultJedisClientConfigurationBuilder poolBuilder = (DefaultJedisClientConfigurationBuilder)clientConfigurationBuilder; Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(DefaultJedisClientConfigurationBuilder.class, "poolConfig"); if(null != field){ ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field); GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig = (GenericObjectPoolConfig)ReflectionUtils.getField(field, poolBuilder); poolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); } } }; return customizer; } }
3、 每个redis node 节点的连接池 pool 中的 空闲连接周期性检查是否过期
(1) JedisClusterInfoCache 类 会为每个 redis node 创建pool,创建 pool 的同时会将池相关配置设置该 pool,其中在 设置 定时清理任务周期时间的时候会开启定时任务
JedisClusterInfoCache类
public void discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(Jedis jedis) { w.lock(); try { reset(); List<Object> slots = jedis.clusterSlots(); for (Object slotInfoObj : slots) { List<Object> slotInfo = (List<Object>) slotInfoObj; if (slotInfo.size() <= MASTER_NODE_INDEX) { continue; } List<Integer> slotNums = getAssignedSlotArray(slotInfo); // hostInfos int size = slotInfo.size(); for (int i = MASTER_NODE_INDEX; i < size; i++) { List<Object> hostInfos = (List<Object>) slotInfo.get(i); if (hostInfos.size() <= 0) { continue; } HostAndPort targetNode = generateHostAndPort(hostInfos); setupNodeIfNotExist(targetNode); if (i == MASTER_NODE_INDEX) { assignSlotsToNode(slotNums, targetNode); } } } } finally { w.unlock(); } } public JedisPool setupNodeIfNotExist(HostAndPort node) { w.lock(); try { String nodeKey = getNodeKey(node); JedisPool existingPool = nodes.get(nodeKey); if (existingPool != null) return existingPool; JedisPool nodePool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, node.getHost(), node.getPort(), connectionTimeout, soTimeout, password, 0, clientName, false, null, null, null); nodes.put(nodeKey, nodePool); return nodePool; } finally { w.unlock(); } }
JedisPool类
public void initPool(final GenericObjectPoolConfig poolConfig, PooledObjectFactory<T> factory) { if (this.internalPool != null) { try { closeInternalPool(); } catch (Exception e) { } } this.internalPool = new GenericObjectPool<T>(factory, poolConfig); }
GenericObjectPool 类
public GenericObjectPool(final PooledObjectFactory<T> factory, final GenericObjectPoolConfig<T> config) { super(config, ONAME_BASE, config.getJmxNamePrefix()); if (factory == null) { jmxUnregister(); // tidy up throw new IllegalArgumentException("factory may not be null"); } this.factory = factory; idleObjects = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(config.getFairness()); setConfig(config); } public void setConfig(final GenericObjectPoolConfig<T> conf) { super.setConfig(conf); setMaxIdle(conf.getMaxIdle()); setMinIdle(conf.getMinIdle()); setMaxTotal(conf.getMaxTotal()); }
public final void setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(
final long timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis) {
this.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis;
startEvictor(timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis);
}
final void startEvictor(final long delay) {
synchronized (evictionLock) {
EvictionTimer.cancel(evictor, evictorShutdownTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
evictor = null;
evictionIterator = null;
if (delay > 0) {
evictor = new Evictor();
EvictionTimer.schedule(evictor, delay, delay);
}
}
} # 父类 protected void setConfig(final BaseObjectPoolConfig<T> conf) { setLifo(conf.getLifo()); setMaxWaitMillis(conf.getMaxWaitMillis()); setBlockWhenExhausted(conf.getBlockWhenExhausted()); setTestOnCreate(conf.getTestOnCreate()); setTestOnBorrow(conf.getTestOnBorrow()); setTestOnReturn(conf.getTestOnReturn()); setTestWhileIdle(conf.getTestWhileIdle()); setNumTestsPerEvictionRun(conf.getNumTestsPerEvictionRun()); setMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(conf.getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis()); setTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(conf.getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis()); setSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(conf.getSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis()); final EvictionPolicy<T> policy = conf.getEvictionPolicy(); if (policy == null) { // Use the class name (pre-2.6.0 compatible) setEvictionPolicyClassName(conf.getEvictionPolicyClassName()); } else { // Otherwise, use the class (2.6.0 feature) setEvictionPolicy(policy); } setEvictorShutdownTimeoutMillis(conf.getEvictorShutdownTimeoutMillis()); }
BaseGenericObjectPool.Evictor 类
public void run() { final ClassLoader savedClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); try { if (factoryClassLoader != null) { // Set the class loader for the factory final ClassLoader cl = factoryClassLoader.get(); if (cl == null) { // The pool has been dereferenced and the class loader // GC'd. Cancel this timer so the pool can be GC'd as // well. cancel(); return; } Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); } // Evict from the pool try { evict(); } catch(final Exception e) { swallowException(e); } catch(final OutOfMemoryError oome) { // Log problem but give evictor thread a chance to continue // in case error is recoverable oome.printStackTrace(System.err); } // Re-create idle instances. try { ensureMinIdle(); } catch (final Exception e) { swallowException(e); } } finally { // Restore the previous CCL Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(savedClassLoader); } }
evict 方法还是在 GenericObjectPool 类中 ------ 这个才是周期性清理 pool 中过期空闲连接的关键方法
@Override public void evict() throws Exception { assertOpen(); if (idleObjects.size() > 0) { PooledObject<T> underTest = null; final EvictionPolicy<T> evictionPolicy = getEvictionPolicy(); synchronized (evictionLock) { final EvictionConfig evictionConfig = new EvictionConfig( getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(), getSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(), getMinIdle()); final boolean testWhileIdle = getTestWhileIdle(); for (int i = 0, m = getNumTests(); i < m; i++) { if (evictionIterator == null || !evictionIterator.hasNext()) { evictionIterator = new EvictionIterator(idleObjects); } if (!evictionIterator.hasNext()) { // Pool exhausted, nothing to do here return; } try { underTest = evictionIterator.next(); } catch (final NoSuchElementException nsee) { // Object was borrowed in another thread // Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i; i--; evictionIterator = null; continue; } if (!underTest.startEvictionTest()) { // Object was borrowed in another thread // Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i; i--; continue; } // User provided eviction policy could throw all sorts of // crazy exceptions. Protect against such an exception // killing the eviction thread. boolean evict; try { evict = evictionPolicy.evict(evictionConfig, underTest, idleObjects.size()); //由此可以看到 第一个关卡是 用户可以自定义的驱逐策略,若用户没有自定义则使用默认驱逐策略 } catch (final Throwable t) { // Slightly convoluted as SwallowedExceptionListener // uses Exception rather than Throwable PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t); swallowException(new Exception(t)); // Don't evict on error conditions evict = false; } if (evict) { // 自定义驱逐策略执行过之后,若返回结果需要驱逐,则进行销毁 destroy(underTest); destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet(); } else { if (testWhileIdle) { boolean active = false; try { factory.activateObject(underTest); active = true; } catch (final Exception e) { destroy(underTest); destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet(); } if (active) { if (!factory.validateObject(underTest)) { destroy(underTest); destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet(); } else { try { factory.passivateObject(underTest); } catch (final Exception e) { destroy(underTest); destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet(); } } } } if (!underTest.endEvictionTest(idleObjects)) { // TODO - May need to add code here once additional // states are used } } } } } final AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig; if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnMaintenance()) { removeAbandoned(ac); } }
默认驱逐策略为 DefaultEvictionPolicy 类中方法
public class DefaultEvictionPolicy<T> implements EvictionPolicy<T> { @Override public boolean evict(final EvictionConfig config, final PooledObject<T> underTest, final int idleCount) { if ((config.getIdleSoftEvictTime() < underTest.getIdleTimeMillis() && config.getMinIdle() < idleCount) || config.getIdleEvictTime() < underTest.getIdleTimeMillis()) { return true; } return false; } }
(2) 驱逐的算法具体如下
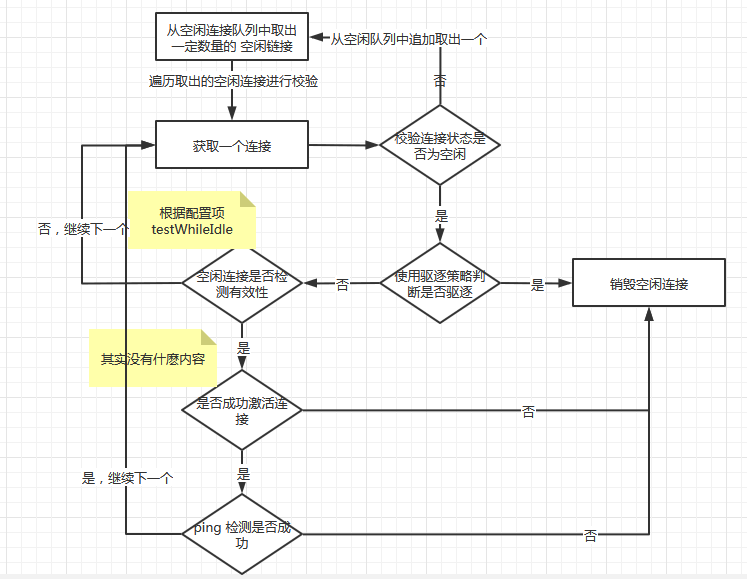
驱逐算法的逻辑按照两类主要是:
- 根据空闲时间、配置的最小空闲连接数/最小停留在池中的空闲时间(达到该事件即可驱逐)进行判断是否驱逐
- 配置可检测,就直接使用连接 ping redis node 进行验证 (个人觉得这个才是真正有意义的)
四、优化
1、程序运行过程中,redis master node 挂掉了,接下来的缓存操作需要连接替补上的 master redis node (原先是备结点),要达到这样的目的,需要怎么操作呢?
分析:
(1) jedis 接入 redis 集群的时候,根据以上代码分析知道 jedis 池里面是维护了 slot 和 master redis node 的关系,若程序运行过程中 master redis node 挂掉了,刷新slot 和它的关系的机遇只有缓存操作发生尝试指定次数都失败之后才会进行。
(2) 在进行缓存操作的时候,会从 jedis 池里面租借一个连接,jedis 提供了配置对租借的连接可以进行 ping;
(3) 每个 redis node 都会有自己的连接池,且会有独立线程不断检测连接池空闲连接是否过期或者能否ping通,可以通过配置将这些开启;
针对 (2)(3) 可以进行如下配置:
| 配置项 | 需设置的值 | 说明 |
| testOnCreate | true | 从池中租借连接,若获取到的是新创建的连接,是否先ping校验下 |
| testOnBorrow | true | 从池中租借的连接是空闲连接,是否先ping校验下 |
| testOnReturn | true | 将用过的连接放入到空闲队列之前没是否先ping校验下 |
| testWhileIdle | true | 在进行周期性驱逐任务时,根据驱逐策略决定不驱逐之后,是否再ping校验下 |
| timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis | 根据需要设置 | 设置周期性驱逐任务执行间隔时间 |
针对 (1) 必须重写 redis.clients.jedis.runWithRetries.JedisClusterCommand 方法中刷新 内存存储 slot 和 redis node 池关系的机遇,保证在尝试最后一次之前就可以刷新。目前采取的做法是在自己的工程中添加,如下类:
其中 JedisClusterCommond 与 jedis 库中的代码无二致,但是修改的方法如下:
private T runWithRetries(final int slot, int attempts, boolean tryRandomNode, boolean asking) { if (attempts <= 0) { throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?"); } Jedis connection = null; try { if (asking) { // TODO: Pipeline asking with the original command to make it // faster.... connection = askConnection.get(); connection.asking(); // if asking success, reset asking flag asking = false; } else { if (tryRandomNode) { connection = connectionHandler.getConnection(); } else { connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(slot); } } return execute(connection); } catch (JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException jnrcne) { throw jnrcne; } catch (JedisConnectionException jce) { // release current connection before recursion releaseConnection(connection); connection = null; if ((attempts-1) <= 1) { //刷新的判定条件做了更改,在剩余尝试的次数为0或1的时候,会刷新 //We need this because if node is not reachable anymore - we need to finally initiate slots renewing, //or we can stuck with cluster state without one node in opposite case. //But now if maxAttempts = 1 or 2 we will do it too often. For each time-outed request. //TODO make tracking of successful/unsuccessful operations for node - do renewing only //if there were no successful responses from this node last few seconds this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(); } return runWithRetries(slot, attempts - 1, tryRandomNode, asking); } catch (JedisRedirectionException jre) { // if MOVED redirection occurred, if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) { // it rebuilds cluster's slot cache // recommended by Redis cluster specification this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(connection); } // release current connection before recursion or renewing releaseConnection(connection); connection = null; if (jre instanceof JedisAskDataException) { asking = true; askConnection.set(this.connectionHandler.getConnectionFromNode(jre.getTargetNode())); } else if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) { } else { throw new JedisClusterException(jre); } return runWithRetries(slot, attempts - 1, false, asking); } finally { releaseConnection(connection); } }
被重新的类一定要保证 和源生的全类路径相同,且优先被加载到内存中。
PS:
虚拟机加载类的时候默认是根据 jar 包的名称字符串升序规则进行查找加载的,若你重新类所属工程最终是以jar包形式提供出去的,一定要保证 jar包名称按照字符串排序排在 redis.clients.jedis.jar 前面



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号