OpenStack 创建虚机过程简要汇总
1. 总体流程
翻译自原文(英文):https://ilearnstack.com/2013/04/26/request-flow-for-provisioning-instance-in-openstack/
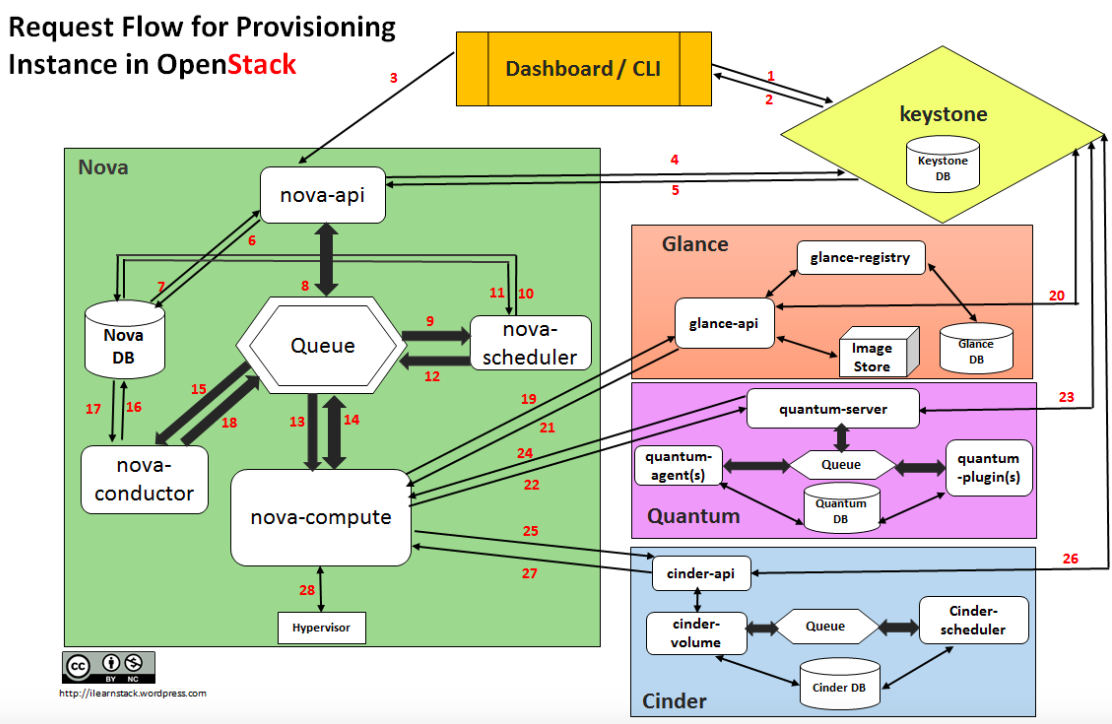
创建虚机的请求流如下:
- Dashboard 或者 CLI 获取用户的登录信息,调用 Keystone 的 REST API 去做用户身份验证。
- Keystone 对用户登录信息进行校验,然后产生验证token并发回。它会被用于后续 REST 调用请求。
- Dashboard 或者 CLI 将创建虚机的 REST请求中的‘launch instance’ 或‘nova-boot’ 部分进行转换,然后调用 nova-api 的 REST 接口。
- nova-api 接到请求,向 keystone 发送 auth-token 校验和权限认证请求。
- Keystone 校验 token,并将 auth headers 发回,它包括了 roles 和 permissions。
- nova-api 和 nova-database 进行交互。
- nova-database 为新实例创建一个数据库条目。
- nova-api 向 nova-scheduler 发送 rpc.call 请求,期望它能通过附带的 host ID 获取到数据库条目。
- nova-scheduler 从 queue 中获取到请求。
- nova-scheduler 和 nova-database 交互,获取集群中计算节点的信息和状态。
- nova-scheuler 通过过滤(filtering)和称重(weighting)找到一个合适的计算节点(host)。
- nova-scheduler 向找到的那个host上的 nova-compute 发送 rpc.cast 请求去启动虚机。
- 目标 host 上的 nova-compute 从 queue 中获取到请求。
- nova-compute 向 nova-condutor 发送 rpc.call 请求去获取待创建虚机的信息比如 host ID 和 flavor 等。
- nova-conductor 从queue 中获取到请求。
- nova-conductor 和 nova-database 交互。
- nova-database 向 nova-conductor 返回虚机的信息。
- nova-conductor 向 nova-compute 发送 rpc.call,附带所请求的信息。图中应该是遗漏了一个步骤,就是 nova-compute 从queue 中获取返回的数据。
- nova-compute 调用 glance-api 的 REST API,传入 auth-token,去根据镜像 ID 获取镜像 URI,从镜像存储中下载(原文为upload)镜像。
- glance-api 向 keystone 校验 auth-token。
- nova-compute 获取 image 的元数据。
- nova-compute 调用 Neutron API ,传入 auth-token,去分配和配置网络,比如虚机的IP地址。
- neutron-server 通过 keystone 校验 auth-token。
- nova-compute 获得网络信息。
- nova-compute 调用 Cinder API,传入 auth-token,去将 volume 挂接到实例。
- cinder-api 通过 keystone 校验 auth-token。
- nova-compute 获得块存储信息。
- nova-compute 为 hypervisor driver 产生数据,并调用 Hypersior 执行请求(通过 libvirt 或者 api)。
下表列出了每个步骤中实例的状态:
| Status | Task | Power state | Steps |
| Build | scheduling | None | 3-12 |
| Build | networking | None | 22-24 |
| Build | block_device_mapping | None | 25-27 |
| Build | spawing | None | 28 |
| Active | none | Running |
2. nova compute 接到创建虚机指令后开始创建虚机的代码流程分析 (第代码在 https://github.com/openstack/nova/blob/master/nova/compute/manager.py 中的 def _build_and_run_instance 函数中
_build_resources // 准备网络和磁盘 //Start building networks asynchronously for instance self._build_networks_for_instance //为 instance 准备网络资源,实际上是创建一个 neutron port macs = self.driver.macs_for_instance(instance) //分配mac地址。多绝大多数hypersivor,返回None,也就是不预先分配 network_info =self._allocate_network //开始异步网络分配 nwinfo = self.network_api.allocate_for_instance //Allocate network resources for the instance _validate_requested_port_ids //校验 port ids _validate_requested_network_ids //校验 network ids _clean_security_groups //删除 default 安全组 _process_security_groups //Processes and validates requested security groups for allocation _create_ports_for_instance //Create port for network_requests that don't have a port_id _create_port_minimal //如果port 没有的话,则Attempts to create a port for the instance on the given network. port_client.create_port //调用 port api 来创建 port,包括创建 port,分配MAC及IP地址,更新数据库
_generate_mac //生成MAC地址
_create_port_with_mac //创建 port
//DHCP 相关操作:port 创建完成后会通知 neutron-dhcp-agent去执行port_create_end函数,它会将port的ip和mac信息加载到dnsmasq所需的配置文件中
_allocate_ips_for_port //为 port 分配 IP,要么用户有指定,要么从subnets 中选择一个
_allocate_specific_ip //如果指定了IP
_generate_ip //如果没指定IP
return requests_and_created_ports _update_ports_for_instance //为特殊case 更新 port _populate_neutron_extension_values _populate_pci_mac_address //只用于处理 SRIOV_PF _populate_mac_address _update_port port_client.update_port //将上述修改通过调用 port api 得以更新port _update_port_dns_name neutron.update_port(port_id, port_req_body) //将 port 的 dns_name 设置为 hostname nw_info = self.get_instance_nw_info _build_network_info_model //Return list of ordered VIFs attached to instance _gather_port_ids_and_networks //Return an instance's complete list of port_ids and networks ifaces = instance.get_network_info() return nw_info
//Start building block device mappings for instance self._prep_block_device //处理挂接到虚机的磁盘,可能有多个,目标可能是 volume,snapshot 和 image。 当是 image 时,其实就是 boot from volume
block_device_info = driver.get_block_device_info(instance, bdms) //Converts block device mappings for instance to driver format mapping = driver.block_device_info_get_mapping(block_device_info) return block_device_mapping driver_block_device.attach_block_devices //nova/virt/block_device.py _log_and_attach //写日志关于instance 将从哪里启动,可能从 volume,snapshot,image 上启动 bdm.attach //这里会调用 cinder api 去创建 volume,并且挂接到 nova compute host 上
//为每个磁盘调用 _log_and_attach _block_device_info_to_legacy return block_device_info
self.driver.spawn //调用 nova/virt/libvirt/driver.py 中的 spawn 函数,首先创建 image,然后创建domain disk_info = blockinfo.get_disk_info _create_configdrive _create_image //创建镜像
fileutils.ensure_tree(libvirt_utils.get_instance_path(instance)) //在计算节点本地创建目录 /var/lib/nova/instances/${uuid}/
_create_and_inject_local_root
if not booted_from_volume //判断是否从 volume 启动
backend = self.image_backend.by_name //根据配置的 image type 获取 image backend,现在支持 rbd(使用 rbd volume),lvm(使用 lvm volume),qcow2(使用本地文件),flat 和 Ploop 等几种。
if backend.SUPPORTS_CLONE: //判断 backend 是否支持 clone
backend.clone(context, disk_images['image_id']) //调用 backend 的 clone 方法
RbdProxy().clone //RBD 的clone 方法,从 image 的 snapshot 上 clone
else
fetch_func = libvirt_utils.fetch_image //从 Glance 下载镜像
_try_fetch_image_cache
self._inject_data(backend, instance, injection_info) //处理数据注入
else
//对boot volume 不允许注入 _create_ephemeral
libvirt_utils.create_image('raw', target, '%dG' % ephemeral_size)
utils.execute('qemu-img', 'create', '-f', disk_format, path, size) _create_swap
libvirt_utils.create_image('raw', target, '%dM' % swap_mb)
nova.privsep.fs.unprivileged_mkfs('swap', target) xml = self._get_guest_xml //生成 domain xml 字符串
conf = self._get_guest_config
_get_guest_numa_config
_get_guest_memory_backing_config
_get_guest_config_meta
_update_guest_cputune
_cpu_config_to_vcpu_model
_configure_guest_by_virt_type
_set_features
_set_clock
_get_guest_storage_config
self.vif_driver.get_config
_create_consoles
_guest_add_spice_channel
_add_video_driver
_set_qemu_guest_agent
_guest_add_pci_devices
_guest_add_watchdog_action
_guest_add_memory_balloon
_guest_add_mdevs
return guest
xml = conf.to_xml()
return xml
self._create_domain_and_network
//nova侧去等待neutron侧发送network-vif-pluggend事件。neutron-linuxbridge-agent服务检测tap设备,neutron-server发送event事件给nova-api
self.virtapi.wait_for_instance_event
self.plug_vifs(instance, network_info)
self.firewall_driver.setup_basic_filtering
self.firewall_driver.prepare_instance_filter
self._create_domain(xml)
libvirt_guest.Guest.create(xml, self._host)
write_instance_config // nova/virt/libvirt/host.py 中
domain = self.get_connection().defineXML(xml)
return libvirt_guest.Guest(domain)
return guest
_wait_for_boot //每隔 0.5秒检查虚机是否启动
_update_instance_after_spawn
_update_scheduler_instance_info
scheduler_client.update_instance_info
_notify_about_instance_usage
补充:
- port 创建成功后的 dhcp 相关操作(参考 https://blog.csdn.net/gj19890923/article/details/51558598):
-
1. 创建VM时,nova-compute与neutron的plugin交互,在neutron的数据库中创建VM所需的port信息。
-
2. neutron数据库中的port信息创建完成后,通知neutron-dhcp-agent去执行port_create_end函数。该函数将数据库中的port中的ip和mac信息加载到dnsmasq所需的配置文件中(包括host和addn_hosts文件)。
-
[root@nova 43c0e274-28e3-482e-a32b-d783980fc3ed]# cat addn_hosts 1.1.1.1 host-1-1-1-1.openstacklocal host-1-1-1-1 1.1.1.2 host-1-1-1-2.openstacklocal host-1-1-1-2 1.1.1.10 host-1-1-1-10.openstacklocal host-1-1-1-10 [root@nova 43c0e274-28e3-482e-a32b-d783980fc3ed]# cat host fa:16:3e:d1:d7:72,host-1-1-1-1.openstacklocal,1.1.1.1 fa:16:3e:da:42:50,host-1-1-1-2.openstacklocal,1.1.1.2 fa:16:3e:3c:a3:3e,host-1-1-1-10.openstacklocal,1.1.1.10[root@nova 43c0e274-28e3-482e-a32b-d783980fc3ed]# cat leases
1464599134 fa:16:3e:3c:a3:3e 1.1.1.10 host-1-1-1-10 01:fa:16:3e:3c:a3:3e
1464598886 fa:16:3e:da:42:50 1.1.1.2 host-1-1-1-2 *
1464598886 fa:16:3e:d1:d7:72 1.1.1.1 host-1-1-1-1 *
-
3. 在VM启动时,广播dhcp discover请求,当dnsmasq进程的监听接口ns-xxx监听到这种请求时,dnsmasq进程将根据配置文件(host和leases文件)中的内容去判定是否有未分配的ip和mac为请求者进行提供。
-
4. 最终VM便真实的获取到与保存在数据库中的ip和mac信息。neutron-dhcp-agent只是将所创建VM的ip和mac信息从数据库中获取到自己的配置文件中,然后等到VM启动时,为它提供。因此neutron-dhcp-agent相当于在VM和数据库之间起了个中间桥梁的作用。
-
- nova 在 domain 被创建后等待 neutron event 的过程(请参考 http://www.aichengxu.com/linux/9307663.htm)
- 创建VM时,nova-compute 服务调用 wait_for_instance_event 函数等待 neutron 侧发送来的event。
- neutron的neutron-linuxbridge-agent定时检测tap设备的增加或删除,当创建VM时,将创建新的tap设备,此时将更新neutron数据库中的ports表,而neutron-server服务创建core_plugin时,将利用sqlalchemy自带的event对neutron数据库中的ports表进行监视,当ports表发生变化时,neutron-server将通过HTTP请求的方式发送event事件给nova。
- nova 收到 neutron 发送来的 event 时间,结束等待,继续创建VM下面的操作。
3. 虚机被创建后的L2网络操作
虚机被创建后,nova-compute 节点上的 neutron-linuxbridge-agent 会检测到新建的 tap 设备(通过轮询 /sys/class/net/ 里面的tap 设备),找到后则执行一系列网络方面的操作,包括设置安全组,
tap设备示例:
[root@test net]# ls
brq8165bc3d-40 eth0 eth1 eth1.120 eth2 lo tap712a2c63-e6 tap83e7c095-f0 tap8f4fcfbb-2b
tap 设备信息:
Port tap93121330-58 updated. Details: {u'profile': {}, u'allowed_address_pairs': [], u'admin_state_up': True, u'network_id': u'8165bc3d-400a-48a0-9186-bf59f7f94b05', u'segmentation_id': 120,u'device_owner': u'compute:nova',
u'physical_network': u'physnet1', u'mac_address': u'fa:16:3e:9f:6f:c5', u'device': u'tap93121330-58', u'port_security_enabled': True, u'port_id': u'93121330-58', u'fixed_ips': [{u'subnet_id': u'ec1028b2-7cb0-4feb-b974-6b8ea7e7f08f', u'ip_address': u'172.16.0.7'}],
u'network_type': u'vlan'}
参考文档:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号