分片上传场景中的进阶JS异步实践
业务里的有大文件上传场景,所以单独封装出分片上传前端库以便各业务复用。
在开发分片上传库的过程中,遇到了并发问题。下面分析下怎么遇到的问题,以及怎么解决的。
目录
topic涉及的内容
- 事件循环:Promise、async await、setTimout执行顺序
- 并发问题:竞态条件、原子性
- 解决并发:在临界区使用同步、乐观锁、悲观锁、消除共享资源
大文件分片上传
功能点
- 分片上传
- 并行上传
- 断点续传
- 引入Web Worker提高性能
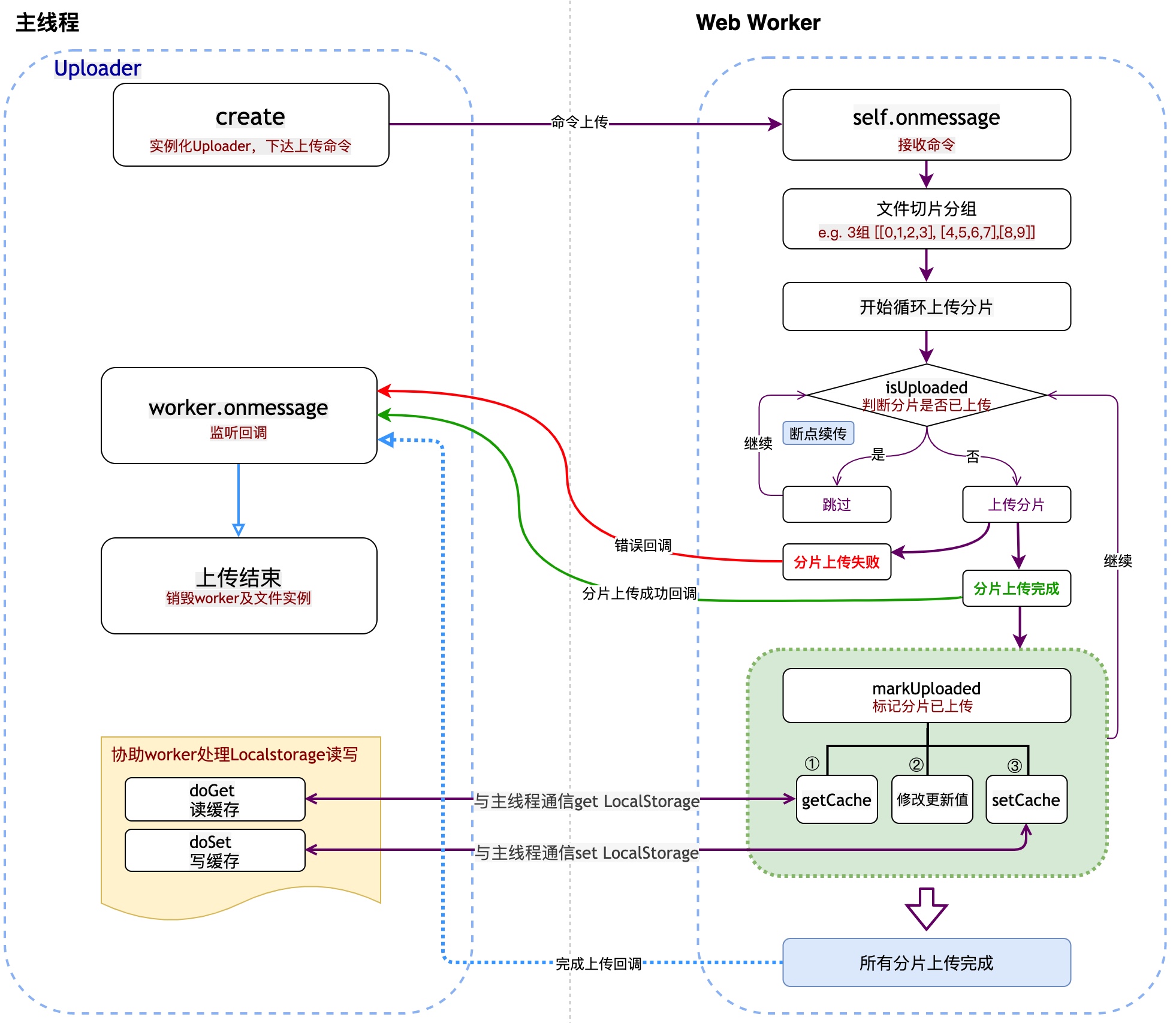
整体方案
- 指定每片大小:sizePerChunk,指定并行数量:parallelNumber
- 将大文件按指定分片大小、并行数量进行切割分组
- 每组间并行上传,同组内串行
- 上传完的存Localstorage记录,上传前判断已经存了就跳过上传
- Web Worker不支持读写Localstorage,需借助主线程读写
- 因太多异步方法,充分利用async await 来保证代码逻辑清晰
分片上传库的伪代码
为了简化问题便于大家理解,此处代码把与问题不相干的逻辑省略。
// Web Worker
function UploadWorker() {
self.onmessage= e => {
// 省略:
// 接受上传文件的命令
// 计算文件属性:fileUid、处理分片等
// 调用uploadParallelly并行上传
}
// 并行上传
uploadParallelly = async parallelNumber => {
// 根据分片大小 计算总分片数
const chuckCount = Math.ceil((fileSize / sizePerChunk));
const loopLen = Math.ceil(chunkCount/parallelNumber);
const loopTaskList = []; // e.g. [[0,1,2,3], [4,5,6,7],[8,9]]
// 允许多少parallelNumber,就有多少个uplodLoop
for(let i = 0; i < chunkCount; i+=loopLen) {
loolTaskList.push(uploadLoop(i, Math.min(i+loopLen, chuckCount)));
}
await Promise.all(loopTaskList);
}
// 循环分片上传
uploadLoop = (start, end) => {
for(let i = 0; i < end; i++) { // [start, end)
// 省略 文件切割逻辑
await doUploadChunk(i);
}
}
// 上传某一片
doUploadChunk = async chunkIndex => {
// 已上传的就跳过,实现断点续传
if(await isUploaded(chunkIndex)) return;
// 省略 await上传chunkContent
await markUploaded(chunkIndex);
}
// 标记分片已上传
markUploaded = async chunkIndex => {
const chunkList = await getCache(fileUid);
const nextList = [...chunkList, chunkIndex];
await setCache(fileUid, nextList);
}
// 判断分片是否已上传
isUploaded = chunkIndex => {
const chunkList = await getCache(fileUid);
return chunkList.includes(chunkIndex);
}
getCache = async key {
// 省略 与主线程通信get LocalStorage
}
setCache = () => {
// 省略 与主线程通信set LocalStorage
}
}
// 主进程
class Uploader {
create() {
// 实例化Uploader,下达上传命令
// 协助worker处理Localstorage读写
}
}
- 流程图
![分片上传流程图]()
问题
Localstorage记录的某一个fileUid 已上传分片数组,偶尔会少几片,例如:
| key | value | 现象 |
|---|---|---|
| upload_task_xxxx | [0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9] | 发现4,5两片不见了(并发数为3) |
原因分析
我们看下markUploaded方法的实现,异步先读 - 再改 - 异步再写,加上并发调用,典型地容易触发竞态条件。
竞态条件:当多个线程竞争同一资源时,如果对资源的访问顺序敏感,就称 存在竞态条件。
导致竞态条件发生的代码区称作临界区。
接下来详细分析这个问题,看下markUploaded方法干了件什么事情。
// 标记已上传(临界区)
markUploaded = async chunkIndex => {
const chunkList = await getCache(fileUid); // 先读
const nextList = [...chunkList, chunkIndex]; // 再改
await setCache(fileUid, nextList); // 再写
}
因为此处的markUploaded方法不是原子性的,所以产出了并发问题。
原子性: 一个程序执行时不可被中断的,它要么完整的被成功执行,要么完全不执行,即“同生共死”的感觉。这种特性就叫原子性。
举个栗子:
A要从自己的帐户中转1000元到B的帐户里。
从A开始转帐,到转帐结束的这一个过程,称之为一个事务。在这个事务里,要做如下操作:
- 从A的帐户中减去1000元(A的帐户原有3000元,现在就变成2000元了)。
- 在B的帐户里加1000元(B的帐户原有2000元,现在变成3000元了)。
如果在A的帐户已经减去了1000元的时候,忽然发生了意外,比如停电什么的,导致转帐事务意外终止了,而此时B的帐户里还没有增加1000元。那么,我们称这个操作失败了,要进行回滚。
回滚就是回到事务开始之前的状态,也就是回到A的帐户还没减1000元的状态,B的帐户的原来的状态。此时A的帐户仍然有3000块,B的帐户仍然有2000块。
把这种要么一起成功(A帐户成功减少1000,同时B帐户成功增加1000),要么一起失败(A帐户回到原来状态,B帐户也回到原来状态)的操作叫原子性操作。
事件循环
事件循环决定了JS引擎什么时候执行什么代码;
此处对事件循环就不过多展开了,篇尾有相关文档可了解。
这里简单讲下await的等待机制:
如果 await 后面跟的不是一个 Promise,那 await 后面表达式的运算结果就是它等到的东西;
如果 await 后面跟的是一个 Promise 对象,await 它会“阻塞”后面的代码,等着 Promise 对象 resolve,然后得到 resolve 的值作为 await 表达式的运算结果。
await 必须用在 async 函数中。async 函数调用不会造成“阻塞”,它内部所有的“阻塞”都被封装在一个 Promise 对象中异步执行。(这里的阻塞理解成异步等待更合理)
看markUploaded方法中第一行代码,await 后面紧跟着的getCache是立刻执行的,接下来后面的代码就会被“阻塞”,所以markUploaded这个方法就不具备原子性,才会导致并发问题的产生
// 标记已上传(临界区)
markUploaded = async chunkIndex => {
const chunkList = await getCache(fileUid); // 先读
const nextList = [...chunkList, chunkIndex]; // 再改
await setCache(fileUid, nextList); // 再写
}
抽离出问题原型
- worker的逻辑:异步的getCache、异步的setCache和异步的getNPush 用来对一个 数组 进行读、改、写。分析在并发场景下,getNPush的稳定性。
- 主线程的逻辑:配合web worker提供cache data的逻辑
ps:以下模拟问题的代码可直接在控制台执行
// Web Worker
function UploadWorker() {
self.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data, uid} = e.data;
if(type === 'run') run(data);
// 监听主线程的cache读写结果
trigger(type, data, uid);
}
getCache = async key => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if(retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getCache', cb);
};
on('getCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'getCache', data: {key, uid}})
});
}
setCache = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if(retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('setCache', cb);
};
on('setCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'setCache', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
getNPush = async (key, value) => {
const src= await getCache(key) || [];
const next = [...src, value];
console.log('next', JSON.stringify(next))
await setCache(key, next);
}
// 搞个简单的自定义事件
pool = {};
on = (type, cb) => {
pool[type] = pool.hasOwnProperty(type) ? [...pool[type], cb]: [cb];
}
off = (type, cb) => {
if(!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].splice(pool[type].indexOf(cb), 1);
}
trigger = (type, ...args) => {
if(!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].forEach(fn => fn.apply(null, args))
}
// 模拟并发调用
run = async type => {
KEY = 'key';
delay = (sec, fn, ...args) => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(fn(...args)), sec)
});
loop1 = async (start, end) => {
for(let i = start; i < end; i++) {
await delay(Math.random()*100, getNPush, KEY, i); // 随机[0,100)ms触发getNPush
}
}
switch(type) {
case 'loop1':
await setCache(KEY, []); // 先清空一下缓存数据
await Promise.all([loop1(0,10), loop1(10,20), loop1(20,30)]);
console.log('===loop1===', await getCache(KEY));
break;
}
}
}
// 主线程
w = new Worker(URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`(${UploadWorker.toString()})()`])));
w.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data: {key, value, ...extra}} = e.data;
let result;
switch(type) {
case 'setCache':
result = doSet(key, value);
console.log('%c【主线程Set: result,value】','color:#fe950e;',type, result, value)
break;
case 'getCache':
result = doGet(key);
console.log('%c【主线程Get: result】','color:#72c911;font-weight:bold;font-size:10pt',type, result)
break;
}
w.postMessage({type, data: result, ...extra})
}
// 用内存变量代替Localstorage方便观察分析
data = {};
doSet = (key, value) => {
data[key] = value;
return data;
}
doGet = key => {
return key ? data[key] : data;
}
w.postMessage({type: 'run', data: 'loop1'});
// 以上 并不是每次执行完 数组长度都是30.
解决方案
方案1
getNPush不是原子的。因为getCache是异步的,会发生上下文切换。
getNPush = async (key, value) => {
const src= await getCache(key) || []; // 先读
const next = [...src, value]; // 再改
await setCache(key, next); // 再写
}
思路:
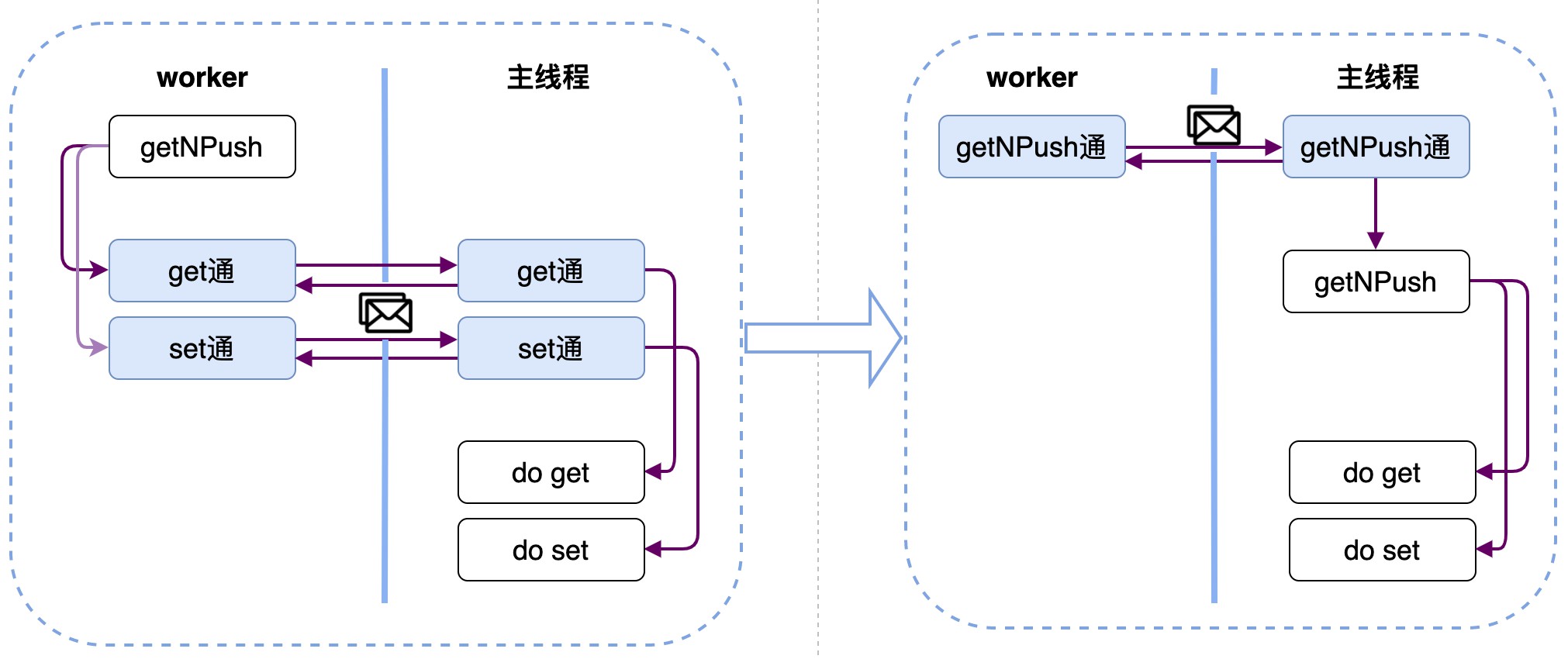
把getNPush改为原子的。
怎么改?
去掉await get 和await set,那么getNPush就是纯同步的代码,对于单线程的JS执行,一定是原子的。所以就可以把getNPush放到主线程实现来达到目的。
// Web Worker
function UploadWorker() {
self.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data, uid} = e.data;
if (type === 'run') run(data);
// 监听主线程的cache读写结果
trigger(type, data, uid);
}
getCache = async key => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getCache', cb);
}
on('getCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'getCache', data: {key, uid}})
});
}
setCache = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('setCache', cb);
}
on('setCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'setCache', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
// >>>>>>>> 修改
getNPush = async(key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getNPush', cb);
}
on('getNPush', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'getNPush', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
// <<<<<<<<< 修改
// 搞个简单的自定义事件
pool = {};
on = (type, cb) => {
pool[type] = pool.hasOwnProperty(type) ? [...pool[type], cb] : [cb]
}
off = (type, cb) => {
if (!pool[type]) return
pool[type].splice(pool[type].indexOf(cb), 1)
}
trigger = (type, ...args) => {
if (!pool[type]) return
pool[type].forEach(fn => fn.apply(null, args))
}
// 模拟并发调用
run = async type => {
KEY = 'key'
delay = (sec, fn, ...args) => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(fn(...args)), sec))
loop1 = async (start, end) => {
for (let i=start; i<end; i++) {
await delay(Math.random()*100, getNPush, KEY, i)
}
}
switch(type) {
case 'loop1':
await setCache(KEY, []);
await Promise.all([loop1(0, 10), loop1(10, 20), loop1(20, 30)]);
console.log('======loop1', await getCache(KEY));
break;
}
}
}
// 主线程
w = new Worker(URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`(${UploadWorker.toString()})()`])))
w.onmessage = (e) => {
const {type, data: {key, value, ...extra}} = e.data;
let result;
switch (type) {
case 'setCache':
result = doSet(key, value);
break
case 'getCache':
result = doGet(key);
break;
// >>>>>>>> 增加
case 'getNPush':
result = getNPush({key, value});
break;
// <<<<<<<<< 增加
}
console.log('%c【主线程 type,result,value】','color:#fe950e;',type, result, value)
w.postMessage({type, data: result, ...extra})
}
// >>>>>>>> 增加
getNPush = data => {
const { key, value } = data;
const src = doGet(key);
const next = [...src, value];
return doSet(key, next);
}
// <<<<<<<<< 增加
// 用内存变量代替LocalStorage方便分析
data = {}
doSet = (key, value) => {
data[key] = value;
return data;
}
doGet = key => {
return key ? data[key] : data;
}
// 触发worker测试并发执行
w.postMessage({type: 'run', data: 'loop1'})
// 每次执行都是稳定的30个了
方案2
乐观锁的思路:写入时CAS+自旋
说明:
乐观锁:本质上是乐观的,认为别的线程不会去修改值。如果发现值被修改了,可以再次重试(自旋)。
CAS机制就是一种乐观锁。
CAS(Compare And Swap):比较并交换,该操作通过将内存中的值与指定数据进行比较,当数值一样时将内存中的数据替换为新的值。
补充:ABA问题
因为CAS需要在操作值的时候检查下值有没有发生变化,如果没有发生变化则更新,但是如果一个值原来是A,变成了B,又变成了A,那么使用CAS进行检查时会发现它的值没有发生变化,但是实际上却变化了。ABA问题的解决思路就是使用版本号(
版本号机制)。在变量前面追加上版本号,每次变量更新的时候把版本号加一,那么A-B-A 就会变成1A-2B-3A。
因为在我这个文件上传更新缓存这个场景是不会遇到ABA问题的,所以是可以直接比对的。
// Web Worker
function UploadWorker() {
self.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data, uid} = e.data;
if (type === 'run') run(data);
// 监听主线程的cache读写结果
trigger(type, data, uid);
}
getCache = async key => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getCache', cb);
};
on('getCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'getCache', data: {key, uid}})
});
}
setCache = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('setCache', cb);
};
on('setCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'setCache', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
getNPush = async(key, value) => {
const src = await getCache(key) || [];
const next = [...src, value];
console.log('next', JSON.stringify(next))
// >>>>>>>> 修改
if (!await setCache(key, {next, src})) await getNPush(key, value) // 自旋锁
// <<<<<<<< 修改
}
// 搞个简单的自定义事件
pool = {};
on = (type, cb) => {
pool[type] = pool.hasOwnProperty(type) ? [...pool[type], cb] : [cb];
}
off = (type, cb) => {
if (!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].splice(pool[type].indexOf(cb), 1);
}
trigger = (type, ...args) => {
if (!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].forEach(fn => fn.apply(null, args))
}
// 模拟并发调用
run = async type => {
KEY = 'key';
delay = (sec, fn, ...args) => new Promise(resolve =>{
setTimeout(() => resolve(fn(...args)), sec)
});
loop1 = async (start, end) => {
for (let i=start; i<end; i++) {
await delay(Math.random()*100, getNPush, KEY, i)
}
}
switch(type) {
case 'loop1':
// >>>>>>>> 修改
await setCache(KEY, {src: await getCache(KEY), next: []});
// <<<<<<<< 修改
await Promise.all([loop1(0, 10), loop1(10, 20), loop1(20, 30)]);
console.log('===loop1===', await getCache(KEY));
break;
}
}
}
// 主线程
w = new Worker(URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`(${UploadWorker.toString()})()`])));
w.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data: {key, value, ...extra}} = e.data;
let result;
switch (type) {
case 'setCache':
// >>>>>>>> 修改
const {src, next} = value;
const now = doGet(key);
if (JSON.stringify(now) !== JSON.stringify(src)) {
result = false // 不允许set缓存
} else {
result = doSet(key, next);
}
// <<<<<<<< 修改
console.log('%c【主线程Set, result, value.next】','color:#fe950e;',type, result, value.next)
break;
case 'getCache':
result = doGet(key);
console.log('%c【主线程Get, result】','color:#72c911;font-weight:bold;font-size:10pt',type, result)
break;
}
w.postMessage({type, data: result, ...extra})
}
// 用内存变量代替LocalStorage方便观察分析
data = {};
doSet = (key, value) => {
data[key] = value;
return data;
}
doGet = key => {
return key ? data[key] : data;
}
// 触发worker测试并发执行
w.postMessage({type: 'run', data: 'loop1'});
// 也是稳定30个了
效果:

方案3
悲观锁思路:worker执行setCache要抢锁,因为JS本身没有多线程的概念,需要强行引入“虚拟线程id”,再根据线程id实现tryLock和unLock。比较复杂。
悲观锁:
总是假设最坏的情况。
每次获取数据的时候,都担心数据被修改,所以每次获取数据的时候都会进行加锁,确保在自己使用的过程中数据不会被别人修改,使用完成后进行数据解锁。
由于数据进行加锁,期间对该数据进行读写的其他线程都会进行等待。
方案4
消除共享资源的竞争
- 把chunkIndex作为cache的key
- 有多少个并行的组,就有多少个key
方案5
引入队列,串行消费
因为JS不支持消息队列消费,用setInterval来定时消费。
此处只是一个思路。
// Web Worker
function UploadWorker() {
self.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data, uid} = e.data;
if(type === 'run') run(data);
// 监听主线程的cache读写结果
trigger(type, data, uid);
}
getCache = async key => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getCache', cb);
};
on('getCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'getCache', data: {key, uid}})
});
}
setCache = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('setCache', cb);
};
on('setCache', cb);
self.postMessage({type: 'setCache', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
getNPush = async(key, value) => {
const src = await getCache(key) || [];
const next = [...src, value];
console.log('next', JSON.stringify(next))
await setCache(key, next);
}
// 搞个简单的自定义事件
pool = {};
on = (type, cb) => {
pool[type] = pool.hasOwnProperty(type) ? [...pool[type], cb] : [cb];
}
off = (type, cb) => {
if (!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].splice(pool[type].indexOf(cb), 1);
}
trigger = (type, ...args) => {
if (!pool[type]) return;
pool[type].forEach(fn => fn.apply(null, args))
}
// >>>>>>>> 新增
getNPushMq = [];
cacheConsumerHandle = null;
writeGetNPushMq = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
const cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('getNPushMq', cb)
};
on('getNPushMq', cb)
getNPushMq.unshift({key, value, uid}) // 进入队列
});
}
// <<<<<<<< 新增
// 模拟并发调用
run = async type => {
KEY = 'key';
delay = (sec, fn, ...args) => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(fn(...args)), sec)
});
loop1 = async (start, end) => {
for (let i=start; i<end; i++) {
// >>>>>>>> 修改
await delay(Math.random()*100, writeGetNPushMq, KEY, i) // 改调用 writeGetNPushMq
// <<<<<<<< 修改
}
}
// >>>>>>>> 新增,todo clearInterval
clearInterval(cacheConsumerHandle);
cacheConsumerHandle = setInterval(async () => {
const msg = getNPushMq.pop();
if (!msg) return;
const {key, value, uid} = msg;
trigger('getNPushMq', await getNPush(key, value), uid) // 消费
}, 10);
// <<<<<<<< 新增
switch(type) {
case 'loop1':
await setCache(KEY, []);
await Promise.all([loop1(0, 10), loop1(10, 20), loop1(20, 30)]);
console.log('===loop1===', await getCache(KEY));
clearInterval(cacheConsumerHandle);
break;
}
}
}
// 主线程
w = new Worker(URL.createObjectURL(new Blob([`(${UploadWorker.toString()})()`])));
w.onmessage = e => {
const {type, data: {key, value, ...extra}} = e.data;
let result;
switch (type) {
case 'setCache':
result = doSet(key, value);
console.log('%c【主线程Set,result,value】','color:#fe950e;',type, result, value)
break;
case 'getCache':
result = doGet(key);
console.log('%c【主线程Get,result】','color:#72c911;font-weight:bold;font-size:10pt',type, result)
break;
}
w.postMessage({type, data: result, ...extra})
}
// 用内存变量代替LocalStorage方便观察分析
data = {};
doSet = (key, value) => {
data[key] = value;
return data;
}
doGet = key => {
return key ? data[key] : data;
}
// 触发worker测试并发执行
w.postMessage({type: 'run', data: 'loop1'});
// 也稳定30个了
引申问题
引申问题1
把delay去掉, 连组之间都是串行的了
引申问题2
全是主线程
pool = {};
on = (type, cb) => {
pool[type] = pool.hasOwnProperty(type) ? [...pool[type], cb] : pool[type] = [cb]
}
off = (type, cb) => {
if (!pool[type]) return
pool[type].splice(pool[type].indexOf(cb), 1)
}
trigger = (type, ...args) => {
if (!pool[type]) return
pool[type].forEach(fn => fn.apply(null, args))
}
data = {}
wSet = (key, value) => {
data[key] = value;
console.log('wSet', value);
return null;
}
wGet = key => {
console.log('wGet', key ? data[key] : data);
return key ? data[key] : data;
}
noWorker = (e) => {
const {type, data: {key, value, ...extra}} = e;
let result;
switch (type) {
case 'set':
result = wSet(key, value);
break
case 'get':
result = wGet(key);
break;
}
console.log('worker on type', {type, result, ...extra})
trigger(type, result, extra.uid)
}
get = async key => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('get', cb);
}
on('get', cb);
noWorker({type: 'get', data: {key, uid}})
});
}
set = async (key, value) => {
const uid = Math.random();
return new Promise(resolve => {
let cb = (result, retUid) => {
if (retUid !== uid) return;
resolve(result);
off('set', cb);
}
on('set', cb);
noWorker({type: 'set', data: {key, value, uid}})
});
}
getNAppend = async(key, value) => {
const src = await get(key) || [];
const next = [...src, value];
console.log('next', JSON.stringify(next))
return await set(key, next)
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号