1. 基本描述
inotify提供了一种监控文件系统事件的机制,可以用来监控单个的文件以及目录。当一个目录被监控,inotify会返回该目录以及该目录下面文件的事件。
2. 原理以及使用
2.1 内核原理
inotify机制借用了内核里面的notify通知链技术,针对文件系统里面的使用主要是在inode结构体里面加入了相关的字段(内核版本3.10):
linux系统中每一个常规文件都有唯一的一个inode和它对应
struct inode {
。。。
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */ 具体可能监控的事件,事件基本上是一些位段
struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks; /* 具体的链表,链表上可以挂入多个mask结构(事件) */
#endif
。。。
}
对于每一个监控内核都有一个fsnotify_mark和它相对应
struct fsnotify_mark {
__u32 mask; /* mask this mark is for */
atomic_t refcnt; /* active things looking at this mark */
struct fsnotify_group *group; /* group this mark is for */
struct list_head g_list; /* list of marks by group->i_fsnotify_marks */
spinlock_t lock; /* protect group and inode */
union {
struct fsnotify_inode_mark i;
struct fsnotify_vfsmount_mark m;
};
__u32 ignored_mask; /* events types to ignore */
unsigned int flags; /* vfsmount or inode mark? */
struct list_head destroy_list;
void (*free_mark)(struct fsnotify_mark *mark); /* called on final put+free */
};
每新建一个inotify实例,内核都会分配一个fsnotify_group
struct fsnotify_group {
atomic_t refcnt; /* 引用次数 */
const struct fsnotify_ops *ops; /* 操作函数指针结构体 */
/* needed to send notification to userspace */
struct list_head notification_list; /* 属于这个group的需要发送到用户控件的事件链表 */
wait_queue_head_t notification_waitq; /* 读事件阻塞时的等待队列头 */
unsigned int q_len; /* events on the queue */
unsigned int priority;
struct list_head marks_list; /* 属于这个group的fsnotify_mark结构体链表 */
struct fasync_struct *fsn_fa; /* async notification */
union {
void *private;
#ifdef CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER
struct inotify_group_private_data {
spinlock_t idr_lock;
struct idr idr;
struct user_struct *user;
} inotify_data;
#endif
};
};
内核下面的函数执行流程为:
初始化新建一个notify实例,新建一个组
./fs/notify/inotify/inotify_user.c inotify_init1 group = inotify_new_group(inotify_max_queued_events); // 新建一个组 // 新建一个fd,名为 inotify,建立起 dentry anon_inode_inode(全局)结构 ret = anon_inode_getfd("inotify", &inotify_fops, group, O_RDONLY | flags); file = anon_inode_getfile(name, fops, priv, flags); // priv 为之前的 group file->private_data = priv; // file->private_data = group fd对应的file结构体为 file_operation为 const struct fsnotify_ops inotify_fsnotify_ops = { .handle_event = inotify_handle_event, // 处理事件函数 .should_send_event = inotify_should_send_event, .free_group_priv = inotify_free_group_priv, .free_event_priv = inotify_free_event_priv, .freeing_mark = inotify_freeing_mark, };
向系统中增加一个监控
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(inotify_add_watch, int, fd, const char __user *, pathname, u32, mask) /* create/update an inode mark */ f = fdget(fd); ret = inotify_find_inode(pathname, &path, flags); inode = path.dentry->d_inode; // 找到需要监控的目录或文件的 inode group = f.file->private_data; // 获取到 之前创建的group ret = inotify_update_watch(group, inode, mask); // 更新新的mask参数 /* try to update and existing watch with the new arg */ ret = inotify_update_existing_watch(group, inode, arg); // /* no mark present, try to add a new one */ if (ret == -ENOENT) ret = inotify_new_watch(group, inode, arg); /* arg就是对应的mask(events), 没有找到,则直接新建一个新的 */ ret = inotify_new_watch(group, inode, arg); /* arg就是对应的mask(events) */ struct idr *idr = &group->inotify_data.idr; spinlock_t *idr_lock = &group->inotify_data.idr_lock; struct inotify_inode_mark tmp_i_mark = kmem_cache_alloc(inotify_inode_mark_cachep, GFP_KERNEL); fsnotify_init_mark(&tmp_i_mark->fsn_mark, inotify_free_mark); tmp_i_mark->fsn_mark.mask = mask; tmp_i_mark->wd = -1; // 设置填充tmp_i_mark,基本的初始化 ret = inotify_add_to_idr(idr, idr_lock, tmp_i_mark); // 增加idr的一个条目 i_mark->wd = ret(idr_alloc_cyclic(idr, i_mark, 1, 0, GFP_NOWAIT)) ret = fsnotify_add_mark(&tmp_i_mark->fsn_mark, group, inode, NULL, 0); ret = fsnotify_add_mark_locked(mark, group, inode, mnt, allow_dups); mark->group = group; list_add(&mark->g_list, &group->marks_list); // 把mark添加到group里面 atomic_inc(&group->num_marks); fsnotify_get_mark(mark); /* for i_list and g_list */ fsnotify_add_inode_mark(mark, group, inode, allow_dups); // 把mark和具体的监控inode挂钩 mark->i.inode = inode; hlist_add_head_rcu(&mark->i.i_list, &inode->i_fsnotify_marks); // 把mark挂入到具体的inode的i_fsnotify_marks列表上 __fsnotify_update_child_dentry_flags(inode); // 如果是目录,则更新目录下面下面的 if (!S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) return; if (watched) child->d_flags |= DCACHE_FSNOTIFY_PARENT_WATCHED; // 设置监控子目录或文件 else child->d_flags &= ~DCACHE_FSNOTIFY_PARENT_WATCHED; atomic_inc(&group->inotify_data.user->inotify_watches); // 增加用户的watch号 return ret(tmp_i_mark->wd)
当有事件被监控到了以后的执行流程
static int inotify_handle_event(struct fsnotify_group *group, struct fsnotify_mark *inode_mark, struct fsnotify_mark *vfsmount_mark, struct fsnotify_event *event) /* 通过已有的fsnotify_mark 获取到宿主结构 inotify_inode_mark*/ struct inotify_inode_mark *i_mark = container_of(inode_mark, struct inotify_inode_mark, fsn_mark); wd = i_mark->wd; fsnotify_get_group(group); fsn_event_priv->group = group; event_priv->wd = wd; // 把事件挂入到group下面的notification_list,并且唤醒group下面的等待队列notification_waitq; added_event = fsnotify_add_notify_event(group, event, fsn_event_priv, inotify_merge); struct list_head *list = &group->notification_list; fsnotify_get_event(event); list_add_tail(&holder->event_list, list); // 把事件挂入到group->notification_list wake_up(&group->notification_waitq); // 唤醒等待队列 kill_fasync(&group->fsn_fa, SIGIO, POLL_IN); // 发送信号
当监控的文件被删除后具体的执行流程
static void destroy_inode(struct inode *inode) __destroy_inode(struct inode *inode) fsnotify_inode_delete(inode); __fsnotify_inode_delete(inode); fsnotify_clear_marks_by_inode(inode); // fs/notify/inode_mark.c struct fsnotify_mark *mark, *lmark; struct hlist_node *n; LIST_HEAD(free_list); // 遍历inode->i_fsnotify_marks上挂的所有fsnotify_mark条目 hlist_for_each_entry_safe(mark, n, &inode->i_fsnotify_marks, i.i_list) { // 挂入free_list链表,mark->i.free_i_list是在释放mask时用的临时的list_head list_add(&mark->i.free_i_list, &free_list); // 把fsnotify_mark正式从监控文件inode的链表里面取出 hlist_del_init_rcu(&mark->i.i_list); } // 至此需要释放的fsnotify_mark都已经挂载到了free_list list_for_each_entry_safe(mark, lmark, &free_list, i.free_i_list) { struct fsnotify_group *group; fsnotify_get_group(mark->group); group = mark->group; fsnotify_destroy_mark(mark, group); fsnotify_destroy_mark_locked(mark, group); fsnotify_destroy_inode_mark(mark); mark->i.inode = NULL; // 指向的inode为空,和具体的文件无任何关系 list_del_init(&mark->g_list); // 把mark从group(也就是创建的fd实例)出链表 list_add(&mark->destroy_list, &destroy_list); wake_up(&destroy_waitq); if (group->ops->freeing_mark) group->ops->freeing_mark(mark, group); // 释放 fsnotify_put_mark(mark); mark->free_mark(mark); // 释放 fsnotify_put_group(group); // 如果group的引用为0,则释放group }
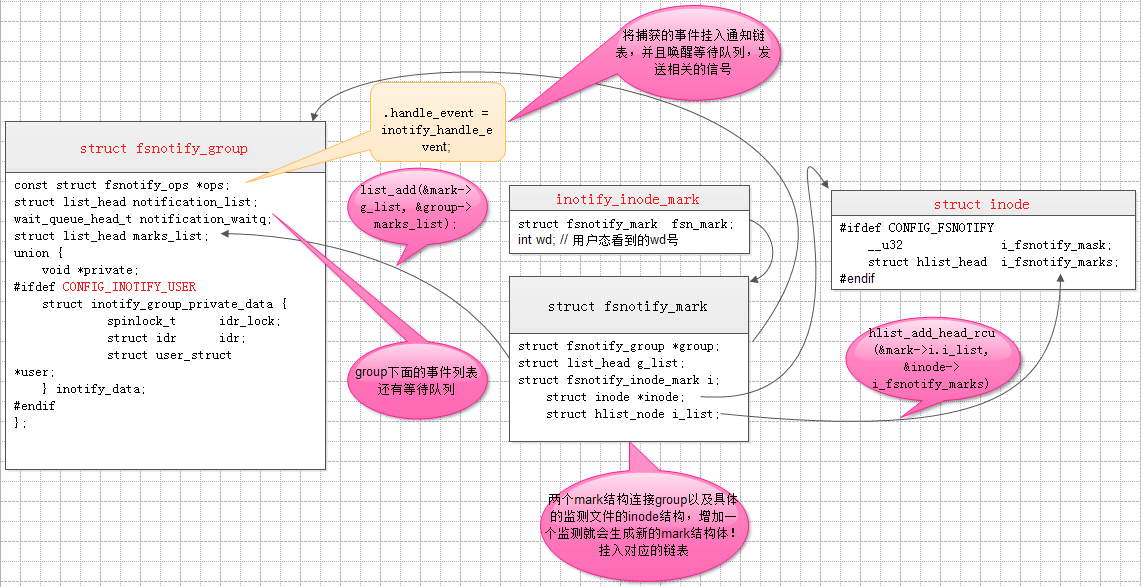
具体的关系结构图如图所示:
图1 inotify机制内核下面各结构体关系图
2.2 用户态接口原理
用户态接口的基本思路是初始化一个具体的inotify实例,并设置实例以及具体监控哪些事件。当有具体的事件以后可以读取对应的
结构体来解析。事件结构体为:
struct inotify_event {
int wd; /* Watch descriptor */ 监控描述符
uint32_t mask; /* Mask of events */ 具体的事件(文件创建、删除、属性修改等)
uint32_t cookie; /* Unique cookie associating related
events (for rename(2)) */
uint32_t len; /* Size of name field */
char name[]; /* Optional null-terminated name */ 具体的文件名
};
具体可以监控的事件主要有:(注释比较清晰了)
IN_ACCESS File was accessed (read) (*).
IN_ATTRIB Metadata changed, e.g., permissions, timestamps, extended attributes, link count (since Linux 2.6.25), UID, GID, etc. (*).
IN_CLOSE_WRITE File opened for writing was closed (*).
IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE File not opened for writing was closed (*).
IN_CREATE File/directory created in watched directory (*).
IN_DELETE File/directory deleted from watched directory (*).
IN_DELETE_SELF Watched file/directory was itself deleted.
IN_MODIFY File was modified (*).
IN_MOVE_SELF Watched file/directory was itself moved.
IN_MOVED_FROM Generated for the directory containing the old filename when a file is renamed (*).
IN_MOVED_TO Generated for the directory containing the new filename when a file is renamed (*).
IN_OPEN File was opened (*).
主要的用户态接口函数:
int inotify_init(void);
int inotify_init1(int flags);
初始化一个inotify实例并且返回一个文件描述符,inotify实例和一个evnet队列挂钩,失败返回-1。
int inotify_add_watch(int fd, const char *pathname, uint32_t mask);
添加一个watch对象,fd为具体的inotify实例描述符,pathname为监控的目录或者文件,mask为具体的事件,成功返回非负整数,失败返
回-1.
int inotify_rm_watch(int fd, int wd);
删除一个watch,fd为inotify实例描述符,wd为watch描述符。成功返回0,失败返回-1.
2.3 几个相关的参数
1 /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances // 默认是128
This specifies an upper limit on the number of inotify instances that can be created per real user ID.
最多可以创建的实例,也就是最多可以消耗的fd个数。也是inotify_init这个函数调用的最大次数!
2 /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches // 默认8192
This specifies an upper limit on the number of watches that can be created per real user ID.
可以具体监控的目录(文件)的最大值, 也就是inotify_add_watch这个函数可以监控文件或目录的最
大值,该函数每执行一次,需要指定具体监控的目录或者文件路径。
3 /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events // 默认是16384
The value in this file is used when an application calls inotify_init(2) to set an upper limit on the number
of events that can be queued to the corresponding inotify instance. Events in excess of this limit are
dropped, but an IN_Q_OVERFLOW event is always generated.
可以监控事件的最大值。
3. 测试程序
#include <sys/inotify.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> #include <sys/stat.h> /* * struct inotify_event { * int wd; // Watch descriptor * uint32_t mask; // Mask of events * uint32_t cookie; // Unique cookie associating related events (for rename(2)) * uint32_t len; // Size of name field * char name[]; // Optional null-terminated name * }; * **/ int giNotifyFd; int giaWds[20]; int giCount; int watch_inotify_events(int fd) { char event_buf[512]; int ret; int event_pos = 0; int event_size = 0; struct inotify_event *event; time_t tNow; struct tm *pTimeNow; /* 读事件是否发生,没有发生就会阻塞 */ ret = read(fd, event_buf, sizeof(event_buf)); /* 如果read的返回值,小于inotify_event大小出现错误 */ if (ret < (int)sizeof(struct inotify_event)) { printf("counld not get event!\n"); return -1; } /* 因为read的返回值存在一个或者多个inotify_event对象,需要一个一个取出来处理 */ while (ret >= (int)sizeof(struct inotify_event)) { event = (struct inotify_event*)(event_buf + event_pos); if (event->len) { /* 这三行可以注释掉,之前出现过加了这三行执行出现core dump的问题 */ // time(&tNow); // pTimeNow = localtime(&tNow); // printf("Local time is:%s", asctime(pTimeNow)); if(event->mask & IN_CREATE) { printf("watch is %d, create file: %s\n", event->wd, event->name); } else { printf("watch is %d, delete file: %s\n", event->wd, event->name); } if (event->mask & IN_ATTRIB) { printf("watch is %d, modify file attribute: %s\n", event->wd, event->name); } } /* event_size就是一个事件的真正大小 */ event_size = sizeof(struct inotify_event) + event->len; ret -= event_size; /* 指向下一个事件 */ event_pos += event_size; } return 0; } /* 递归处理目录 */ void init_all_iwds(char *pcName) { int iWd; struct stat tStat; DIR *pDir; struct dirent *ptDirent; char caNametmp[100]; // 存储目录名字 iWd = inotify_add_watch(giNotifyFd, pcName, IN_CREATE|IN_DELETE|IN_ATTRIB|IN_MODIFY); giaWds[giCount] = iWd; giCount++; if (-1 == stat(pcName, &tStat)) { printf("stat %s error\n", pcName); return; } if (!S_ISDIR(tStat.st_mode)) return; /* 处理子目录 */ pDir = opendir(pcName); if (NULL == pDir) { printf("opendir %s error\n", pcName); return; } // 循环读目录下面的子项 while (NULL != (ptDirent = readdir(pDir))) { if ((0 == strcmp(ptDirent->d_name, ".")) || (0 == strcmp(ptDirent->d_name, ".."))) continue; // 跳过当前目录和上一级父目录 // printf("sub name is %s, d_type is 0x%x\n", ptDirent->d_name, ptDirent->d_type); sprintf(caNametmp, "%s/%s", pcName, ptDirent->d_name); //获取子目录或文件名字 if (-1 == stat(caNametmp, &tStat)) { printf("stat error:%s\n", caNametmp); // 获取统计数据 return; } if (!S_ISDIR(tStat.st_mode)) //看是否是子目录,原则只处理目录 continue; printf("sub absoulte dir name is %s\n", caNametmp); // iWd = inotify_add_watch(giNotifyFd, caNametmp, IN_CREATE|IN_DELETE|IN_ATTRIB|IN_MODIFY); init_all_iwds(caNametmp); //处理子目录 } // 关闭 closedir(pDir); } int main(int argc, char** argv) { int iNotifyRet; fd_set fds; int iaWd[10]; int icount = 0; if (argc != 2) { printf("Usage: %s <dir>\n", argv[0]); return -1; } /* inotify初始化 */ iNotifyFd = inotify_init(); if (iNotifyFd == -1) { printf("inotify_init error!\n"); return -1; } /* 递归处理具体的目录,添加watch对象 */ init_all_iwds(argv[1]); /* 处理事件 */ while (1) { FD_ZERO(&fds); FD_SET(iNotifyFd, &fds); if (select(iNotifyFd+1, &fds, NULL, NULL, NULL) > 0) { iNotifyRet = watch_inotify_events(iNotifyFd); if (-1 == iNotifyRet) break; } } /* 删除inotify的watch对象 */ for (icount = 0; icount < giCount; icount++) { if (inotify_rm_watch(iNotifyFd, giaWds[icount ]) == -1) { printf("notify_rm_watch %d error!\n", giaWds[icount]); return -1; } } /* 关闭inotify描述符 */ close(iNotifyFd); return 0; }
文件命名为:inotify.c
编译: gcc -o inotify inotify.c 生成可执行文件
执行: ./inotify输出 Usage: ./inotify <dir> 提示需要输入具体监控的目录或者文件。
执行: ./inotify /home/work/0604_inotify/ &
创建 aaa 文件,打印出 watch is 1, create file: aaa
修改aaa文件属性,打印出 watch is 1, modify file attribute: aaa



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号