Linux驱动入门篇(四):基本的字符设备模块(3)
此节讨论字符设备模块如何实现文件操作,以供用户调用。在基本字符设备模块的讨论期间,只实现设备文件的打开、读、写、关闭功能。
文件操作结构
首先,我们需要知道内核提供了一个文件操作接口,即 struct file_operations 结构。它位于<linux/fs.h>中。
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
...//此处省略了部分成员
};
上述结构只节选部分目前关注的成员,struct module 前面介绍过,是一个模块信息相关的结构,其他五个成员皆为函数指针。它们分别对应用层文件操作中的 read、write、ioctl、open、close 函数。也就是说,在应用层中调用的文件操作函数,是由这些函数指针指向的函数实现的。
代码的实现
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
dev_t devno; //设备号
static struct class *my_class;
static struct cdev my_cdev;
int mycdev_open(struct inode * inode, struct file *flip)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Device mycdev has opened.");
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_read (struct file *flip, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Device mycdev has read.");
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_write (struct file *flip, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Device mycdev has wrote.");
return 0;
}
int mycdev_release (struct inode *inode, struct file *flip)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Device mycdev has released.");
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations my_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = mycdev_open,
.read = mycdev_read,
.write = mycdev_write,
.release = mycdev_release,
};
static int __init mycdev_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "mycdev");
if(ret != 0){
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Alloc device number failed.");
return -1;
}
//开始实现cdev_setup()
cdev_init(&my_cdev, &my_fops);
my_cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
ret = cdev_add(&my_cdev, devno, 1);
if(ret < 0){
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Add cdev failed.");
return -2;
}
//cdev_setup()结束
my_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "mycdev");
device_create(my_class, NULL, devno, NULL, "mycdev");
return 0;
}
static void mycdev_exit(void)
{
//mycdev_del()实现
cdev_del(&my_cdev);
//mycdev_del()结束
device_destroy(my_class, devno);
class_destroy(my_class);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
}
module_init(mycdev_init);
module_exit(mycdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
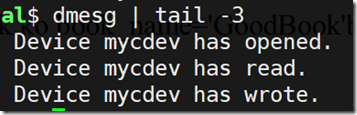
在用户程序中使用 open 函数打开 /dev/mycdev 设备文件时,实际调用的就是 my_fops 的 open 成员指向的函数 mycdev_open,read 等函数同理。
接下来,我们来写一个用户程序,对 mycdev 设备进行操作,看看是否调用了这些函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd;
fd = open("/dev/mycdev", O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
printf("Can't open mycdev, error %d.\n", fd);
return -1;
}
read(fd, NULL, 0);
write(fd, NULL, 0);
close(fd);
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号