【Swift学习】Swift编程之旅---字符与字符串(五)
String是swift的字符串类型。一个字符串是一个有效的字符序列,因此还可以使字符集合表示。通过+符号可以连接字符串。 String 类型是一种快速、现代化的字符串实现。每一个字符串都是由独立编码的 Unicode 字符组成,并提供了用于访问这些字符在不同Unicode表示的支持。使用""来标示字符串。
一、初始化空字符串
var emptyString = "" var anotherEmptyString = String()
这2种初始化方法是等价的。
isEmpty可以判断当前字符串是否为空字符串。
if emptyString.isEmpty {
print("Nothing to see here")
}
Swift 的 String 类型是值类型。如果您创建了一个新的字符串值,那么当其进行常量、变量赋值操作或在函数/方法中传递时,会进行值拷贝。在不同情况下,都会对已有字符串值创建新副本,并对该新副本进行传递或赋值。
二、字符(Characters)的使用
你可以通过for-in循环来访问字符串单独的字符
for character in "Dog!🐶".characters {
print(character)
}
let yenSign: Character = "¥"
字符串值可以使用传递一个字符数组来构造。
let catCharacters: [Character] = ["C", "a", "t", "!", "🐱"]
let catString = String(catCharacters)
print(catString)
// Prints "Cat!🐱
三、连接字符串和字符
字符串值可以通过+符号来实现字符串连接来建立新的字符串值。
let string1 = "hello"
let string2 = " there"
var welcome = string1 + string2
// welcome now equals "hello there
您还可以使用赋值操作符(+ =)将一个字符串值附加到一个已有的字符串变量
var instruction = "look over"
instruction += string2
// instruction now equals "look over there
使用append()方法讲一个字符值附加到一个字符串值后面。
let exclamationMark: Character = "!"
welcome.append(exclamationMark)
// welcome now equals "hello there!
你不能将字符串或字符附加到现有的字符变量,因为字符值必须包含一个字符
四、字符串插值
字符串插值是一种全新的构建字符串的方式,可以在其中包含常量、变量、字面量和表达式。您插入的字符串字面量的每一项都被包裹在以反斜线为前缀的圆括号中:
let multiplier = 3
let message = "\(multiplier) times 2.5 is \(Double(multiplier) * 2.5)"
// message is "3 times 2.5 is 7.5
注意:您插值字符串中写在括号中的表达式不能包含非转义双引号 (") 和反斜杠 (\),并且不能包含回车或换行符。
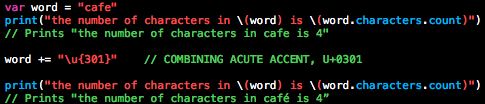
五、字符计数
我们可以使用String的characters属性的count属性来取得字符串的字符数也就是字符串的长度。看如下例子

输出

注意swift的特征值扩展字形集群的使用意味着字符串连接和修改可能不会影响一个字符串的字符数
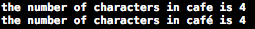
输出
六、访问和修改字符串(Accessing and Modifying a String)
我们通过String的方法和属性,或使用下标语法访问和修改字符串。
1.字符串索引
每一个字符串值都关联一个索引类型,String.Index,该索引对应于字符串中的每个字符的位置,不同的角色需要不同数量的内存来存储,所以为了确定哪些字符是在一个特定的位置,你必须遍历每个Unicode标量从字符串的开始或结束。基于这个原因,无法用整型值来索引swift的字符串。
使用startIndex属性来访问字符串的第一个字符的位置,使用endIndex属性来访问最后一个字符之后的位置,作为一个结果,endIndex属性不是一个有效的字符串下标的参数。
如果一个字符串为空,那么startIndex和endIndex是相等的。
String.Index值可以使用successor()方法来访问它的下一个字符。试图访问一个字符串的范围之外的索引将触发一个运行时错误。使用predecessor()方法来访问字符串的上一个字符
下面通过一个例子来说明这些方法
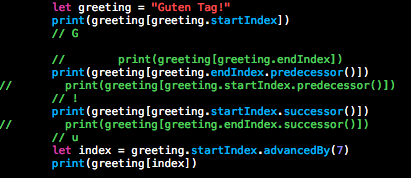
输出结果

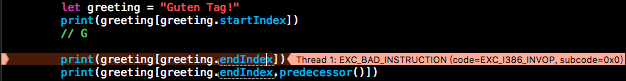
当我们试图这样写代码时
print(greeting[greeting.startIndex.predecessor()])访问起始位置的上一个字符
print(greeting[greeting.endIndex.successor()])访问末尾位置的下一个字符
都会发生运行时错误
使用characters属性的indices属性来创建一个所有索引的范围
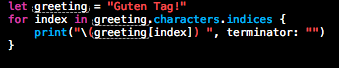
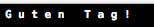
2.插入和删除(Inserting and Removing)
使用insert(_:atIndex:)向一个字符串在指定位置的插入一个字符
var welcome = "hello"
welcome.insert("!", atIndex: welcome.endIndex)
// welcome now equals "hello!
使用insertContentsOf(_:at:)向一个字符串在指定位置的插入一个字符串
welcome.insertContentsOf(" there".characters, at: welcome.endIndex.predecessor())
// welcome now equals "hello there!
使用removeAtIndex(_:)向一个字符串在指定位置删除一个字符
welcome.removeAtIndex(welcome.endIndex.predecessor())
// welcome now equals "hello there
使用removeRange(_:)向一个字符串在指定位置删除一段子字符串
let range = welcome.endIndex.advancedBy(-6)..<welcome.endIndex
welcome.removeRange(range)
// welcome now equals "hello"
七、比较字符串
let quotation = "We're a lot alike, you and I."
let sameQuotation = "We're a lot alike, you and I."
if quotation == sameQuotation {
println("These two strings are considered equal")
}
// prints "These two strings are considered equal"
2.前缀/后缀相等
let romeoAndJuliet = [
"Act 1 Scene 1: Verona, A public place",
"Act 1 Scene 2: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 3: A room in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 4: A street outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 5: The Great Hall in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 1: Outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 2: Capulet's orchard",
"Act 2 Scene 3: Outside Friar Lawrence's cell",
"Act 2 Scene 4: A street in Verona",
"Act 2 Scene 5: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 6: Friar Lawrence's cell"
]
利用 hasPrefix 方法使用romeoAndJuliet数组来计算话剧中第一幕的场景数:
var act1SceneCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasPrefix("Act 1 ") {
++act1SceneCount
}
}
println("There are \(act1SceneCount) scenes in Act 1")
// prints "There are 5 scenes in Act 1"
同样,可使用hasSuffix方法来计算发生在Capulet公馆和Lawrence牢房内以及周围的场景数。
var mansionCount = 0
var cellCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasSuffix("Capulet's mansion") {
++mansionCount
} else if scene.hasSuffix("Friar Lawrence's cell") {
++cellCount
}
}
println("\(mansionCount) mansion scenes; \(cellCount) cell scenes")
// prints "6 mansion scenes; 2 cell scenes"
3.大写和小写字符串
通过字符串的 uppercaseString 和 lowercaseString 属性来获取一个字符串的大写/小写版本。
let normal = "Could you help me, please?"
let shouty = normal.uppercaseString
// shouty 值为 "COULD YOU HELP ME, PLEASE?"
let whispered = normal.lowercaseString
// whispered 值为 "could you help me, please?"






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架