C语言二级指针间接赋值
重要意义:间接赋值的意义,实现了模块的功能划分,实现了软件作品的分层,使得模块接口和信息系统得以实现。
所谓二级指针就是指向指针的指针,其声明形式如下
int *p=NULL int **p1=NULL; p1=&p;
一级指针*运算,从所指向内存空间取出数值(类比:一级指针是藏宝图,所指向的内存空间是宝藏的存放的地点,宝藏是数值)
二级指针*运算,从所指向内存空间取出地址(类比:二级指针是一个写有藏宝图存放地点的纸条,所指向的内存空间是藏宝图的存放的地点,藏宝图是数值)
- 通过二级指针改变一级指针
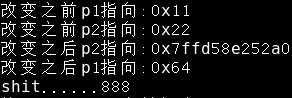
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> int main() { char *p1=NULL; char **p2=NULL; p1=0x11; printf("改变之前p1指向:%p\n",p1); p2=0x22; printf("改变之前p2指向:%p\n",p2); p2=&p1; *p2=100; printf("改变之后p2指向:%p\n",p2); printf("改变之后p1指向:%p\n",p1); printf("shit......%d\n",888); return 0; }
输出结果:
- 间接指针赋值的意义
#include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> void modelfor2(char **line1,int *len1,char **line2,int *len2) { char *writeinln1 = (char*)malloc(100); *line1=writeinln1; strcpy(*line1,"九九那个艳阳天来嘿哟~"); *len1=strlen(writeinln1); printf("%s\n","==========================================="); char *writeinln2 = (char*)malloc(100); *line2=writeinln2; strcpy(*line2,"20多的弟弟呀,爱上那丁锅锅~"); *len2=strlen(writeinln2); } int main() { int len1=0; char *story1=NULL; int len2=0; char *story2=NULL; modelfor2(&story1,&len1,&story2,&len2); printf("第一行文本:%s\n",story1); printf("第一行文本长度:%d\n",len1); printf("第二行文本:%s\n",story2); printf("第二行文本长度:%d\n",len2); if (story1!=NULL) { free(story1); story1=NULL; } if (story2!=NULL) { free(story2); story2=NULL; } printf("%d\n",888); return 0; }
输出结果:

间接赋值的意义,实现了模块的功能划分,实现了软件作品的分层,使得模块接口和信息系统得以实现。




