javaweb-JSP(一)
一、什么是JSP
JSP全称java Servlet Pages,它和servlet技术一样,都是SUN公司定义的一种用于开发动态web资源技术。JSP这门技术的最大的特点在于,写jsp就像在写html,但是相对html而言,html只能为用户提供静态数据,而JSP技术允许在页面中嵌套java代码,为用户提供动态数据。
二、JSP原理
2.1、web服务器如何调用并执行一个JSP页面的?
浏览器向服务器发请求你,不管访问的是什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet,所以当访问一个jsp页面时,其实也是在访问一个Servlet,服务器在执行jsp的时候,首先把jsp翻译成一个Servlet,所以我们访问jsp时,其实不是在访问jsp时,其实不是在访问jsp,而是在访问jspl翻译过后的那个Servlet,例如下面代码:
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>First Jsp</title> </head> <body> <h1>Jsp</h1> <% String s = "Hello Jsp"; out.print(s); %> </body> </html>

当浏览器访问index.jsp时,服务器首先将index.jsp翻译成一个index_jsp.class,在Tomcat服务器的 盘:\apache-tomcat-7.0.52\work\Catalina\localhost\test\org\apache\jsp 目录下可以看到index_jsp.class的源文件index_jsp.java,index_jsp.java代码如下:
/* * Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat * Version: Apache Tomcat/7.0.52 * Generated at: 2019-10-03 06:36:04 UTC * Note: The last modified time of this file was set to * the last modified time of the source file after * generation to assist with modification tracking. */ package org.apache.jsp; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.servlet.jsp.*; public final class index_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent { private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory = javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory(); private static java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> _jspx_dependants; private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory; private org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager; public java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> getDependants() { return _jspx_dependants; } public void _jspInit() { _el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory(); _jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig()); } public void _jspDestroy() { } public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException { final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; final java.lang.Object page = this; javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null; javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null; try { response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8"); pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; out.write("\r\n"); out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd\">\r\n"); out.write("<html>\r\n"); out.write("<head>\r\n"); out.write("<meta http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\">\r\n"); out.write("<title>First Jsp</title>\r\n"); out.write("</head>\r\n"); out.write("<body>\r\n"); out.write("\t<h1>Jsp</h1>\r\n"); out.write("\t"); String s = "Hello Jsp"; out.print(s); out.write("\r\n"); out.write("</body>\r\n"); out.write("</html>"); } catch (java.lang.Throwable t) { if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException)){ out = _jspx_out; if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0) try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {} if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t); else throw new ServletException(t); } } finally { _jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context); } } }
我们可以看到,index_jsp这个类是继承 org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase这个类的,通过查看Tomcat服务器的源代码,可以知道在apache-tomcat-6.0.20-src\java\org\apache\jasper\runtime目录下存HttpJspBase这个类的源代码文件,如下图所示:

HttpJsBase源代码,如下所示:
/* * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.jasper.runtime; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.jsp.HttpJspPage; import org.apache.jasper.compiler.Localizer; /** * This is the super class of all JSP-generated servlets. * * @author Anil K. Vijendran */ public abstract class HttpJspBase extends HttpServlet implements HttpJspPage { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; protected HttpJspBase() { } @Override public final void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { super.init(config); jspInit(); _jspInit(); } @Override public String getServletInfo() { return Localizer.getMessage("jsp.engine.info"); } @Override public final void destroy() { jspDestroy(); _jspDestroy(); } /** * Entry point into service. */ @Override public final void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { _jspService(request, response); } @Override public void jspInit() { } public void _jspInit() { } @Override public void jspDestroy() { } protected void _jspDestroy() { } @Override public abstract void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException; }
HttpJspBase类是继承HttpServlet的,所以HttpJspBase类是一个Servlet,而index_jsp又是继承HttpJspBase类的,所以index_jsp类也是一个Servlet,所以当浏览器访问服务器上的index.jsp页面时,其实就是在访问index_jsp这个Servlet,index_jsp这个Servlet使用_jspService这个方法处理请求。
2.2、jsp页面中的html排版标签是如何被发送到客户端的?
out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd\">\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write("<head>\r\n");
out.write("<meta http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\">\r\n");
out.write("<title>First Jsp</title>\r\n");
out.write("</head>\r\n");
out.write("<body>\r\n");
out.write("\t<h1>Jsp</h1>\r\n");
out.write("\t");
String s = "Hello Jsp";
out.print(s);
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("</body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>");
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
在jsp中编写的java代码和html代码都会被翻译到_jspService方法中去,在jsp中编写的java代码会原封不动地翻译成java代码,如<%String s = "Hello Jsp"; out.print("Hello Jsp");%>直接翻译成 String a = "Hello Jsp" ; out.print(s);,而HTML代码则会翻译成使用out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器。在jsp页面中编写的html排版标签都是以out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器,浏览器拿到html代码后才能够解析执行html代码。
2.3、Jsp页面中的java代码服务器是如何执行的?
在jsp中编写的java代码会被翻译到_jspService方法中去,当执行_jspService方法处理请求时,就会执行在jsp编写的java代码了,所以Jsp页面中的java代码服务器是通过调用_jspService方法处理请求时执行的。
2.4、Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给jsp提供一些什么java对象?
查看_jspService方法可以看到,Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给Jsp提供如下的8个java对象:
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; final java.lang.Object page = this;
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
其中page对象,request和response已经完成了实例化,而其它5个没有实例化的对象通过下面的方式实例化
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut();
这8个java对象在Jsp页面中是可以直接使用的,如下所示:
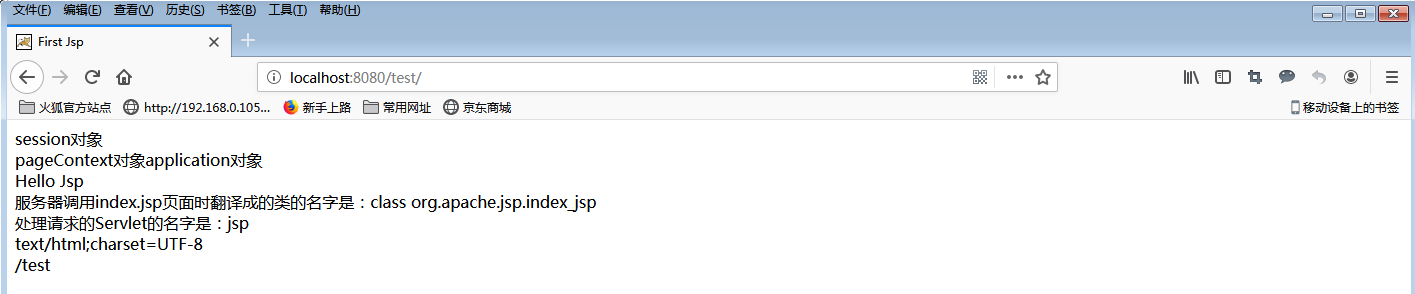
<% session.setAttribute("name", "session对象"); //使用session设置,设置session对象属性 out.print(session.getAttribute("name") + "<br/>"); //获取session对象的属性 pageContext.setAttribute("name", "pageContext对象"); //使用pageContext对象,设置pageContext属性 out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("name"));//获取pageContext对象的属性 application.setAttribute("name", "application对象");//使用application对象,设置application对象的属性 out.print(application.getAttribute("name")+"<br/>");//获取application对象的属性 out.print("Hello Jsp"+"<br/>");//使用out对象 out.print("服务器调用index.jsp页面时翻译成的类的名字是:"+page.getClass()+"<br/>");//使用page对象 out.print("处理请求的Servlet的名字是:"+config.getServletName()+"<br/>");//使用config对象 out.print(response.getContentType()+"<br/>");//使用response对象 out.print(request.getContextPath()+"<br/>");//使用request对象 %>
结果:
2.5、Jsp最佳实践
Jsp最佳实践就是jsp技术在开发中该怎么去用。
不管是JSP还是Servlet,虽然都可以用于开发动态web资源。但由于这2门技术各自的特点,在长期的软件实践中,人们逐渐把servlet作为web应用中的控制器组件来使用,而把JSP技术作为数据显示模板来使用。其原因为,程序的数据通常要美化后再输出:让jsp既用java代码产生动态数据,又做美化会导致页面难以维护。让servlet既产生数据,又在里面嵌套html代码美化数据,同样也会导致程序可读性差,难以维护。因此最好的办法就是根据这两门技术的特点,让它们各自负责各的,servlet只负责响应请求产生数据,并把数据通过转发技术带给jsp,数据的显示jsp来做。
2.6、Tomcat服务器的执行流程

第一次执行:
- 客户端通过电脑连接服务器,因为是请求是动态的,所以所有的请求交给WEB容器来处理
- 在容器中找到需要执行的*.jsp文件
- 之后*.jsp文件通过转换变为*.java文件
- *.java文件经过编译后,形成*.class文件
- 最终服务器要执行形成的*.class文件
第二次执行:
- 因为已经存在了*.class文件,所以不在需要转换和编译的过程
修改后执行:
1.源文件已经被修改过了,所以需要重新转换,重新编译。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号