micro-service web framework
services
1. directory
2. generate model
3. MD5: asymmetric
salt: to prevent "brute force cracking" by using rainbow table
import "github.com/anaskhan96/go-password-encoder"
// Using custom options options := &password.Options{16, 100, 30, sha512.New} // use sha512 better than MD5 salt, encodedPwd := password.Encode("generic password", options) newPwd := fmt.Sprintf("$sha512$%s$%s", salt, encodedPwd) pwdInfo := strings.Split(newPwd, "$")// len: 4; the first:"" fmt.Println(pwdInfo[1]) check := password.Verify("generic password", pwdInfo[2], pwdInfo[3], options) fmt.Println(check) // true
4. handler
pagination
func Paginate(pg, pgSize int) func(db *gorm.DB) *gorm.DB { return func(db *gorm.DB) *gorm.DB { switch { case pgSize > 100: pgSize = 100 case pgSize <= 0: pgSize = 10 } offset := (pg - 1) * pgSize return db.Offset(offset).Limit(pgSize) } }
global.DB.Scopes(Paginate(int(in.Pn), int(in.PSize))).Find(&users)
model to proto.rsp
func ModelToRsp(usr model.User) proto.UserInfoRsp { rsp := proto.UserInfoRsp{ Id: usr.ID, PassWord: usr.Password, NickName: usr.NickName, Gender: usr.Gender, Role: int32(usr.Role), } if usr.Birthday != nil { rsp.BirthDay = uint64(usr.Birthday.Unix()) } return rsp }
5. Birthday的类型转换
User 中 birthday *time.Time <--- proto中 message: birthday uint64
time := time.Unix(int64(req.BirthDay), 0) user.Birthday = &time
---> message中都有默认值,但是user中是指针类型,为nil,赋值之前要判断不为nil
rsp.BirthDay = uint64(usr.Birthday.Unix())
获取JSON数据的时候转换birthday
protobuf中birthday:uint64
response中birthday:JSONtime
uint64 -1-> time.Time -2-> JSONtime(custom struct) -3-> 序列化成JSON
-1-2-> Birthday: response.TimeJson(time.Unix(int64(value.BirthDay), 0)),
-3-修改 MarshalJSON 方法转换birthday格式: stmp := fmt.Sprintf("\"%s\"", time.Time(t).Format("2006-01-01"))
6. 用flag.String 启动grpc
IP := flag.String("ip", "0.0.0.0", "ip addr") // default: 0.0.0.0 PORT := flag.String("port", "50051", "port") flag.Parse() fmt.Println("ip:", *IP) fmt.Println("port:", *PORT)
组合: fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", *IP, *PORT)
使用:go build main.go -> CMD窗口 -> main.exe -h 可查看help
启动指定参数:main.exe -port 50053 -ip 0.0.0.0
goods-srvs
1.
model中:BaseModel被继承,在数据库中default:bigint
problem: when creating foreign key, if the type of id is not consistent
---> create fail
resolve:(designate int32 to save space) ID int32 `gorm:"primarykey;type:int"`
2. third level classification: 必须使用pointer类型
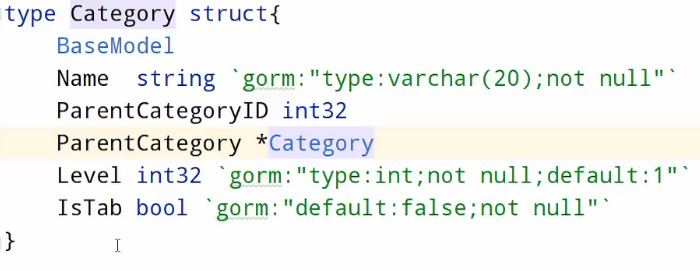
3. field 尽量not null
4. 优化:wants to add img-list into goods
1) goodsImg table 记录 goodsid和imgid
this table canbe really large
JOIN the large table when searching for a list of imgs is not efficient
search for the table also affect performance
=> put id-url into distributed database: mongodb/hbase
=> url only save non-repeating
2) use []string: custom type, save JSON to db
type GormList []string func (g *GormList) Scan(value interface{}) error { return json.Unmarshal(value.([]byte), &g) } func (g GormList) Value() (driver.Value, error) { return json.Marshal(g) }
5. how to design the gorm model : category
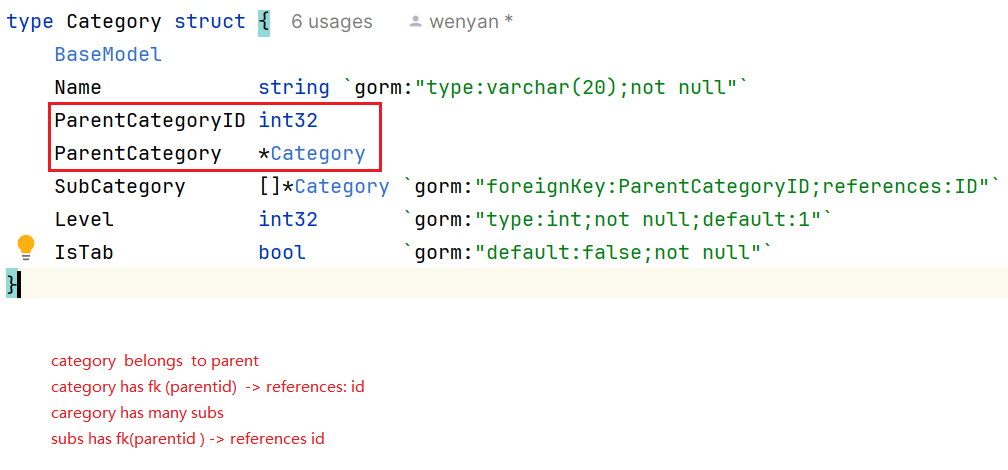
【ERROR】
1. 复制service目录,使用dir下replace all,还要全部检查一遍import
2. 如果db的table开头没有用namingstrategy (prefix), init db的时候也不应该用!connect to db failed
api
1》zap
package main import "time" import "go.uber.org/zap" func main() { logger, _ := zap.NewProduction() defer logger.Sync() // flushes buffer, if any sugar := logger.Sugar() sugar.Infow("failed to fetch URL", // Structured context as loosely typed key-value pairs. "url", "123", "attempt", 3, "backoff", time.Second, ) sugar.Infof("Failed to fetch URL: %s", "123") }
2. zap to file
package main import ( "go.uber.org/zap" "time" ) func NewLogger() (*zap.Logger, error) { cfg := zap.NewProductionConfig() cfg.OutputPaths = []string{ "./myproject.log", "stderr", // red output "stdout", // black output } return cfg.Build() } func main() { //logger, _ := zap.NewProduction() logger, err := NewLogger() if err != nil { panic(err) //panic("初始化logger失败") } su := logger.Sugar() defer su.Sync() url := "https://imooc.com" su.Info("failed to fetch URL", // Structured context as strongly typed Field values. zap.String("url", url), zap.Int("attempt", 3), zap.Duration("backoff", time.Second), ) }
3. set a global logger to use zap.S() -> secure access by goroutines with Mutex lock
logger, _ := zap.NewDevelopment()
zap.ReplaceGlobals(logger)
初始化后,zap.S(); zap.Errorw()可以随便用
2》 相对路径的读取问题
goProject
--dir
--ch01
-main.go
-xxx.yaml
1. cd 目录下 -> go build main.go -> ./main.exe (内有路径 "xxx.yaml")
2. Edit Configuration -> working directory -> 说明是在这个路径下运行 -> main.go改成路径(“dir/ch01/xxx.yaml”)
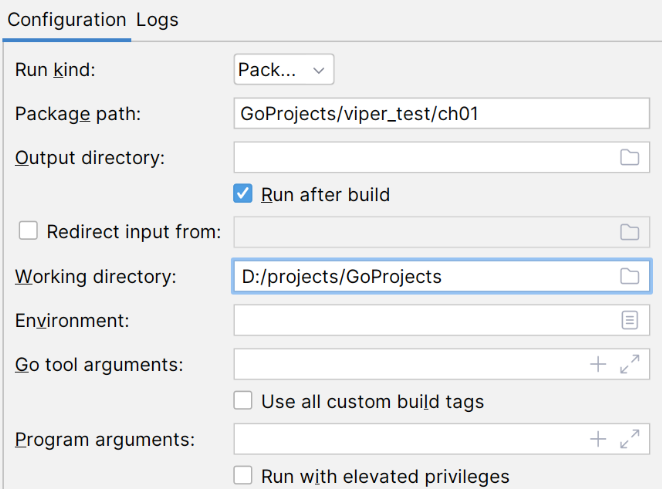
3. cd 到goproject,go run dir/ch01/main.go -> 在goproject目录下识别到(“dir/ch01/xxx.yaml”)
3》JWT to authorization
monolithic solution:
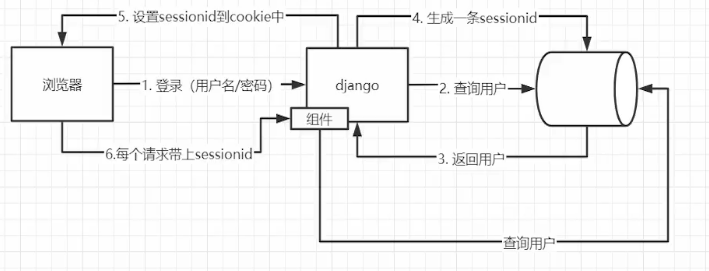
micro-srv solution1: common redis cluster to store session_id
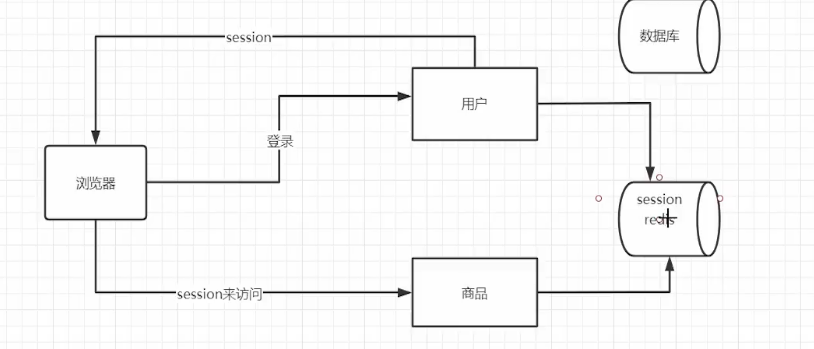
solution2: JWT(json web token) 利用加密技术,不需要存储id
token放在header中
1. create token
逻辑:JWT分成三段,前两段可以反解(no sensitive info!!),第三段必须通过server密钥才能verified
操作:1)需要 jwt.go 文件和 request.go
package middlewares import ( "errors" "github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "mxshop-api/user-web/global" "mxshop-api/user-web/models" "net/http" "time" ) func JWTAuth() gin.HandlerFunc { return func(c *gin.Context) { // 我们这里jwt鉴权取头部信息 x-token 登录时回返回token信息 这里前端需要把token存储到cookie或者本地localSstorage中 不过需要跟后端协商过期时间 可以约定刷新令牌或者重新登录 token := c.Request.Header.Get("x-token") if token == "" { c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, map[string]string{ "msg": "请登录", }) c.Abort() return } j := NewJWT() // parseToken 解析token包含的信息 claims, err := j.ParseToken(token) if err != nil { if err == TokenExpired { if err == TokenExpired { c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, map[string]string{ "msg": "授权已过期", }) c.Abort() return } } c.JSON(http.StatusUnauthorized, "未登陆") c.Abort() return } c.Set("claims", claims) c.Set("userId", claims.ID) c.Next() } } type JWT struct { SigningKey []byte } var ( TokenExpired = errors.New("Token is expired") TokenNotValidYet = errors.New("Token not active yet") TokenMalformed = errors.New("That's not even a token") TokenInvalid = errors.New("Couldn't handle this token:") ) func NewJWT() *JWT { return &JWT{ []byte(global.SrvConfig.JwtConfig.Key), } } // 创建一个token func (j *JWT) CreateToken(claims models.CustomClaims) (string, error) { token := jwt.NewWithClaims(jwt.SigningMethodHS256, claims) return token.SignedString(j.SigningKey) } // 解析 token func (j *JWT) ParseToken(tokenString string) (*models.CustomClaims, error) { token, err := jwt.ParseWithClaims(tokenString, &models.CustomClaims{}, func(token *jwt.Token) (i interface{}, e error) { return j.SigningKey, nil }) if err != nil { if ve, ok := err.(*jwt.ValidationError); ok { if ve.Errors&jwt.ValidationErrorMalformed != 0 { return nil, TokenMalformed } else if ve.Errors&jwt.ValidationErrorExpired != 0 { // Token is expired return nil, TokenExpired } else if ve.Errors&jwt.ValidationErrorNotValidYet != 0 { return nil, TokenNotValidYet } else { return nil, TokenInvalid } } } if token != nil { if claims, ok := token.Claims.(*models.CustomClaims); ok && token.Valid { return claims, nil } return nil, TokenInvalid } else { return nil, TokenInvalid } } // 更新token func (j *JWT) RefreshToken(tokenString string) (string, error) { jwt.TimeFunc = func() time.Time { return time.Unix(0, 0) } token, err := jwt.ParseWithClaims(tokenString, &models.CustomClaims{}, func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) { return j.SigningKey, nil }) if err != nil { return "", err } if claims, ok := token.Claims.(*models.CustomClaims); ok && token.Valid { jwt.TimeFunc = time.Now claims.StandardClaims.ExpiresAt = time.Now().Add(1 * time.Hour).Unix() return j.CreateToken(*claims) } return "", TokenInvalid }
package models import ( "github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go" ) type CustomClaims struct { ID uint NickName string AuthorityId uint jwt.StandardClaims }
2)server配置secret key --> config.yaml --> read to ServiceConfig struct
type JwtKey struct { Key string `mapstructure:"key"` } type ServiceConfig struct { Ip string `mapstructure:"ip"` Name string `mapstructure:"name"` Port int32 `mapstructure:"port"` UserConfig UserConfig `mapstructure:"usr_srv"` JwtConfig JwtKey `mapstructure:"jwt"` }
对应yaml中
jwt: key: 'h0JqVUD23NI9m1Rq361ru41OvUGvNScS'
3) 插入login的逻辑
j := middlewares.NewJWT() claim := models.CustomClaims{ ID: uint(userInfo.Id), NickName: userInfo.NickName, AuthorityId: uint(userInfo.Role), StandardClaims: jwt.StandardClaims{ NotBefore: time.Now().Unix(), // start from now ExpiresAt: time.Now().Unix() + 60*60*24*30, // 30 days Issuer: "bobby", }, } token, err := j.CreateToken(claim) if err != nil { c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{ "msg": "create token error", }) return } c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{ "msg": "login success", "token": token, "id": userInfo.Id, "nickname": userInfo.NickName, "token_expire": (time.Now().Unix() + 60*60*24*30) * 1000, })
2. add token
group.GET("/list", middlewares.JWTAuth(), api.GetUserList)
3. get user_info from token
// get user_id from token claim, _ := c.Get("claims") customClaim, _ := claim.(*models.CustomClaims) // assertion: interface{} -> *model.customclaims zap.S().Debugf("user_id is %+v", customClaim.ID)
4》cross-domain request
浏览器在什么情况下会发起options预检请求?
在非简单请求且跨域的情况下,浏览器会发起options预检请求。
Preflighted Requests是CORS中一种透明服务器验证机制。预检请求首先需要向另外一个域名的资源发送一个 HTTP OPTIONS 请求头,其目的就是为了判断实际发送的请求是否是安全的。
下面的情况需要进行预检
关于简单请求和复杂请求:
1 简单请求
简单请求需满足以下两个条件
- 请求方法是以下三种方法之一:
- HEAD
- GET
- POST
- HTTP 的头信息不超出以下几种字段
- Accept
- Accept-Language
- Content-Language
- Last-Event-ID
- Content-Type: 只限于 (application/x-www-form-urlencoded、multipart/form-data、text/plain)
2 复杂请求
非简单请求即是复杂请求
常见的复杂请求有:
- 请求方法为 PUT 或 DELETE
- Content-Type 字段类型为 application/json
- 添加额外的http header 比如access_token
在跨域的情况下,非简单请求会先发起一次空body的OPTIONS请求,称为"预检"请求,用于向服务器请求权限信息,等预检请求被成功响应后,才发起真正的http请求。
解决办法:router开始配置(router.use()) middleware 来允许“OPTIONS”请求
func Cors() gin.HandlerFunc { return func(c *gin.Context) { method := c.Request.Method c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*") c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST,GET,OPTIONS,DELETE,PATCH,PUT") c.Header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type,AccessToken,X-CSRF-Token,Authorization,Token,x-token") c.Header("Access-Control-Expose-Headers", "Access-Control-Allow-Origin,Access-Control-Allow-Methods,Access-Control-Allow-Headers") if method == "OPTIONS" { c.AbortWithStatus(http.StatusNoContent) } } }
5》 captcha
1. generate captcha: get id & img src
package api import ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "github.com/mojocn/base64Captcha" "go.uber.org/zap" "net/http" ) var store = base64Captcha.DefaultMemStore func GetCaptcha(c *gin.Context) { driver := base64Captcha.NewDriverDigit(80, 240, 5, 0.7, 80) // length = 5 cp := base64Captcha.NewCaptcha(driver, store) id, b64s, err := cp.Generate() if err != nil { zap.S().Errorf("generate captcha error") c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{ "msg": "generate captcha error", }) return } c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{ "captcha_id": id, "captcha_path": b64s, }) }
2. verify the captcha: in: captcha数字 + captcha_id;
// 1,1 verify the captcha if !store.Verify(login.CaptchaId, login.Captcha, true) { c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{ "msg": "captcha not verified", }) return }
3. html: img src = {{.captcha_path}}
base64 picture convertion URL: https://tool.chinaz.com/tools/imgtobase
6》Redis
install on docker
docker run -p 6379:6379 -d redis:latest redis-server docker container update --restart=always 容器名字 // enable auto restart redis when restarting docker
install GUI: https://rdm.dev/
quick start: https://github.com/redis/go-redis
rdb := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{ Addr: fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", global.SrvConfig.RedisConfig.Host, global.SrvConfig.RedisConfig.Port), }) rdb.Set(c, sms.Mobile, smsCode, 15*time.Second)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号