Leetcode: Algorithm
1. Boyer-Moore Voting Algorithm
identify the majority element (frequency > n/2)

class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { int count = 0; Integer candidate = null; for (int num : nums) { if (count == 0) { candidate = num; } count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1; } return candidate; } }
2. 判断是否连续
(参考 228.Summary Ranges)
class Solution { public List<String> summaryRanges(int[] nums) { List<String> res = new ArrayList<>(); // 判断连续还是不连续的算法 int i = 0; while(i < nums.length){ int start = i; while(i < nums.length-1 && nums[i+1] == nums[i] + 1){ i++; } if(nums[start] == nums[i]){ res.add(nums[i] + ""); }else{ res.add(nums[start] + "->" + nums[i]); } i++; } return res; } }
3. intervals merge (57. Insert Interval)
class Solution { public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) { List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>(); int n = intervals.length; if(n == 1) return intervals; Arrays.sort(intervals,(a,b)->a[0]-b[0]); int i = 0; while(i<n){ int[] curr = intervals[i]; while(i<n-1 && overLap(curr,intervals[i+1])){ curr = merge(curr,intervals[i+1]); i++; } res.add(curr); i++; } return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]); } public boolean overLap(int[] curr, int[] next){ return (curr[1] >= next[0]); } public int[] merge(int[] curr, int[] next){ return new int[]{Math.min(curr[0],next[0]), Math.max(curr[1],next[1]) }; } }
4. 判断是否存在circle:1 - 0 - 2- 3- 1
class Solution { static int WHITE = 1; static int GRAY = 2; static int BLACK = 3; boolean isPossible; Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map; List<Integer> topolst; Map<Integer,Integer> color; public void init(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites){ this.isPossible = true; this.topolst = new ArrayList<>(); this.color = new HashMap<>(); this.map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 0;i<prerequisites.length;i++){ List<Integer> lst = map.getOrDefault(prerequisites[i][1],new ArrayList<>()); lst.add(prerequisites[i][0]); map.put(prerequisites[i][1],lst);// } for(int i = 0; i<numCourses; i++ ){ color.put(i,WHITE); } } public void dfs(int i){ if(!this.isPossible) return; color.put(i,GRAY); if(map.containsKey(i)){ for(Integer neighbor: map.get(i)){ if(color.get(neighbor) == GRAY){ // this.isPossible = false; } if(color.get(neighbor) == WHITE){ // dfs(neighbor); } } } topolst.add(0,i); // color.put(i,BLACK); } public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) { init(numCourses,prerequisites); for(int i = 0; i<numCourses; i++ ){ if(color.get(i) == WHITE){ dfs(i); } } return isPossible ? topolst.stream().mapToInt(i->i).toArray() : new int[0]; } }
5. Graph - shortest path
<1> BFS
BFS can only be used to find shortest path in a graph if:
-
There are no loops
-
All edges have same weight or no weight.
PriorityQueue<Integer[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer[]>((a,b)->a[1].compareTo(b[1]));
class Solution { class Cell{ Integer val; Integer dist; public Cell(Integer val, Integer dist){ this.val = val; this.dist = dist; } } public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) { Map<Integer,List<Cell>> map = new HashMap<>();
// this is directed graph, if undirected also put time[i][1] for(int i = 0; i<times.length; i++){ if(!map.containsKey(times[i][0])){ map.put(times[i][0],new ArrayList<>()); } map.get(times[i][0]).add(new Cell(times[i][1],times[i][2])); } // boolean[] seen = new boolean[n+1]; dont need int[] dist = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(dist,Integer.MAX_VALUE); dist[k] = 0; PriorityQueue<Cell> q = new PriorityQueue<Cell>((a,b) -> a.dist.compareTo(b.dist)); // get the smallest one q.add(new Cell(k,0)); while(!q.isEmpty()){ Cell curr = q.remove(); // seen[curr.val] = true; if(dist[curr.val] != curr.dist){ // 旧的不管了 continue; } if(!map.containsKey(curr.val)) continue; for(Cell next : map.get(curr.val)){ // if(seen[next.val]) continue; if(curr.dist + next.dist < dist[next.val]){ // update dist[next.val] = curr.dist + next.dist; q.add(new Cell(next.val,dist[next.val])); } } } int max = -1; for(int i = 1; i<=n ; i++){ if(i == k) continue; if(max < dist[i]) max = dist[i]; } return max == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : max; } }
6. 有向的用dfs,无向的用bfs
int[][] mat = new int[n][n]; for(int i=0; i <n ; i++){ for(int j =0; j< n ; j++){ if(i==j) mat[i][j] = 0; mat[i][j] = 100001; } } for(int[] edge : edges){ mat[edge[0]][edge[1]] = edge[2]; mat[edge[1]][edge[0]] = edge[2]; } for(int x =0; x< n ; x++){ for(int i =0; i < n ; i++){ for(int j =0; j < n ; j++){ mat[i][j] = Math.min(mat[i][j], mat[i][x] + mat[x][j]); } } }
7. Trie (prefix tree)
<reference: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/trie-insert-and-search/>
class Trie { class TrieNode{ TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26]; boolean isEnd; public TrieNode(){ this.isEnd = false; for(int i = 0; i<26; i++){ children[i] = null; } } } TrieNode root; public Trie() { this.root = new TrieNode(); } public void insert(String word) { char[] arr = word.toCharArray(); TrieNode curr = root; // this is important for(char c : arr){ if(curr.children[c - 'a'] == null){ curr.children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode(); } curr = curr.children[c - 'a']; } curr.isEnd = true; } public boolean search(String word) { char[] arr = word.toCharArray(); TrieNode curr = root; for(char c : arr){ if(curr.children[c - 'a'] == null){ return false; } curr = curr.children[c - 'a']; } return curr.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { char[] arr = prefix.toCharArray(); TrieNode curr = root; for(char c : arr){ if(curr.children[c - 'a'] == null){ return false; } curr = curr.children[c - 'a']; } return true; } } /** * Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: * Trie obj = new Trie(); * obj.insert(word); * boolean param_2 = obj.search(word); * boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix); */
8. frequency majority
(指超过n/2)不用 hashmap 而用count
class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { int count = 0; int candidate = 0; for(int num : nums){ if(count == 0){ candidate = num; } count += num == candidate ? 1:-1; } return candidate; } }
9. ArrayList
当我要在arraylist中特定的index remove,同时保持其他所有的index不变
=> index 对应的value和last element交换,然后remove last element
10. rotate the matrix
1. 左上 和 左下 row 和 col 互换;左上和右下 row 和 col是对应的
2. 从左上来看,row 移动两格(n/2),col移动3格(n/2 + n%2);
implement:
class Solution { // j i ; i,n-1-j // n-1-i j ; n-1-j n-1-i public void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int n = matrix.length; for(int i = 0; i< n/2 + n%2; i++){ for(int j = 0; j< n/2; j++){ int temp = matrix[n-1-i][j]; matrix[n-1-i][j] = matrix[n-1-j][n-1-i]; matrix[n-1-j][n-1-i] = matrix[i][n-1-j]; matrix[i][n-1-j] = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = temp; } } } }
11. linkedlist
如果要实现queue中任意一个位置pop(), use Map<Integer,LinkNode>
ListNode has prev & next
12. tree
BST property: in-order traversal can guarantee sorted sequence
13. graph
verticle - edge
dont understand why time complexity is O(N+M) verticles + edges
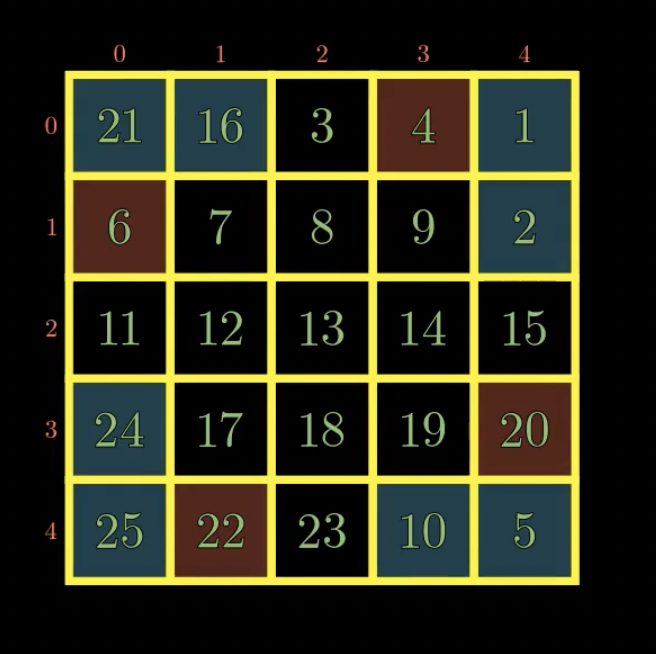
14. 棋盘如何用表示: label -> row & col
int n = board.length; Pair<Integer,Integer>[] pair = new Pair[n * n + 1]; Integer[] cols = new Integer[n]; for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){ cols[i] = i; } int label = 1; for(int r = n-1; r>=0; r--){ for(int c : cols){ pair[label++] = new Pair<Integer,Integer>(r,c); } Collections.reverse(Arrays.asList(cols)); // *** }
15. 2D coordinate
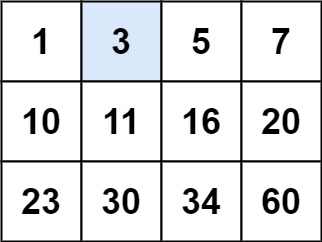
l = 0; r = rows * cols - 1;
mid = (l+r)/2; get the index
then
row = mid / cols;
col = mid % col;
16. 最大公约数
// greatest common divisor class Solution { // 1. greatest common divisor // 6 4 -> 2 public int gcd(int a, int b){ // do not need to care which one is larger if(b == 0) return a; return gcd(b,a%b); } public String gcdOfStrings(String str1, String str2) { if(!(str2 + str1).equals(str1+str2) ) return ""; return str1.substring(0,gcd(str1.length(),str2.length())); } }
17. cal the profit
left[i]: from l to r, <= i day sell, the maximum profit
right[i]: from r to l, >= i day buy, the maximum profit
int Lmin = prices[0]; int Rmax = prices[n-1]; int LmaxDiff = 0; int RmaxDiff = 0; for(int i = 1; i<n; i++){ LmaxDiff = Math.max(LmaxDiff,prices[i]-Lmin); // record the maxDiff, not the max; 否则:下降? left[i] = LmaxDiff; Lmin = Math.min(Lmin,prices[i]); // record the min, we need to know the min of the past int j = n-1-i; RmaxDiff = Math.max(RmaxDiff,Rmax-prices[j]); right[j] = RmaxDiff; Rmax = Math.max(Rmax,prices[j]); // record the max, need to know the max in the future }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号