机器学习之 线性回归
一、理论
https://www.cnblogs.com/futurehau/p/6105011.html
二、代码
1)一元一次线性方程 y=kx+b
注意x和y一定是[[1],[2],[3],[4],...]
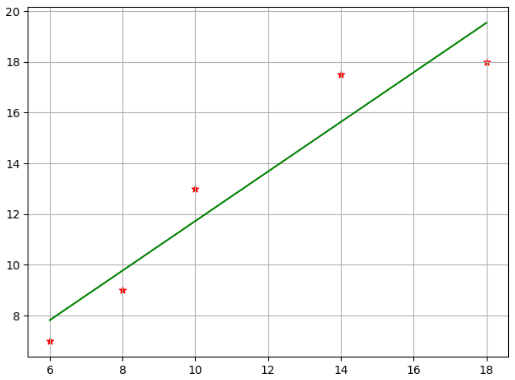
#-*-coding:gb2312-*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression if __name__ == '__main__': x = np.array([6,8,10,14,18]) y = np.array([7,9,13,17.5,18]) # 散点图标记为*,颜色为red plt.scatter(x,y,marker='*',c='r') plt.grid(True) # plt.show() # 改二维 # 用数据建立LR模型 # print(x.reshape(-1,1)) # -1 自动计算 x_,y_ = x.reshape(-1,1),y.reshape(-1,1) lr = LinearRegression() # 截距对结果影响不大 lr.fit(x_,y_) print(lr.intercept_) print(lr.coef_) # y = 0.9762931x + 1.96551724 # 用回归模型预测,颜色用green x2 = x y2 = lr.predict(x2.reshape(-1,1)).reshape(-1,1) plt.plot(x2,y2,'g') plt.show()
结果:
2)一元二次方程
输入的x**2和x形式是:[[100,10],[81,9],...]
#-*-coding:gb2312-*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression if __name__ == '__main__': # x = np.array([[10],[9]]) # print(np.concatenate([x**2,x],axis=1)) # 设置年份 year = np.arange(1,12) #print(year) sale = np.array([0.52,9.36,52,191,350,571,912.17,1207,1682,2135,2684]) plt.scatter(year,sale,marker="*",c='r') plt.grid(True) lr = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False) # 重新计算一元二次方程组 # 输入的x**2和x形式是:[[100,10],[81,9],...] x2 = year.reshape(-1,1) x2_train = np.concatenate([x2**2,x2],axis=1) lr.fit(x2_train,sale.reshape(-1,1)) print(lr.predict([[144,12]])) x3 = x2 y3 = lr.predict(x2_train).reshape(-1, 1) plt.plot(x3, y3, 'g') plt.show()
结果:



