Spring之架构(一)启动入口
一、Spring配置启动类

1 package config; 2 3 import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; 4 5 /** 6 * Servlet3.0环境下,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类; 7 * Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为SpringServletContainerInitializer; 8 * 而这个类返回来又会去查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置任务交给他们来实现。 9 * Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,也就是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; 10 * 我们自己建的SpitterWebInitializer继承了AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; 11 * 因此当部署到Servlet3.0容器的时候,容器会自动发现它,并用它来配置Servlet上下文; 12 */ 13 public class SpitterWebInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { 14 15 /** 将DispatcherServlet映射到"/",这表示他会是应用默认的Servlet,他会处理进入应用的所有请求. */ 16 @Override 17 protected String[] getServletMappings() { 18 return new String[] { "/" }; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * DispatcherServlet启动时,他会创建Spring应用上下文,并加载配置文件或者配置类中的bean; 23 * 我么要求DispatcherServlet启动时,会加载WebConfig中的bean 24 */ 25 @Override 26 protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { 27 return new Class<?>[] { WebConfig.class }; 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 但是在Spring Web中,通常还有另一个上下文应用。它是由ContextLoaderListener创建的; 32 * DispatcherServlet加载包含Web组件的bean如controller,视图解析器,处理映射器; 33 * ContextLoaderListener要加载应用中的其他的bean,通常是驱动后端的中间层和数据层组件; 34 * 比如没有扫描到service层时,controller层bean的依赖注入就会在ContextLoaderListener加载时报错; 35 */ 36 @Override 37 protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { 38 return new Class<?>[] { RootConfig.class }; 39 } 40 41 }
通过intellij idea查看继承树:

----------------------------------------------------------------
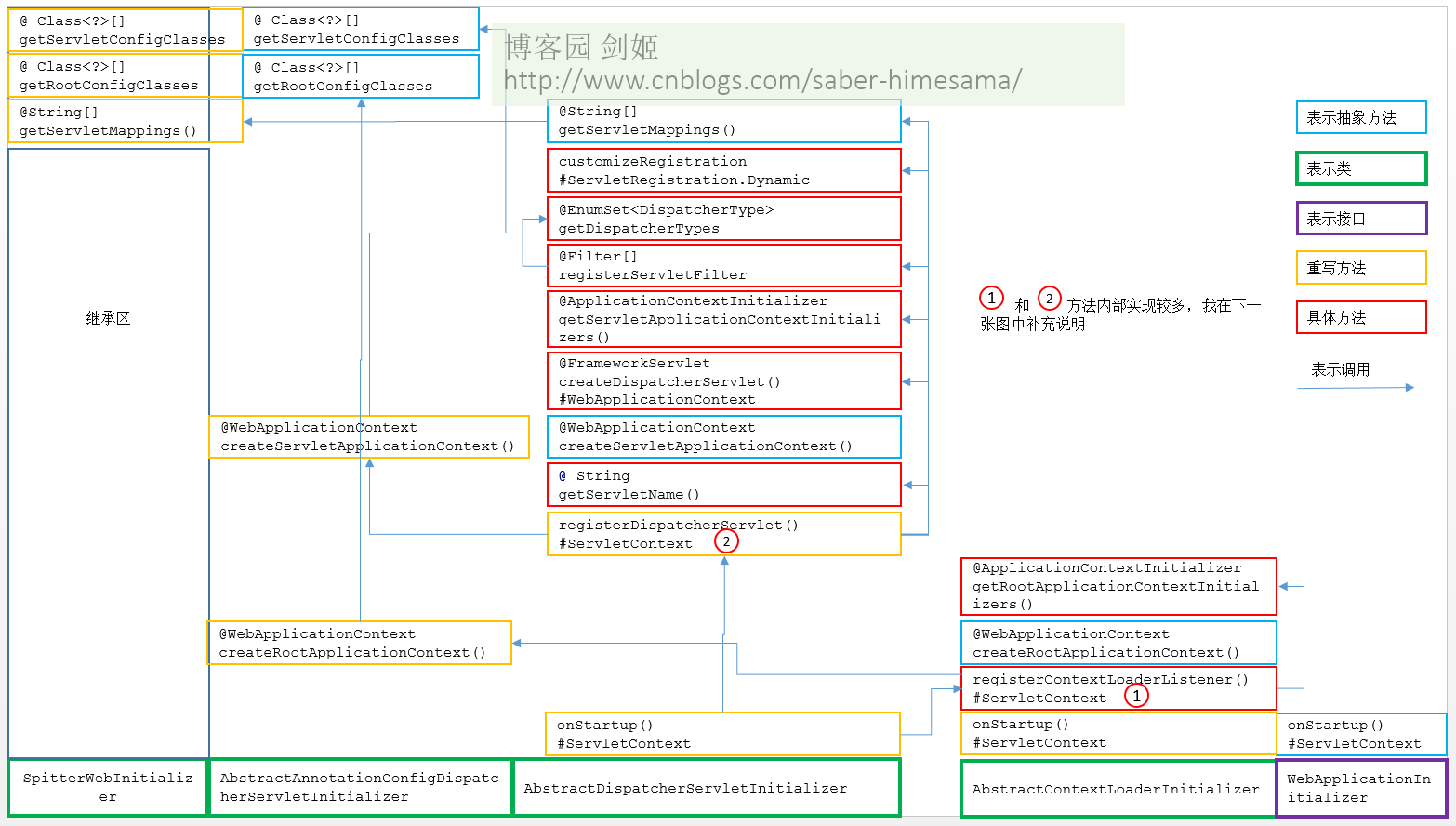
我们发现树顶是个interface,Classname: WebApplicationInitializer

1 public interface WebApplicationInitializer { 2 3 /** 4 * Configure the given {@link ServletContext} with any servlets, filters, listeners 5 * context-params and attributes necessary for initializing this web application. See 6 * examples {@linkplain WebApplicationInitializer above}. 7 * @param servletContext the {@code ServletContext} to initialize 8 * @throws ServletException if any call against the given {@code ServletContext} 9 * throws a {@code ServletException} 10 */ 11 void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException; 12 13 }
WebApplicationInitializer接口只有一个void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext)抽象方法,顾名思义就是启动web容器。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我再来看AbstractContextLoaderInitializer是如何实现这个WebApplicationInitializer接口的:

1 public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { 2 3 /** Logger available to subclasses */ 4 protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); 5 6 7 @Override 8 public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { 9 registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext); 10 } 11 12 /** 13 * Register a {@link ContextLoaderListener} against the given servlet context. The 14 * {@code ContextLoaderListener} is initialized with the application context returned 15 * from the {@link #createRootApplicationContext()} template method. 16 * @param servletContext the servlet context to register the listener against 17 */ 18 protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) { 19 WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext(); 20 if (rootAppContext != null) { 21 ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext); 22 listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers()); 23 servletContext.addListener(listener); 24 } 25 else { 26 logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " + 27 "createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * Create the "<strong>root</strong>" application context to be provided to the 33 * {@code ContextLoaderListener}. 34 * <p>The returned context is delegated to 35 * {@link ContextLoaderListener#ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)} and will 36 * be established as the parent context for any {@code DispatcherServlet} application 37 * contexts. As such, it typically contains middle-tier services, data sources, etc. 38 * @return the root application context, or {@code null} if a root context is not 39 * desired 40 * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 41 */ 42 protected abstract WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(); 43 44 /** 45 * Specify application context initializers to be applied to the root application 46 * context that the {@code ContextLoaderListener} is being created with. 47 * @since 4.2 48 * @see #createRootApplicationContext() 49 * @see ContextLoaderListener#setContextInitializers 50 */ 51 protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getRootApplicationContextInitializers() { 52 return null; 53 } 54 55 }
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer重写了onStartup并且追加了2个抽象方法和一个具体方法
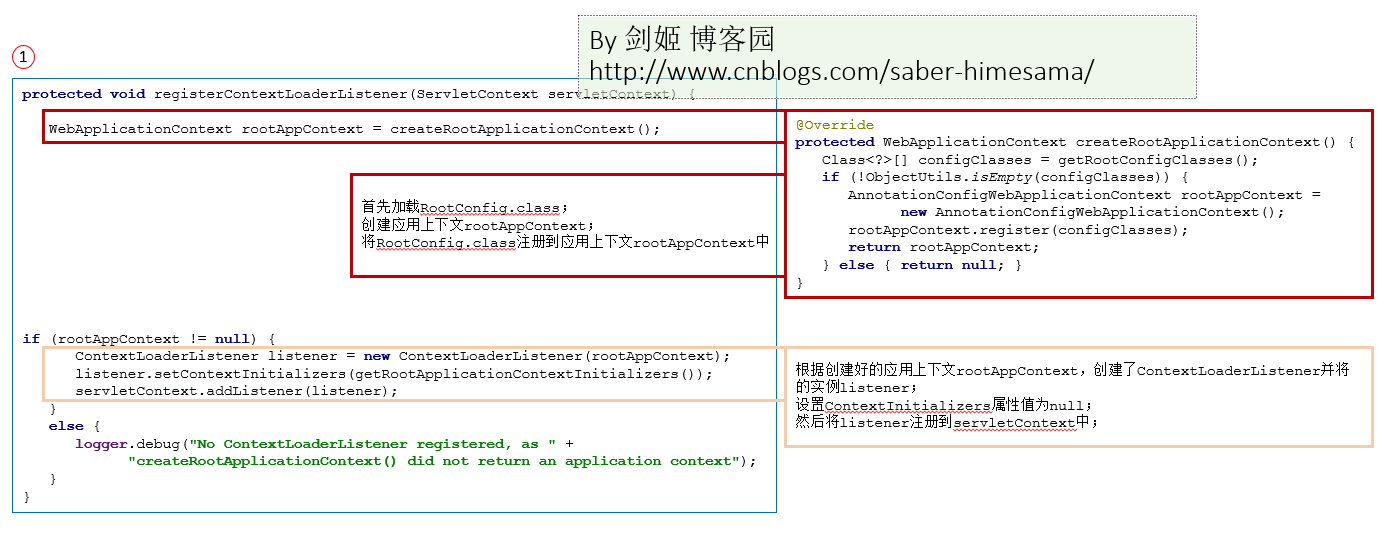
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer调用onStartup方法时,直接调用registerContextLoaderListener方法,
而registerContextLoaderListener先是调用了createRootApplicationContext返回一个WebApplicationContext rootAppContext,
registerContextLoaderListener然后创建ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext)对象;
通过listener的setContextInitializers方法,又调用了本类另一个抽象方法getRootApplicationContextInitializers().
最后通过addListener方法把listener注册到servletContext。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我们再来看继承树的下一个AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer

1 public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer { 2 3 /** 4 * The default servlet name. Can be customized by overriding {@link #getServletName}. 5 */ 6 public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcher"; 7 8 9 @Override 10 public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { 11 super.onStartup(servletContext); 12 registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext); 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * Register a {@link DispatcherServlet} against the given servlet context. 17 * <p>This method will create a {@code DispatcherServlet} with the name returned by 18 * {@link #getServletName()}, initializing it with the application context returned 19 * from {@link #createServletApplicationContext()}, and mapping it to the patterns 20 * returned from {@link #getServletMappings()}. 21 * <p>Further customization can be achieved by overriding {@link 22 * #customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic)} or 23 * {@link #createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)}. 24 * @param servletContext the context to register the servlet against 25 */ 26 protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) { 27 String servletName = getServletName(); 28 Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return empty or null"); 29 30 WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext(); 31 Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, 32 "createServletApplicationContext() did not return an application " + 33 "context for servlet [" + servletName + "]"); 34 35 FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext); 36 dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers()); 37 38 ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet); 39 Assert.notNull(registration, 40 "Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'." + 41 "Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name."); 42 43 registration.setLoadOnStartup(1); 44 registration.addMapping(getServletMappings()); 45 registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported()); 46 47 Filter[] filters = getServletFilters(); 48 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) { 49 for (Filter filter : filters) { 50 registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter); 51 } 52 } 53 54 customizeRegistration(registration); 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Return the name under which the {@link DispatcherServlet} will be registered. 59 * Defaults to {@link #DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME}. 60 * @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext) 61 */ 62 protected String getServletName() { 63 return DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME; 64 } 65 66 /** 67 * Create a servlet application context to be provided to the {@code DispatcherServlet}. 68 * <p>The returned context is delegated to Spring's 69 * {@link DispatcherServlet#DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)}. As such, 70 * it typically contains controllers, view resolvers, locale resolvers, and other 71 * web-related beans. 72 * @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext) 73 */ 74 protected abstract WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext(); 75 76 /** 77 * Create a {@link DispatcherServlet} (or other kind of {@link FrameworkServlet}-derived 78 * dispatcher) with the specified {@link WebApplicationContext}. 79 * <p>Note: This allows for any {@link FrameworkServlet} subclass as of 4.2.3. 80 * Previously, it insisted on returning a {@link DispatcherServlet} or subclass thereof. 81 */ 82 protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) { 83 return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext); 84 } 85 86 /** 87 * Specify application context initializers to be applied to the servlet-specific 88 * application context that the {@code DispatcherServlet} is being created with. 89 * @since 4.2 90 * @see #createServletApplicationContext() 91 * @see DispatcherServlet#setContextInitializers 92 * @see #getRootApplicationContextInitializers() 93 */ 94 protected ApplicationContextInitializer<?>[] getServletApplicationContextInitializers() { 95 return null; 96 } 97 98 /** 99 * Specify the servlet mapping(s) for the {@code DispatcherServlet} — 100 * for example {@code "/"}, {@code "/app"}, etc. 101 * @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext) 102 */ 103 protected abstract String[] getServletMappings(); 104 105 /** 106 * Specify filters to add and map to the {@code DispatcherServlet}. 107 * @return an array of filters or {@code null} 108 * @see #registerServletFilter(ServletContext, Filter) 109 */ 110 protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { 111 return null; 112 } 113 114 /** 115 * Add the given filter to the ServletContext and map it to the 116 * {@code DispatcherServlet} as follows: 117 * <ul> 118 * <li>a default filter name is chosen based on its concrete type 119 * <li>the {@code asyncSupported} flag is set depending on the 120 * return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported} 121 * <li>a filter mapping is created with dispatcher types {@code REQUEST}, 122 * {@code FORWARD}, {@code INCLUDE}, and conditionally {@code ASYNC} depending 123 * on the return value of {@link #isAsyncSupported() asyncSupported} 124 * </ul> 125 * <p>If the above defaults are not suitable or insufficient, override this 126 * method and register filters directly with the {@code ServletContext}. 127 * @param servletContext the servlet context to register filters with 128 * @param filter the filter to be registered 129 * @return the filter registration 130 */ 131 protected FilterRegistration.Dynamic registerServletFilter(ServletContext servletContext, Filter filter) { 132 String filterName = Conventions.getVariableName(filter); 133 Dynamic registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName, filter); 134 if (registration == null) { 135 int counter = -1; 136 while (counter == -1 || registration == null) { 137 counter++; 138 registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName + "#" + counter, filter); 139 Assert.isTrue(counter < 100, 140 "Failed to register filter '" + filter + "'." + 141 "Could the same Filter instance have been registered already?"); 142 } 143 } 144 registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported()); 145 registration.addMappingForServletNames(getDispatcherTypes(), false, getServletName()); 146 return registration; 147 } 148 149 private EnumSet<DispatcherType> getDispatcherTypes() { 150 return (isAsyncSupported() ? 151 EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE, DispatcherType.ASYNC) : 152 EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE)); 153 } 154 155 /** 156 * A single place to control the {@code asyncSupported} flag for the 157 * {@code DispatcherServlet} and all filters added via {@link #getServletFilters()}. 158 * <p>The default value is "true". 159 */ 160 protected boolean isAsyncSupported() { 161 return true; 162 } 163 164 /** 165 * Optionally perform further registration customization once 166 * {@link #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)} has completed. 167 * @param registration the {@code DispatcherServlet} registration to be customized 168 * @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext) 169 */ 170 protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) { 171 } 172 173 }
抽象类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer也重写了onStartup,先是通过super.onStartup(servletContext)完成父类servletContext的初始化,
然后调用registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext)方法来注册DispatcherServlet;
具体流程:String servletName = getServletName()来获取servletName,获取一个WebApplicationContext servletAppContext对象,
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);来建一个dispatcherServlet
而protected abstract String[] getServletMappings()抽象了servlet映射的路径;
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
我们再来看看继承树的下一个AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer抽象类

1 public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 2 extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer { 3 4 /** 5 * {@inheritDoc} 6 * <p>This implementation creates an {@link AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext}, 7 * providing it the annotated classes returned by {@link #getRootConfigClasses()}. 8 * Returns {@code null} if {@link #getRootConfigClasses()} returns {@code null}. 9 */ 10 @Override 11 protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() { 12 Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses(); 13 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) { 14 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); 15 rootAppContext.register(configClasses); 16 return rootAppContext; 17 } 18 else { 19 return null; 20 } 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * {@inheritDoc} 25 * <p>This implementation creates an {@link AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext}, 26 * providing it the annotated classes returned by {@link #getServletConfigClasses()}. 27 */ 28 @Override 29 protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() { 30 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext servletAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); 31 Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses(); 32 if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) { 33 servletAppContext.register(configClasses); 34 } 35 return servletAppContext; 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * Specify {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration} 40 * and/or {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Component @Component} classes to be 41 * provided to the {@linkplain #createRootApplicationContext() root application context}. 42 * @return the configuration classes for the root application context, or {@code null} 43 * if creation and registration of a root context is not desired 44 */ 45 protected abstract Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses(); 46 47 /** 48 * Specify {@link org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration @Configuration} 49 * and/or {@link org.springframework.stereotype.Component @Component} classes to be 50 * provided to the {@linkplain #createServletApplicationContext() dispatcher servlet 51 * application context}. 52 * @return the configuration classes for the dispatcher servlet application context or 53 * {@code null} if all configuration is specified through root config classes. 54 */ 55 protected abstract Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses(); 56 57 }
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer创建了2个WebApplicationContext,
rootAppContext和servletAppContext
servletAppContext将getServletConfigClasses()方法返回的Class进行注册
rootAppContext将getRootConfigClasses()方法返回的Class进行注册
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
最后作为SpitterWebInitializer指定两个上下文AppContext需要注册Class,并且实现servlet映射的路径即可。
由于继承了父类的各种方法,当servlet3.0环境以上时,tomcat启动时会寻找实现AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
的SpitterWebInitializer,并调用onstart方法进行不断的方法调用直到把上下文和映射路径加载完毕,即完成了启动。




