多进程测试
1. 编写程序 rxx(xx为你学号后两位), rxx -o 生成并打印一个奇数随机数,rxx -e 生成并打印一个偶数随机数。提交代码和运行结果截图。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv)
{
int n;
char s1[]="-o",s2[]="-e";
if(strcmp(argv,s1)==0){
n=rand()*2+1;
}
if(strcmp(argv,s2)==0){
n=rand()*2;
}
printf("%d\n",n);
return 0;
}

2. 编写一个多进程程序,父进程通过调用exec和rxx 打印奇数随机数,同时打印自己PID,子进程通过调用exec和rxx 打印奇数随机数,同时打印PPID和PID,提交代码和运行结果截图。
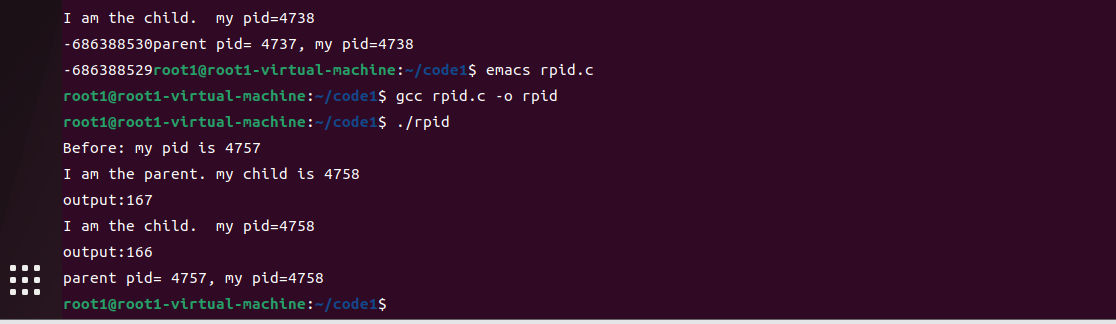
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
char *args[3];
args[0]="r02";
args[1]="-e";
args[2]=0;
char *args1[3];
args1[0]="r02";
args1[1]="-o";
args1[2]=0;
printf("Before: my pid is %d\n", getpid());
if(fork()!=0){
execv("r01",args);
printf("Father's PID:%d\n",getpid());
sleep(4);
}
if(fork()!=0 || -1){
printf("I'm Child\n");
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d\",getpid());
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d\n",getppid());
if(fork()!=0){
execv("r02",args1);
}
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)