Java 异常处理与输入输出
一、异常

1.1
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[10];
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
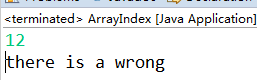
int index=in.nextInt();
try
{
a[index]=25;
System.out.println("right");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException b)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
in.close();
}
}

出现异常就会到catch。
1.2 调用的函数中出现异常
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("right");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
f();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException b)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
1.3
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void g()
{
f();
}
public static void h()
{
int i=10;
if(i<100)
g();
}
public static void k()
{
try {
h();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("k()");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
k();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
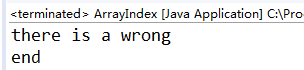
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}

try ...catch 里出现嵌套时,只会输出里层嵌套的内容。
catch的存在就是为了处理出现的异常。
相当于在k()函数中发现了异常,并且利用catch已经将异常解决了。所以在main()中便默认k()没有了异常,所以不会输出“there is a wrong”。
1.4
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void g()
{
f();
}
public static void h()
{
int i=10;
if(i<100)
g();
}
public static void k()
{
try {
h();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
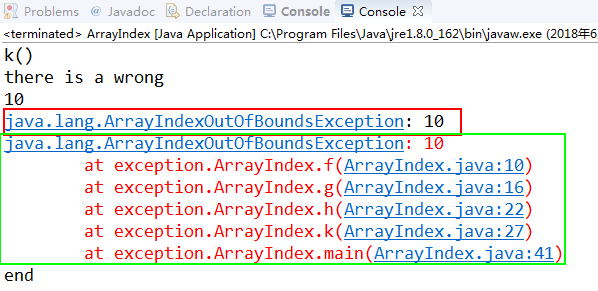
System.out.println("k()");
throw e;//抛出异常
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
k();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//输出e的值,10,这是指数组a[10]处赋值出现问题
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();//显示调用路径
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
throw e:相当于将处理的异常又重新添加加进来,这样“there is a wrong ”也便会输出。
或者说对于异常catch没有处理完全。所以还需要再度输出。
1.5
二、流


2.1 二进制数据
package Hello;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];//定义了字节数组
try {
int len=System.in.read(buffer);//往buffer中写入数据,并返回长度
String s=new String(buffer, 0, len);//从buffer中0的位置开始,获取len长度的字节
System.out.println("读到了"+len+"字节");
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("s的长度是:"+s.length());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
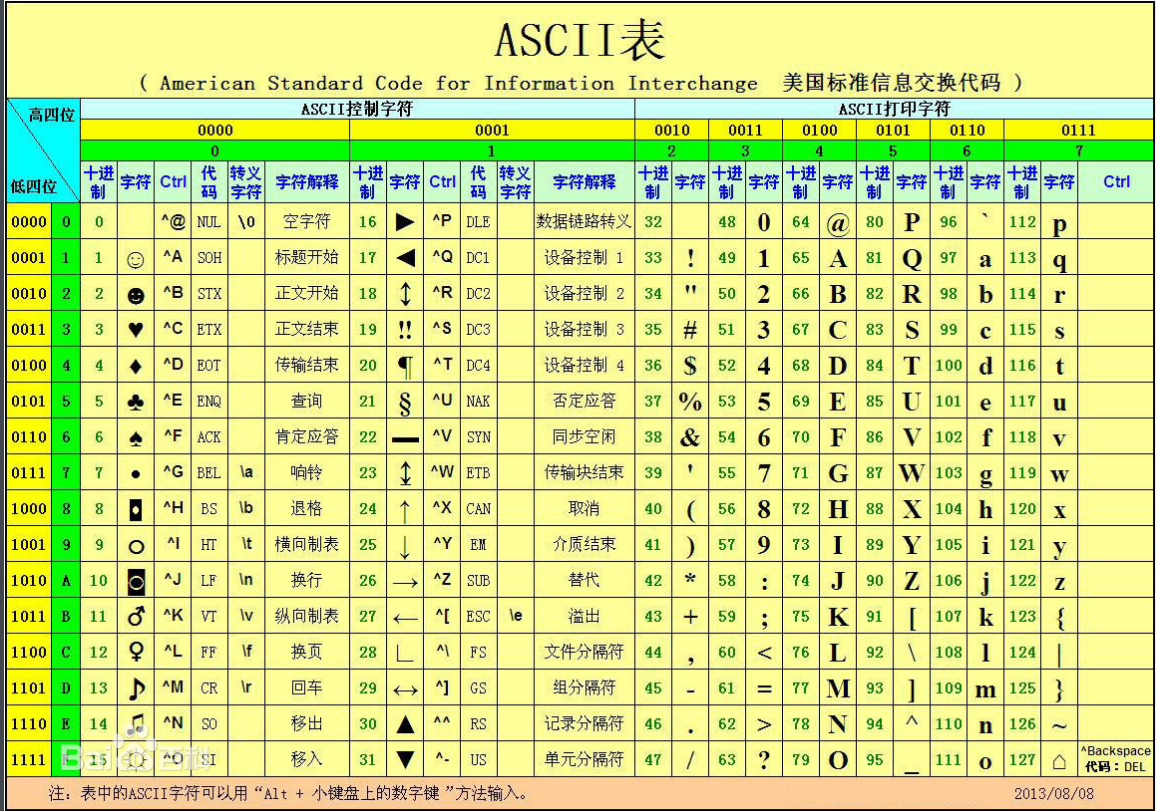
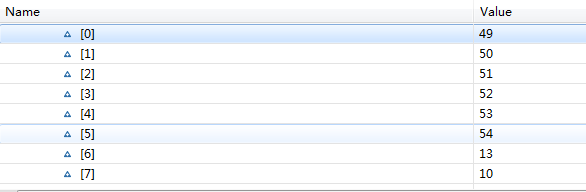

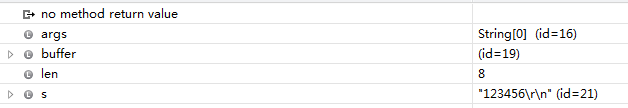
回车和换行算两个字符。

2.2
package Hello;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[5];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]='a';
}
try {
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
out.write(buffer);
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
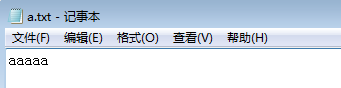

2.3 过滤器

package Hello;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
DataOutputStream out=new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
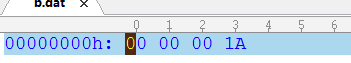
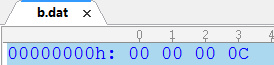
new FileOutputStream("b.dat")));//只能处理字节
int i=123454;
out.writeInt(i);
out.close();
DataInputStream in=new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("b.dat")));
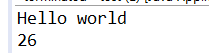
int j=in.readInt();
System.out.println(j);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以16进制存储。

2.4 文本


package Hello;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("c.txt"))));//
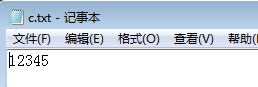
int i=12345;
out.println(i);
out.close();
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("c.txt")));
String line;
while((line=in.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(line);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}



2.5编码格式
package Hello;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("c.txt"))));//
int i=12345;
out.println(i);
out.close();
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("a.txt"),"GBk"));//设置编码格式
String line;
while((line=in.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(line);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
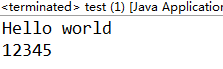
GBK编码时,正确读出

utf8时

2.6 格式化输出


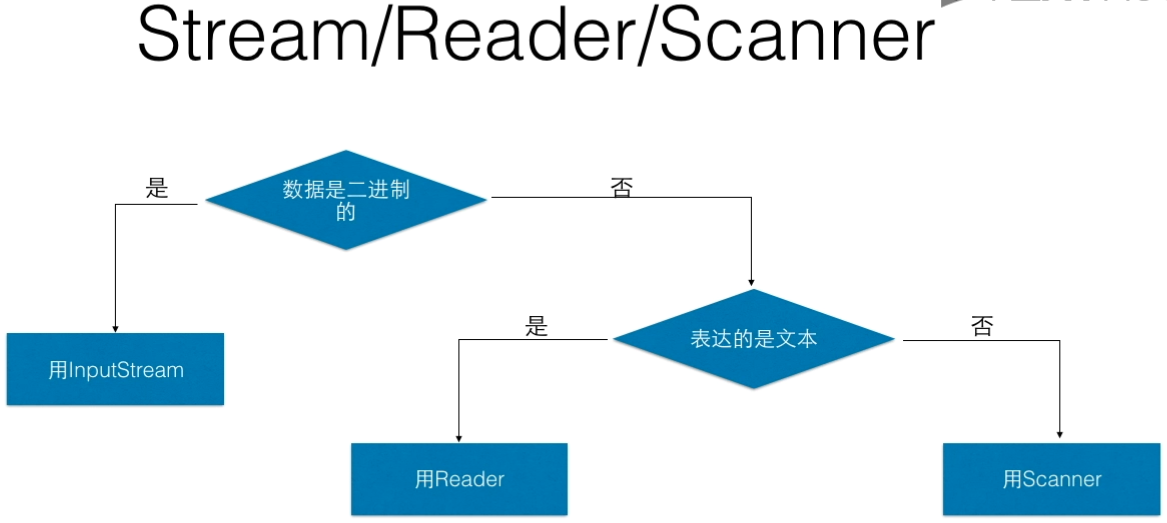
三、流应用
package Hello;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket=new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("localhost"),12345);
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream())));//
out.println("hello");
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream()));//设置编码格式
String line;
line=in.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
out.close();
socket.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、对象串行化
package Hello;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
class Student implements Serializable{ //可串行化的类
private String name;
private int age;
private int grade;
public Student(String name,int age,int grade)
{
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.grade=grade;
}
public String toString()
{
return name+" "+age+" "+grade;
}
}
public class hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
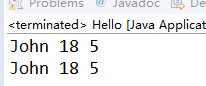
Student s1=new Student("John",18,5);
System.out.println(s1);
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("obj.dat"));
out.writeObject(s1);
out.close();
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("obj.dat"));
Student s2=(Student)in.readObject();
System.out.println(s2);
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
保存在obj.dat中的值