Python math库和random库
1、math库
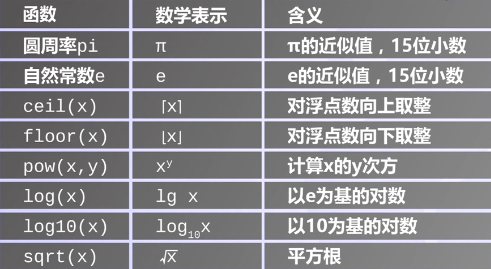
1 >>> from math import * 2 >>> 2*pi 3 6.283185307179586 4 >>> e 5 2.718281828459045 6 >>> ceil(2.3) 7 3 8 >>> floor(2.3) 9 2 10 >>> pow(2,3) 11 8.0 12 >>> log(e) 13 1.0 14 >>> log10(100) 15 2.0 16 >>> sqrt(16) 17 4.0

1 >>> from math import * 2 >>> exp(2) 3 7.38905609893065 4 >>> e**2 5 7.3890560989306495 6 >>> degrees(pi) 7 180.0 8 >>> radians(120) 9 2.0943951023931953 10 >>> sin(pi/2) 11 1.0 12 >>> cos(pi/3) 13 0.5000000000000001 14 >>> tan(pi/4) 15 0.9999999999999999 16 >>> atan(1) 17 0.7853981633974483 18 >>> asin(1) 19 1.5707963267948966 20 >>> acos(1) 21 0.0
2、random库
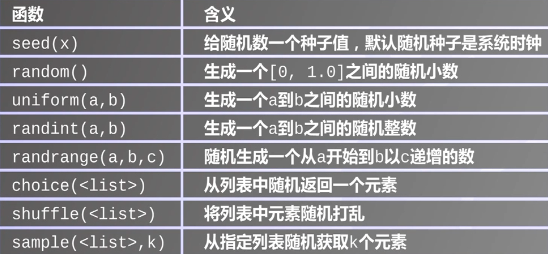
1 from random import * 2 >>> random() 3 0.6606648937887478 4 >>> uniform(1,10) 5 8.316837423419921 6 >>> randint(1,10) 7 5 8 >>> randrange(0,10,2) 9 4 10 >>> randrange(0,10,2) 11 8 12 >>> randrange(0,10,2) 13 6 14 >>> randrange(0,10,2) 15 0 16 >>> ra=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] 17 >>> choice(ra) 18 1 19 >>> shuffle(ra) 20 >>> ra 21 [0, 2, 3, 9, 7, 8, 5, 6, 1, 4] 22 >>> sample(ra,4) 23 [1, 8, 5, 9]
3、随机种子
1 >>> seed(10) 2 >>> random() 3 0.5714025946899135 4 >>> random() 5 0.4288890546751146 6 >>> random() 7 0.5780913011344704 8 >>> seed(1) 9 >>> random() 10 0.13436424411240122 11 >>> random() 12 0.8474337369372327 13 >>> seed(10) 14 >>> random() 15 0.5714025946899135 16 >>> random() 17 0.4288890546751146 18 >>> random() 19 0.5780913011344704
可以看出,通过随机种子生成的是伪随机数。
4、蒙特卡洛(Monte Carlo)方法
又称随机抽样或统计试验方法。当所求解问题是某种事件出现的概率,或某随机变量期望值时,可以通过某种“试验”的方法求解。简单说,蒙特卡洛是利用随机试验求解问题的方法。
π计算问题的IPO表示如下:
输入:抛点的数量
处理:对于每个抛洒点,计算点到圆心的距离,通过距离判断该点在圆内或是圆外。统计在圆内点的数量
输出:π值
1 from math import sqrt 2 from random import random 3 from time import clock #时间库 4 5 Darts=150000 #投掷次数 6 hits=0 #击中次数 7 clock() 8 for i in range(Darts): 9 x,y=random(),random() #同步赋值 10 if sqrt((x**2+y**2))<=1: 11 hits=hits+1 12 pai=4*hits/Darts 13 print("Pi的值是:%f"%pai) 14 print("程序运行时间%s s"%clock())




