第11課-Channel Study For Create Custom Restful Service
这节课我们一起学习利用Mirth Connect的HTTP Listener源通道与JavaScript Writer目的通道搭建自定义Restful风格webapi服务。
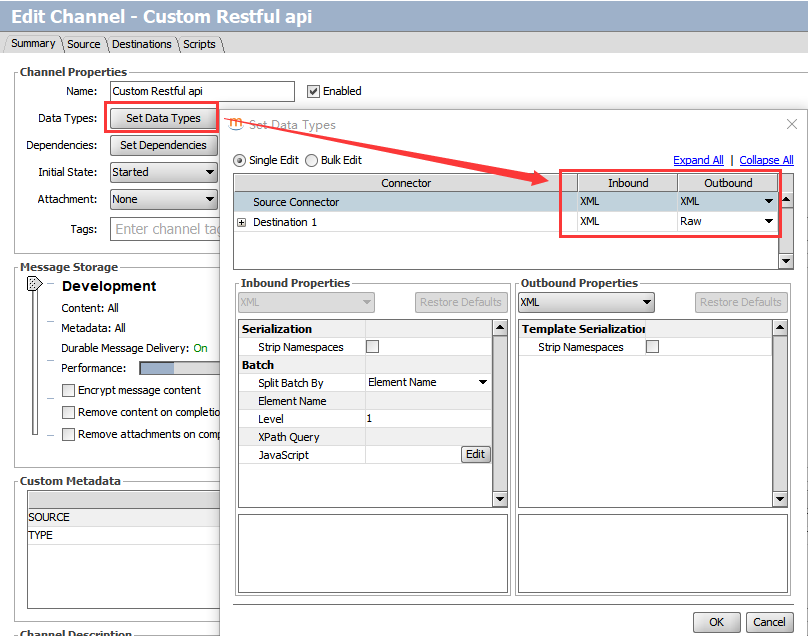
1.新建名为‘Custom Restful api’的信道,指定源通道与目的通道的输入输出消息格式
2.设置HTTP Listener类型源通道参数
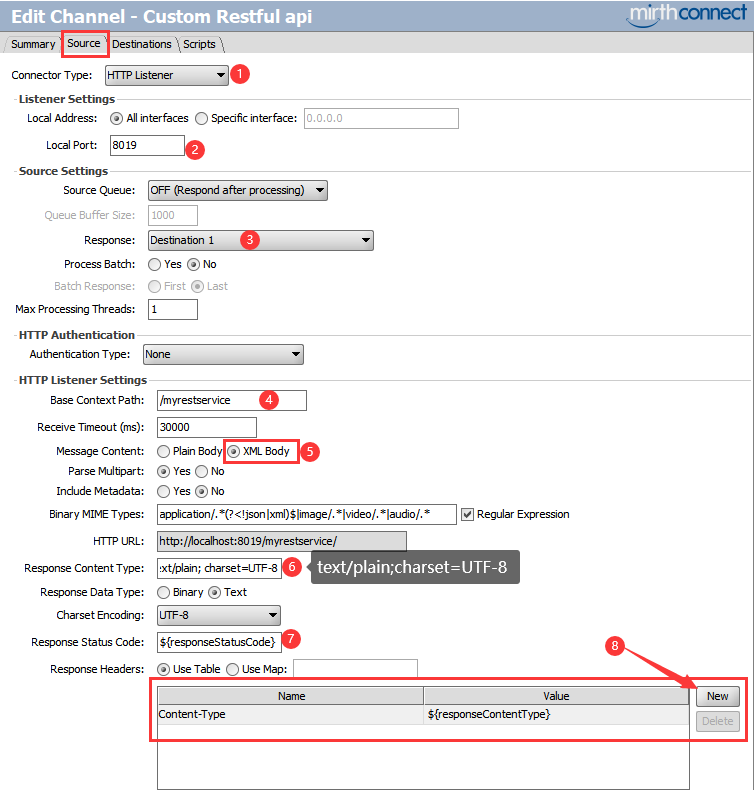
- 把 "Response" 响应指定为 destination 1
- 输入‘Base context path’ 为
/myrestservice - 设置 "Message Content" 为 XML Body
- 设置默认"Response Content Type" 为
text/plain; charset=UTF-8我们将在目的通道中通过channel map重写它的值为application/xml或application/json - 设置 "Response Status Code" 响应码为
${responseStatusCode}我们将在目的通道中通过channel map重写它的值为200(成功)或500(失败) - 在 "Response Header" 中添加一个变量 "Content-Type" ,指定其值为
${responseContentType}我们将在目的通道中通过channel map重写它的值为application/xml或application/json
3.设置JavaScript Writer目的通道参数并编写JS实现脚本
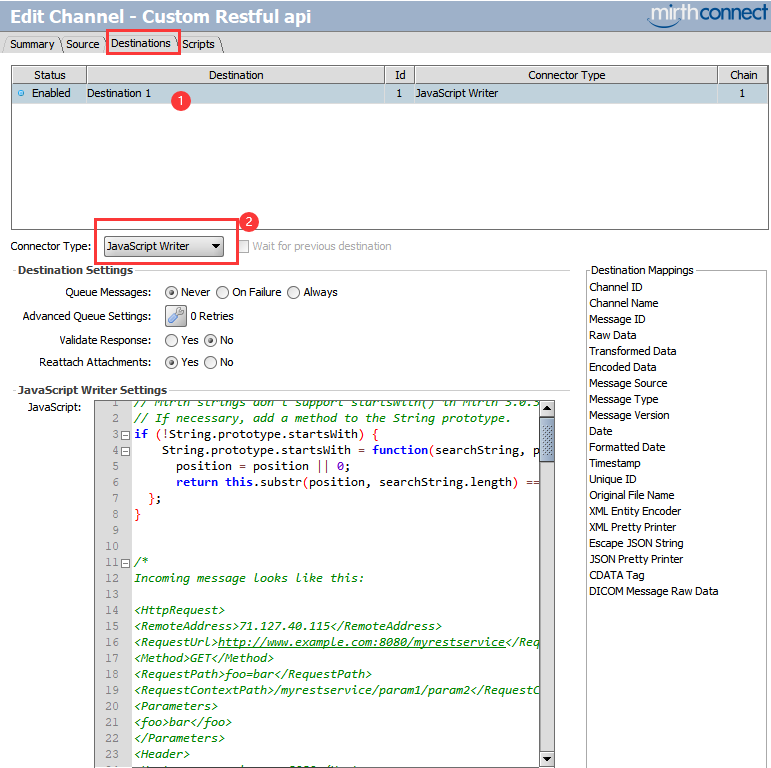
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 | // Mirth strings don't support startsWith() in Mirth 3// If necessary, add a method to the String prototype.if (!String.prototype.startsWith) { String.prototype.startsWith = function(searchString, position){ position = position || 0; return this.substr(position, searchString.length) === searchString; };} /*Incoming message looks like this: <HttpRequest><RemoteAddress>71.127.40.115</RemoteAddress><RequestUrl>http://www.example.com:8080/myrestservice</RequestUrl><Method>GET</Method><RequestPath>foo=bar</RequestPath><RequestContextPath>/myrestservice/param1/param2</RequestContextPath><Parameters><foo>bar</foo></Parameters><Header><Host>www.example.com:8080</Host><Accept-Encoding>identity</Accept-Encoding><User-Agent>Wget/1.18 (darwin15.5.0)</User-Agent><Connection>keep-alive</Connection><Accept>application/xml</Accept></Header><Content/></HttpRequest><HttpRequest><RemoteAddress>71.127.40.115</RemoteAddress><RequestUrl>http://www.example.com:8080/myrestservice</RequestUrl><Method>GET</Method><RequestPath>foo=bar</RequestPath><RequestContextPath>/myrestservice/param1/param2</RequestContextPath><Parameters><foo>bar</foo></Parameters><Header><Host>www.example.com:8080</Host><Accept-Encoding>identity</Accept-Encoding><User-Agent>Wget/1.18 (darwin15.5.0)</User-Agent><Connection>keep-alive</Connection><Accept>application/json</Accept></Header><Content/></HttpRequest>*/ // Just in case we fail, set a sane responseContentTypechannelMap.put('responseContentType', 'text/plain'); var msg = XML(connectorMessage.getRawData()); logger.info(msg);// Get the REST data from the "context path" which is actually// the "path info" of the request, so it will start with '/myrestservice'.var rest = msg['RequestContextPath'];logger.info(rest);var myServicePrefix = '/myrestservice';var minimumURLParameterCount = 4; // This is the minimum you require to do your workvar maximumExpectedURLParameterCount = 5; // however many you expect to getvar params = rest.substring(myServicePrefix).split('/', maximumExpectedURLParameterCount);if(params.length < minimumURLParameterCount) return Packages.com.mirth.connect.server.userutil.ResponseFactory.getErrorResponse('Too few parameters in request');var mrn = params[1]; // params[0] will be an empty stringlogger.info(mrn);// Now, determine the client's preference for what data type to return (XML vs. JSON).// We will default to XML.var clientWantsJSON = false;var responseContentType = 'text/xml'; // If we see any kind of JSON before any kind of XML, we'll use// JSON. Otherwise, we'll use XML.//// Technically, this is incorrect resolution of the "Accept" header,// but it's good enough for an example.var mimeTypes = msg['Header']['Accept'].split(/\s*,\s*/);for(var i=0; i<mimeTypes.length; ++i) { var mimeType = mimeTypes[i].toString(); if(mimeType.startsWith('application/json')) { clientWantsJSON = true; responseContentType = 'application/json'; break; } else if(mimeType.startsWith('application/xml')) { clientWantsJSON = false; responseContentType = 'application/xml'; break; } else if(mimeType.startsWith('text/xml')) { clientWantsJSON = false; responseContentType = 'text/xml'; break; }} var xml;var json; if(clientWantsJSON) json = { status : '' };else xml = new XML('<response></response>'); try { /* Here is where you do whatever your service needs to actually do. */ if(clientWantsJSON) { json.data = { foo: 1, bar: 'a string', baz: [ 'list', 'of', 'strings'] }; } else { xml['@foo'] = 1; xml['bar'] = 'a string'; xml['baz'][0] = 'list'; xml['baz'][1] = 'of'; xml['baz'][3] = 'strings'; } // Set the response code and content-type appropriately. // http://www.mirthproject.org/community/forums/showthread.php?t=12678 channelMap.put('responseStatusCode', 200); if(clientWantsJSON) { json.status = 'success'; var content = JSON.stringify(json); channelMap.put('responseContent', content); channelMap.put('responseContentType', responseContentType); return content; } else { channelMap.put('responseContentType', responseContentType); var content = xml.toString(); channelMap.put('responseContent', content); return content; }}catch (err){ channelMap.put('responseStatusCode', '500'); if(clientWantsJSON) { json.status = 'error'; if(err.javaException) { // If you want to unpack a Java exception, this is how you do it: json.errorType = String(err.javaException.getClass().getName()); json.errorMessage = String(err.javaException.getMessage()); } channelMap.put('responseContentType', responseContentType); // Return an error with our "error" JSON return Packages.com.mirth.connect.server.userutil.ResponseFactory.getErrorResponse(JSON.stringify(json)); } else { if(err.javaException) { xml['response']['error']['@type'] = String(err.javaException.getClass().getName()); xml['response']['error']['@message'] = String(err.javaException.getMessage()); } channelMap.put('responseContentType', responseContentType); // Return an error with our "error" XML return Packages.com.mirth.connect.server.userutil.ResponseFactory.getErrorResponse(xml.toString()); }} |
我们通过目的通道以上JS脚本,学习到以下特别重要的知识:
- 获取输入请求的原始消息并自动格式化为XML格式:
var xml = new XML(connectorMessage.getRawData()) - 设置响应类型,如:
channelMap.put('responseContentType', 'application/json') - 设置响应码,如:
channelMap.put('responseStatusCode', '200') - 设置响应内容并通过JS脚本返回XML实体或者Json实体的字符串格式值
- 异常处理通过JS脚本调用Mirth的API函数Packages.com.mirth.connect.server.userutil.ResponseFactory.getErrorResponse(string)返回字符串格式错误消息
4.部署信道并测试
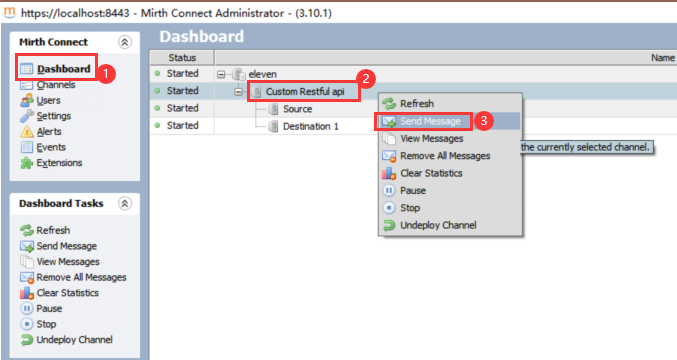
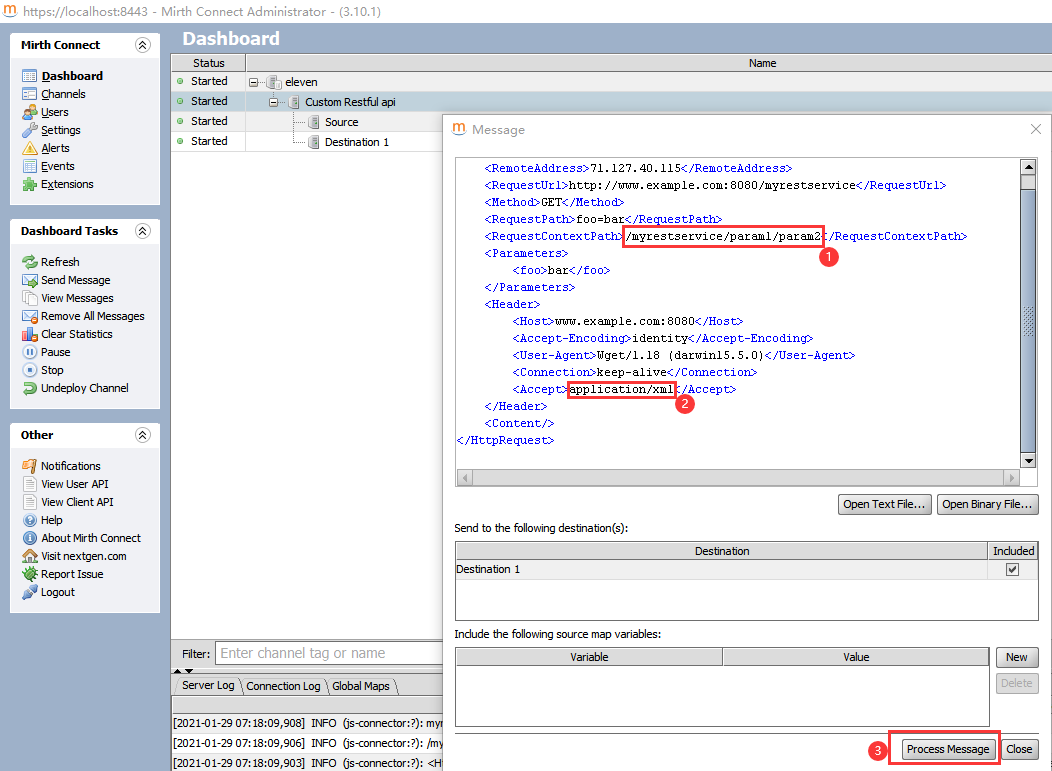
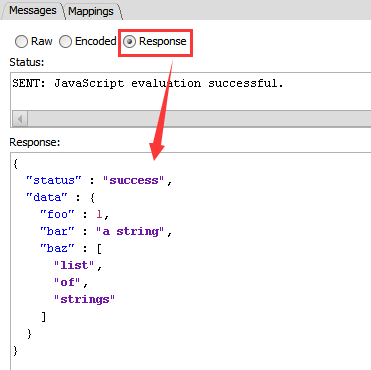
发送消息要区分application/json和application/xml,可以看到响应值格式会相应变化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | <HttpRequest> <RemoteAddress>71.127.40.115</RemoteAddress> <RequestUrl>http://www.example.com:8080/myrestservice</RequestUrl> <Method>GET</Method> <RequestPath>foo=bar</RequestPath> <RequestContextPath>/myrestservice/param1/param2</RequestContextPath> <Parameters> <foo>bar</foo> </Parameters> <Header> <Host>www.example.com:8080</Host> <Accept-Encoding>identity</Accept-Encoding> <User-Agent>Wget/1.18 (darwin15.5.0)</User-Agent> <Connection>keep-alive</Connection> <Accept>application/json</Accept> </Header> <Content/></HttpRequest> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | <HttpRequest> <RemoteAddress>71.127.40.115</RemoteAddress> <RequestUrl>http://www.example.com:8080/myrestservice</RequestUrl> <Method>GET</Method> <RequestPath>foo=bar</RequestPath> <RequestContextPath>/myrestservice/param1/param2</RequestContextPath> <Parameters> <foo>bar</foo> </Parameters> <Header> <Host>www.example.com:8080</Host> <Accept-Encoding>identity</Accept-Encoding> <User-Agent>Wget/1.18 (darwin15.5.0)</User-Agent> <Connection>keep-alive</Connection> <Accept>application/xml</Accept> </Header> <Content/></HttpRequest> |
潤沁網路大學






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具