水果管理系统
1. 概述
水果管理系统是最简单的一个javaWeb项目,主要对水果表进行增删改查。
- 页面上有添加水果按钮,点击后可以跳转到添加页面,添加水果(增)
- 有关键字查询,在页面上输入关键字,可以按照关键字检索,没有关键字就默认全部,页面展示了查询出来的数据(查)
- 数据名称有一个链接,点击后可以到编辑页面,修改这个数据(改)
- 数据旁边有一个删除按钮,点击后删除数据(删)
- 展示页面按5条一页的形式进行分页(分页)
2. 数据库设计
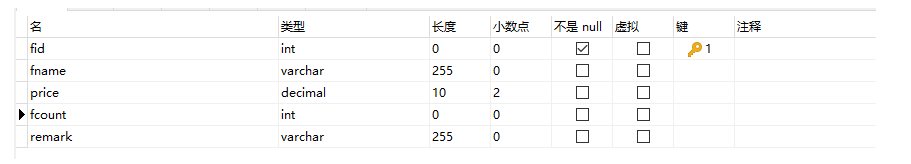
一共一张fruit表,有5个字段,fid为主键,设置自增。其他的分别是名称,价格,库存和备注。
3. JDBC与数据库连接
3.1 设置数据连接的properties文件
在src目录下,创建JDBC.properties。
user=root
password=123456
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/atguigu
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
3.2 导入JDBC需要的jar包
在工程下新建一个lib文件夹,将官网上下载下来的jar包导入,右键Add as Library。
3.3 编写JDBC工具类
package com.zhen.util;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
// 把数据库连接和资源释放都封装起来
public class JDBCUtils {
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
//1.加载配置文件
//用线程的上下文类加载器将文件变成一个输入流
InputStream is = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
//2.读取配置信息
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//3.加载驱动
Class clazz = Class.forName(driverClass);
//4.获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps) { //传入需要关闭的资源
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps, ResultSet rs) { //传入需要关闭的资源,构成重载
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
4. 编写pojo
这里只有一张表,所以只要一个Fruit类即可。
package com.zhen.pojo;
// ORM编程思想,数据库的一张表对应一个类,字段对应属性
public class Fruit {
private int fid;
private String fname;
private double price;
private int fcount;
private String remark;
public Fruit() {
}
public Fruit(int fid, String fname, double price, int fcount, String remark) {
this.fid = fid;
this.fname = fname;
this.price = price;
this.fcount = fcount;
this.remark = remark;
}
public int getFid() {
return fid;
}
public void setFid(int fid) {
this.fid = fid;
}
public String getFname() {
return fname;
}
public void setFname(String fname) {
this.fname = fname;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getFcount() {
return fcount;
}
public void setFcount(int fcount) {
this.fcount = fcount;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Fruit{" +
"fid=" + fid +
", fname='" + fname + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", fcount=" + fcount +
", remark='" + remark + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
5. 编写DAO层
5.1 编写BaseDao
BaseDao是通用的对数据库进行操作的代码。
package com.zhen.dao;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// 在之前的版本中,由于通过反射返回的对象,所以在查询函数中都要传入一个当前类的对象,但实际上我们可以通过将BaseDAO变成泛型类,在初始化时通过反射获取父类的泛型,就可以直接获取这个当前类的对象了,就不必再每次都传入当前类的对象了。
// 把BaseDao变成泛型类,在子类继承时确定要操作的类,省去了之前对类的指定
public abstract class BaseDao<T> {
// 通用的增删改操作
private Class<T> clazz = null;
// 写在代码块内,在实现类的子类创建时初始化clazz,获得子类的类型
{
Type genericSuperclass = this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass(); // 注意,这里的this是当前类,即初始化时的子类
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass; // 强转为ParameterizedType类
//获取泛型类型
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments(); // 调用这个方法获取泛型
clazz = (Class<T>) actualTypeArguments[0]; //获得第一个参数,即对应的泛型,获得对应的子类的类对象
}
public int update(Connection conn, String sql, Object ... args){
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); //这里直接使用setObject,注意下标从1开始
}
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps);
}
return 0;
}
// 获取一个对象
public T getBean(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) { // 这时候就不用传Class对象进来了,直接使用clazz即可
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
// 获取所有对象
public List<T> getForList(Connection conn, String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
while (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 7.关闭资源
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
//获取一个只有一个值的方法,专门用来执行像 select count(*)...这样的sql语句
public <E> E getValue(Connection conn,String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return (E) rs.getObject(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
}
5.2 编写FruitDao接口
FruitDao接口用于规范对fruit表进行的操作。
package com.zhen.dao;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.List;
public interface FruitDao {
// 添加一条水果数据
void addFruit(Connection conn, Fruit fruit);
// 获取所有的水果信息
List<Fruit> getFruitList(Connection conn);
// 获取指定关键字指定页码的水果信息
List<Fruit> getFruitList(Connection conn,String keyword,int pageNo);
// 根据id获取水果信息
Fruit getFruitById(Connection conn,int fid);
// 根据id修改水果信息
void updateFruit(Connection conn,Fruit fruit);
// 根据指定的id删除水果信息
void delFruit(Connection conn,Integer fid);
// 获取总记录条数
int getFruitCount(Connection conn, String keyword);
}
5.3 编写FruitDaoImpl
package com.zhen.dao;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitDaoImpl extends BaseDao<Fruit> implements FruitDao{
@Override
public void addFruit(Connection conn, Fruit fruit) {
String sql = "insert into fruit(fname,price,fcount,remark)values(?,?,?,?)";
update(conn,sql,fruit.getFname(),fruit.getPrice(),fruit.getFcount(),fruit.getRemark());
}
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList(Connection conn) {
String sql = "select * from fruit";
return getForList(conn, sql);
}
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList(Connection conn,String keyword,int pageNo) {
String sql = "select * from fruit where fname like ? or remark like ? limit ?,5";
return getForList(conn, sql,"%"+keyword+"%", "%"+keyword+"%",(pageNo-1)*5);
}
@Override
public Fruit getFruitById(Connection conn, int fid) {
String sql = "select * from fruit where fid = ?";
return getBean(conn, sql, fid);
}
@Override
public void updateFruit(Connection conn, Fruit fruit) {
String sql = "update fruit set fname = ?,price = ?,fcount = ?,remark = ? where fid = ?";
update(conn, sql, fruit.getFname(), fruit.getPrice(), fruit.getFcount(), fruit.getRemark(), fruit.getFid());
}
@Override
public void delFruit(Connection conn, Integer fid) {
String sql = "delete from fruit where fid = ?";
update(conn,sql,fid);
}
@Override
public int getFruitCount(Connection conn, String keyword) {
String sql = "select count(*) from fruit where fname like ? or remark like ?";
// count(*)查询出来的是Long类型,需要转化为int类型
return ((Long)getValue(conn,sql,"%"+keyword+"%","%"+keyword+"%")).intValue();
}
}
6. 编写Servlet层
注意导包:在tomcat的lib目录下找到servlet-api的jar包,复制到刚刚创建的lib目录下。前端需要themeleaf,也是一样的导包。
6.1 编写themeleaf的基类
package com.zhen.servlets;
import org.thymeleaf.TemplateEngine;
import org.thymeleaf.context.WebContext;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ViewBaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
private TemplateEngine templateEngine;
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 1.获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
// 2.创建Thymeleaf解析器对象
ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver(servletContext);
// 3.给解析器对象设置参数
// ①HTML是默认模式,明确设置是为了代码更容易理解
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
// ②设置前缀
String viewPrefix = servletContext.getInitParameter("view-prefix");
templateResolver.setPrefix(viewPrefix);
// ③设置后缀
String viewSuffix = servletContext.getInitParameter("view-suffix");
templateResolver.setSuffix(viewSuffix);
// ④设置缓存过期时间(毫秒)
templateResolver.setCacheTTLMs(60000L);
// ⑤设置是否缓存
templateResolver.setCacheable(true);
// ⑥设置服务器端编码方式
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 4.创建模板引擎对象
templateEngine = new TemplateEngine();
// 5.给模板引擎对象设置模板解析器
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver);
}
protected void processTemplate(String templateName, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
// 1.设置响应体内容类型和字符集
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
// 2.创建WebContext对象
WebContext webContext = new WebContext(req, resp, getServletContext());
// 3.处理模板数据
templateEngine.process(templateName, webContext, resp.getWriter());
}
}
6.2 编写对应主页面的servlet:IndexServlet
package com.zhen.servlets;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.List;
// Servlet从3.0版本后开始支持注解的注册,这样就省去了配置web.xml
@WebServlet("/index")
public class IndexServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
private FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
// doPost方法调用doGet,这样就通用了
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
doGet(req,resp);
}
// 处理查询与分页,根据关键词和页码查询数据后返回给前端
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String oper = req.getParameter("oper");
int pageNo = 1;
String keyword = null;
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 如果oper不为空且为search,说明这是前端通过查询按钮来的,我们需要把页数置为1,把keyword放到session中
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(oper) && "search".equals(oper)) {
pageNo = 1;
keyword = req.getParameter("keyword");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(keyword)) {
keyword = "";
}
session.setAttribute("keyword",keyword);
}else {
// 否则当前页码从参数中获得
String pageNoStr = req.getParameter("pageNo");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(pageNoStr)) {
pageNo = Integer.parseInt(pageNoStr);
}
Object keyword1 = session.getAttribute("keyword");
if (keyword1 == null) {
keyword = "";
}else {
keyword = (String) keyword1;
}
}
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获得对应的数量与总页数
int fruitCount = fruitDao.getFruitCount(conn,keyword);
int pageCount = (fruitCount+4)/5;
List<Fruit> fruitList = fruitDao.getFruitList(conn,keyword,pageNo);
// 信息存到session中
session.setAttribute("fruitList",fruitList);
session.setAttribute("pageNo",pageNo);
session.setAttribute("pageCount",pageCount);
// 这里的第一个参数是逻辑视图,这样信息就发往视图前缀+逻辑视图+视图后缀
// 这也是为什么需要这个基类的原因,这样我们才可以把信息通过thymeleaf传给指定的网页
super.processTemplate("index",req,resp);
}
}
6.3 编写对应添加水果页面的servlet:AddServlet
package com.zhen.servlets;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
@WebServlet("/add.do")
public class AddServlet extends ViewBaseServlet {
private FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取前端传来的信息
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String fname = req.getParameter("fname");
int price = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
int fcount = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fcount"));
String remark = req.getParameter("remark");
// 获取数据库连接,插入数据
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
fruitDao.addFruit(connection, new Fruit(0,fname,price,fcount,remark));
// 重定向到首页,这样就能刷新数据了
resp.sendRedirect("index");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
}
}
}
6.4 编写对应编辑的servlet:EditServlet与UpdateServlet
- 先根据id查询出对应的数据展示在编辑页面
package com.zhen.servlets;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
// 根据前端传来的id,跳转到指定的编辑页面,并且查询对应的内容发送到前端
@WebServlet("/edit.do")
public class EditServlet extends ViewBaseServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String fidStr = req.getParameter("fid");
FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(fidStr)) {
Fruit fruit = fruitDao.getFruitById(connection, Integer.parseInt(fidStr));
System.out.println(fruit);
req.setAttribute("fruit", fruit);
super.processTemplate("edit",req,resp);
}
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
}
}
- 编辑页面写好后再对数据库进行修改
package com.zhen.servlets;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
@WebServlet("/update.do")
public class UpdateServlet extends ViewBaseServlet{
private FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
int fid = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fid"));
String fname = req.getParameter("fname");
int price = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
int fcount = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fcount"));
String remark = req.getParameter("remark");
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fruitDao.updateFruit(connection,new Fruit(fid,fname,price,fcount,remark));
resp.sendRedirect("index");
}
}
7. 编写前端页面
7.1 编写前端展示页面:index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--加上标头,xmlns:th=...-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css">
<script src="js/index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div_container">
<div id="div_fruit_list">
<p>水果库存信息2</p>
<form th:action="@{index}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="oper" value="search">
请输入查询关键字:<input type="text" name="keyword" th:value="${session.keyword}"/>
<input type="submit" value="查询" class="btn">
</form>
<a th:href="@{add.html}">添加水果</a>
<table id="tbl_fruit">
<tr>
<th>名称1</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>库存</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
<!--使用分支判断-->
<tr th:if="${#lists.isEmpty(session.fruitList)}">
<td colspan="4">对不起,库存为空!</td>
</tr>
<tr th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(session.fruitList)}" th:each="fruit : ${session.fruitList}">
<!--链接的路径使用绝对路径,@{}从当前项目开始-->
<!--这里的friut.fid,是调用了fruit类的get方法-->
<td><a th:text="${fruit.fname}" th:href="@{edit.do(fid=${fruit.fid})}">苹果</a></td>
<td th:text="${fruit.price}">5</td>
<td th:text="${fruit.fcount}">20</td>
<td><div th:onclick="|delFruit(${fruit.fid})|">删除</div></td>
</tr>
</table>
<div>
<input type="button" value="首 页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(1)|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==1}"/>
<input type="button" value="上一页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageNo-1})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==1}"/>
<input type="button" value="下一页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageNo+1})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==session.pageCount}"/>
<input type="button" value="尾 页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageCount})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==session.pageCount}"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7.2 编写添加水果页面:add.html
页面这里写在web目录下。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--action中的add,到web.xml中匹配对应的servlet类.method这里用post,这样对应了doPost方法-->
<form action="add" method="post">
<!--这里表单必须有name属性,这样servlet才能获取到信息-->
名称:<input type="text" name="fname"/><br/>
价格:<input type="text" name="price"/><br/>
库存:<input type="text" name="fcount"/><br/>
备注:<input type="text" name="remark"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="添加">
</form>
</body>
</html>
7.3 编写编辑水果页面:edit.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--加上标头,xmlns:th=...-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="div_container">
<div id="div_fruit_list">
<p>编辑库存信息</p>
<form th:action="@{update.do}" method="post">
<table id="tbl_fruit" th:object="${fruit}">
<tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="fid" th:value="*{fid}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>名称:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="fname" th:value="*{fname}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>单价:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="price" th:value="*{price}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>库存:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="fcount" th:value="*{fcount}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>备注:</th>
<td><input type="text" name="remark" th:value="*{remark}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th colspan="2">
<input type="submit" value="修改"/>
</th>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
8. 根据需要编写css与js
css与js在web下都建立一个文件夹。
index.css
body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div{
position: relative;
float: left;
}
#div_container{
width: 80%;
height: 100%;
border: 1px solid blue;
margin-left: 10%;
float: left;
}
#tbl_fruit {
width: 100%;
}
#tbl_fruit th,tr {
width: 20%;
}
index.js
function delFruit(fid) {
if (confirm("是否确认删除")) {
window.location.href='del.do?fid='+fid;
}
}
function page(pageNo) {
window.location.href="index?pageNo="+pageNo;
}
9. 配置web.xml
配置好web.xml,让前端的请求可以发送给对应的servlet处理。
如果servlet加了注解,就不用配置web.xml了。
配置themeleaf的上下文。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>view-prefix</param-name>
<param-value>/</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>view-suffix</param-name>
<param-value>.html</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
10. 可能出现的问题
10.1 包找不到
这是由于后面加入的包并没有加到artifact中,点击File-Project Structure-Problems,添加包到artifact中即可。
10.2 复制Module
直接复制这个Module,然后修改名称及对应的.iml文件,在File-Project Structure-Module中导入Module,选择对应的.iml文件。
然后在Artifact中添加Web Application:Exploded中选择我们的Module导入。
11. 系统的优化
11.1 整合Servlet
这个系统,对水果表的增删改查,写了好几个servlet,这样显得很臃肿。我们可以将其整合到一个Servlet中,让这些servlet都变成函数。前端通过传来一个operate参数,来决定调用哪个函数。
这里规定格式,要求传来的operate参数与函数名是相同的,这样我们就可以通过反射来直接调用,而不必写那些if判断了。
- 将所有关于水果数据库的请求都整合到FruitServlet中,由fruit.do统一访问。注意这里的重定向,就要是fruit.do了,之前的Servlet路径已经都删掉了。
package com.zhen.servlets;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet("/fruit.do")
public class FruitServlet extends ViewBaseServlet{
private FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
// 编写这个service函数,前端任何关于fruit表的操作,都访问fruit.do,后面跟上对应的operate参数即可
// 根据operate参数来决定调用哪个方法
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String operate = req.getParameter("operate");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(operate)) {
operate = "index";
}
// 获得当前类的所有方法
Method[] Methods = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m: Methods) {
// 获得当前方法名
String name = m.getName();
// 如果方法名与operate名称相同,则调用
if (operate.equals(name)) {
try {
m.invoke(this,req,resp);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 之前的indexServlet变成了对应的index方法
private void index(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String oper = req.getParameter("oper");
int pageNo = 1;
String keyword = null;
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(oper) && "search".equals(oper)) {
pageNo = 1;
keyword = req.getParameter("keyword");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(keyword)) {
keyword = "";
}
session.setAttribute("keyword",keyword);
}else {
String pageNoStr = req.getParameter("pageNo");
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(pageNoStr)) {
pageNo = Integer.parseInt(pageNoStr);
}
Object keyword1 = session.getAttribute("keyword");
if (keyword1 == null) {
keyword = "";
}else {
keyword = (String) keyword1;
}
}
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int fruitCount = fruitDao.getFruitCount(conn,keyword);
int pageCount = (fruitCount+4)/5;
List<Fruit> fruitList = fruitDao.getFruitList(conn,keyword,pageNo);
session.setAttribute("fruitList",fruitList);
session.setAttribute("pageNo",pageNo);
session.setAttribute("pageCount",pageCount);
super.processTemplate("index",req,resp);
}
private void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String fname = req.getParameter("fname");
int price = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
int fcount = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fcount"));
String remark = req.getParameter("remark");
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
fruitDao.addFruit(connection, new Fruit(0,fname,price,fcount,remark));
resp.sendRedirect("fruit.do");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
}
}
private void del(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
int fid = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fid"));
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
fruitDao.delFruit(conn,fid);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,null);
resp.sendRedirect("fruit.do");
}
private void edit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String fidStr = req.getParameter("fid");
FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(fidStr)) {
Fruit fruit = fruitDao.getFruitById(connection, Integer.parseInt(fidStr));
System.out.println(fruit);
req.setAttribute("fruit", fruit);
super.processTemplate("edit",req,resp);
}
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
}
private void update(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
int fid = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fid"));
String fname = req.getParameter("fname");
int price = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("price"));
int fcount = Integer.parseInt(req.getParameter("fcount"));
String remark = req.getParameter("remark");
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fruitDao.updateFruit(connection,new Fruit(fid,fname,price,fcount,remark));
resp.sendRedirect("fruit.do");
}
}
- 前端页面的请求也要修改一下,统一访问fruit.do,再额外加上一个operate参数。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!--加上标头,xmlns:th=...-->
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/index.css">
<script src="js/index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div_container">
<div id="div_fruit_list">
<p>水果库存信息2</p>
<form th:action="@{fruit.do}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="oper" value="search">
请输入查询关键字:<input type="text" name="keyword" th:value="${session.keyword}"/>
<input type="submit" value="查询" class="btn">
</form>
<a th:href="@{add.html}">添加水果</a>
<table id="tbl_fruit">
<tr>
<th>名称1</th>
<th>单价</th>
<th>库存</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
<!--使用分支判断-->
<tr th:if="${#lists.isEmpty(session.fruitList)}">
<td colspan="4">对不起,库存为空!</td>
</tr>
<tr th:unless="${#lists.isEmpty(session.fruitList)}" th:each="fruit : ${session.fruitList}">
<!--链接的路径使用绝对路径,@{}从当前项目开始-->
<!--这里的friut.fid,是调用了fruit类的get方法-->
<td><a th:text="${fruit.fname}" th:href="@{fruit.do(fid=${fruit.fid},operate='edit')}">苹果</a></td>
<td th:text="${fruit.price}">5</td>
<td th:text="${fruit.fcount}">20</td>
<td><div th:onclick="|delFruit(${fruit.fid})|">删除</div></td>
</tr>
</table>
<div>
<input type="button" value="首 页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(1)|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==1}"/>
<input type="button" value="上一页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageNo-1})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==1}"/>
<input type="button" value="下一页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageNo+1})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==session.pageCount}"/>
<input type="button" value="尾 页" class="btn" th:onclick="|page(${session.pageCount})|" th:disabled="${session.pageNo==session.pageCount}"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
11.2 新增dispatcherServlet
上一个优化把关于水果库的操作的所有Serlvet整合到一起,但是随着业务的扩展,会有对用户表的操作,对账户表的操作等等。这时候Servlet中反射的那段代码也是冗余的,所以我们可以新增一层dispatcherServlet,让dispatcherServlet处理反射这段代码,减少了冗余。
随着dispatcherServlet的引入,其实请求的参数获取和页面跳转,每个函数都是类似的,也可以提取。这样 ,我们就把原来的FruitServlet类变成了一个普通类,不需要再是一个Servlet了(因为不需要页面跳转了,也不需要作为url资源来访问,这样就可以命名为Controller了)。
注意:在优化参数提取时,需要在idea当中设置,使得反射可以获得参数的名称(jdk8新特性)。在settings-Build-Java Compiler中的Additional command中加入-parameters。
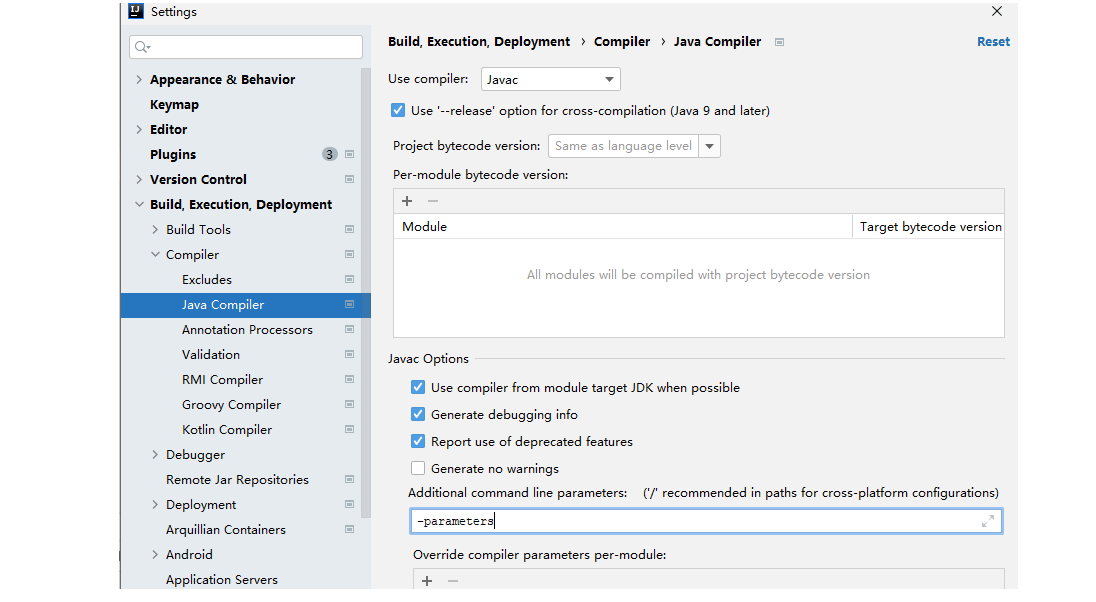
- 修改后的FruitController
package com.zhen.Controller;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.List;
// FruitController不再是一个Servlet了,它只需要调用Dao的方法,处理业务逻辑即可
// 视图跳转与参数获取及根据参数调用对应的方法,都交给DispatcherServlet了
public class FruitController{
private FruitDaoImpl fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
// 把页面跳转提取后,返回一个字符串给DispatcherServlet即可。DispatcherServlet根据返回的字符串,进行重定向或者转发
// 把参数获取提取,每个方法里需要的参数通过函数参数获得,这里要求参数名称必须与前端放进去的参数名称相同
private String index(String oper, String keyword, Integer pageNo, HttpServletRequest req) throws ServletException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
if (pageNo == null) pageNo = 1;
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(oper) && "search".equals(oper)) {
pageNo = 1;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(keyword)) {
keyword = "";
}
session.setAttribute("keyword",keyword);
}else {
if (keyword == null) {
keyword = "";
}
}
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int fruitCount = fruitDao.getFruitCount(conn,keyword);
int pageCount = (fruitCount+4)/5;
List<Fruit> fruitList = fruitDao.getFruitList(conn,keyword,pageNo);
session.setAttribute("fruitList",fruitList);
session.setAttribute("pageNo",pageNo);
session.setAttribute("pageCount",pageCount);
return "index"; //请求转发,返回页面名称即可
}
private String add(String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
fruitDao.addFruit(connection, new Fruit(0,fname,price,fcount,remark));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
}
return "redirect:fruit.do"; // 资源重定向,返回redirect开头+请求名
}
private String del(Integer fid) throws ServletException {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fruitDao.delFruit(conn,fid);
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,null);
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
private String edit(Integer fid, HttpServletRequest req) throws ServletException {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (fid != null) {
Fruit fruit = fruitDao.getFruitById(connection, fid);
req.setAttribute("fruit", fruit);
return "edit";
}
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection,null);
return "error";
}
private String update(Integer fid, String fname, Integer price, Integer fcount, String remark) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fruitDao.updateFruit(connection,new Fruit(fid,fname,price,fcount,remark));
return "redirect:fruit.do";
}
}
- dispatcherServlet
package com.zhen.Controller;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
// 这里是*.do,表示处理所有.do结尾的请求
/* DispatcherServlet的功能
1. 根据url定位到处理这个请求的Controller组件
(1)从servletPath提取id /fruit.do到fruit
(2)根据fruit这个id找到相应的类对象,表现在application.xml中
2. 调用Controller组件的方法
(1)根据operate的值使用反射获取要执行的方法
(2)获取方法需要的参数,参数的值去req中拿
(3)调用函数,获得返回值
3. 视图跳转,根据返回值跳转页面
* */
@WebServlet("*.do")
public class DispatcherServlet extends ViewBaseServlet{
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
// DispatcherServlet是一个Servlet,再第一次访问时会进行实例化,所以在构造方法中写一些初始化的操作
// 通过解析application.xml,让id与相应的类对应起来,放在map中
public DispatcherServlet() throws ParserConfigurationException, IOException, SAXException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// 获得application.xml的文件流
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("application.xml");
// 创建DocumentBuilderFactory
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 用DocumentBuilderFactory创建DocumentBuilder
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
// 这里的Document是org.w3c.dom.Document,用DocumentBuilder创建Document对象
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
//获取所有bean节点
NodeList beanNodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0; i < beanNodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
// 如果这个节点是元素节点
if (beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
// 获得id的值与全类名
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
String className = beanElement.getAttribute("class");
// 通过全类名反射进行初始化获得对应的实例
Object beanObj = Class.forName(className).newInstance();
// 放到map中
beanMap.put(beanId,beanObj);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 通过解析前端页面的请求,对应到相应的类
// 获取/fruit.do -> fruit 再对应到 FruitController
String servletPath = req.getServletPath(); // 获取访问的路径,url为localhost:8080/fruit/fruit.do,获取到/fruit.do
servletPath = servletPath.substring(1);
int lastIndex = servletPath.lastIndexOf(".do");
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0,lastIndex); //将/fruit.do变成fruit
// 通过fruit获得FruitController类的对象
Object controllerBeanObj = beanMap.get(servletPath);
// 通过反射获取要调用的函数
String operate = req.getParameter("operate");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(operate)) {
operate = "index";
}
Method[] Methods = controllerBeanObj.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m: Methods) {
String name = m.getName();
if (operate.equals(name)) {
try {
// 获取对应函数需要的参数列表
Parameter[] parameters = m.getParameters();
Object[] parameterValues = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
Parameter parameter = parameters[i];
// 获得参数名
String parameterName = parameter.getName();
// 去req中获取,也有可能是需要req或是resp,特判一下
if ("req".equals(parameterName)) {
parameterValues[i] = req;
}else if ("resp".equals(parameterName)) {
parameterValues[i] = resp;
}else {
String parameterValue = req.getParameter(parameterName);
String typeName = parameter.getType().getName();
Object parameterObj = parameterValue;
if (parameterObj != null) {
// req中获取的值是String类型,根据参数的类型,不同的需要强转
if ("java.lang.Integer".equals(typeName)) {
parameterObj = Integer.parseInt(parameterValue);
}
}
parameterValues[i] = parameterObj;
}
}
// 调用Controller组件方法
m.setAccessible(true); // 让反射能调用私有方法
// 调用函数获取返回值
Object returnObj = m.invoke(controllerBeanObj,parameterValues);
String methodStr = (String) returnObj;
// 视图处理,根据返回的字符串,决定重定向或转发
if (methodStr.startsWith("redirect:")) {
String redirectStr = methodStr.substring("redirect:".length());
resp.sendRedirect(redirectStr);
}else {
super.processTemplate(methodStr,req,resp);
}
return;
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
11.3 事务处理
对于sql语句的进行,我们必须考虑到事务的处理。一次服务响应做为一次事务,具有原子性。所以处理事务的逻辑使用过滤器则再好不过了。
11.3.1 使用TreadLocal优化数据库连接的参数传递
为了事务的处理,在调用方法时都必须传一个Connection参数。
但随着层数的增多,每次传递一个Connection方法就显得很繁琐。我们可以使用TreadLocal来优化这一过程,把创建的数据库对象存放在TreadLocal中,在BaseDao要执行sql语句时,再通过TreadLocal来获取即可。
这样我们的数据库连接就不必每次都在调用方法时传入,从而节约了代码量。
引入TreadLocal修改JDBCUtils
package com.zhen.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
// 把数据库连接和资源释放都封装起来
public class JDBCUtils {
// 使用threadLocal优化连接的创建,这样整个线程都能共享一个数据库连接
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 创建数据库连接
private static Connection createConn() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1.加载配置文件
//用线程的上下文类加载器将文件变成一个输入流
InputStream is = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties pros = new Properties();
pros.load(is);
//2.读取配置信息
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
String url = pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//3.加载驱动
Class clazz = Class.forName(driverClass);
//4.获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
// 获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn = threadLocal.get(); // 从threadLocal中获取数据库连接
if (conn == null) { // 如果为空则创建一个
try {
conn = createConn();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
threadLocal.set(conn); // 创建好了就放进去,后面使用时可以直接获取
}
return conn;
}
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps) { //传入需要关闭的资源
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
threadLocal.set(null); //关闭资源时threadLocal也要删除掉存放的
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
public static void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps, ResultSet rs) { //传入需要关闭的资源,构成重载
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
threadLocal.set(null);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
11.3.2 使用过滤器来处理事务
过滤器处理事务,就是正常捕获异常即可,捕获到了就回滚,没有异常则提交。
package com.zhen.Filter;
import com.zhen.Transaction.TransactionManager;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OpenSessionViewFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
// 处理事务,发生异常则回滚,正常运行则提交
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
TransactionManager.beginTrans();
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
TransactionManager.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
TransactionManager.rollback();
} catch (Exception exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
编写一个TransactionManager专门用来处理事务逻辑
package com.zhen.Transaction;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
public class TransactionManager {
// 开始事务,设置自动提交为false
public static void beginTrans() throws Exception {
JDBCUtils.getConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}
// commit提交
public static void commit() throws Exception {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
conn.commit();
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,null); // 提交后这个连接就可以关闭了
}
// rollback回滚
public static void rollback() throws Exception {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
conn.rollback();
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,null);
}
}
11.3.3 Dao抛出专属异常
注意过滤器的事务处理在捕获异常,但是DAO层也捕获了异常。这就会导致,即使出现了异常,过滤器也无法获取到这个异常,所以BaseDao应该在处理异常的过程中,自己再抛出一个自定义的异常(DaoException),这样过滤器才可以捕获到异常。
DispatcherServlet中也有捕获异常,也需要抛出自定义的异常。
- 自定义异常类
package com.zhen.exception;
public class BaseDaoException extends RuntimeException{
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897193246939L;
public BaseDaoException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
package com.zhen.exception;
public class DispatcherServletException extends RuntimeException{
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897193246349L;
public DispatcherServletException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
- 修改BaseBao,把异常捕获后抛出自定义的异常
package com.zhen.dao;
import com.zhen.exception.BaseDaoException;
import com.zhen.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class BaseDao<T> {
private Class<T> clazz = null;
{
Type genericSuperclass = this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass();
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();
clazz = (Class<T>) actualTypeArguments[0];
}
public int update(String sql, Object ... args){
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new BaseDaoException("BaseDao update出错了"); // 捕获到异常后,再向上抛一个
}finally{
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps);
}
}
public T getBean(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
return t;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new BaseDaoException("BaseDao select出错了");
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
public List<T> getForList(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
while (rs.next()) {
T t = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
Object columnVal = rs.getObject(i + 1);
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(t, columnVal);
}
list.add(t);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new BaseDaoException("BaseDao select出错了");
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
}
public <E> E getValue(String sql, Object... args) {
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return (E) rs.getObject(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new BaseDaoException("BaseDao getValue出错了");
} finally {
JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps, rs);
}
return null;
}
}
11.4 Service层的加入
根据MVC架构,我们的项目实际上是没有Service层,所以需要添加一个Service层。Service层专门用于处理业务。
11.4.1 编写FruitService接口
package com.zhen.Service;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import java.util.List;
public interface FruitService {
// 往数据库中添加一条水果数据
void addFruit(Fruit fruit);
// 获取所有的水果信息
List<Fruit> getFruitList();
// 获取指定页面的水果信息
List<Fruit> getFruitList(String keyword,int pageNo);
// 根据id获取水果信息
Fruit getFruitById(int fid);
// 根据id修改水果信息
void updateFruit(Fruit fruit);
// 根据指定的id删除水果信息
void delFruit(Integer fid);
// 获取总页数
int getPageCount(String keyword);
}
11.4.2 编写FruitServiceImpl类
由于业务比较简单,所以几乎都是直接调用FruitDao的方法。
相应的Controller层调用的就是FruitServiceImpl类了,而不用管Dao层了。
package com.zhen.Service;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDao;
import com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl;
import com.zhen.pojo.Fruit;
import java.util.List;
public class FruitServiceImpl implements FruitService{
private FruitDao fruitDao = new FruitDaoImpl();
@Override
public void addFruit(Fruit fruit) {
fruitDao.addFruit(fruit);
}
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList() {
return fruitDao.getFruitList();
}
@Override
public List<Fruit> getFruitList(String keyword, int pageNo) {
return fruitDao.getFruitList(keyword, pageNo);
}
@Override
public Fruit getFruitById(int fid) {
return fruitDao.getFruitById(fid);
}
@Override
public void updateFruit(Fruit fruit) {
fruitDao.updateFruit(fruit);
}
@Override
public void delFruit(Integer fid) {
fruitDao.delFruit(fid);
}
@Override
public int getPageCount(String keyword) {
int fruitCount = fruitDao.getFruitCount(keyword);
int pageCount = (fruitCount+4)/5;
return pageCount;
}
}
11.5 IOC的引入
根据上面的优化,我们发现,Controller层需要使用ServiceImpl,Service层需要使用DaoImpl。层与层的依赖关系大(耦合),不易于后期的扩展与改动(比如当Controller依赖的实现类变化时,需要去找到Controller的具体代码进行修改)。
解耦合的方法就是”依赖于抽象,而不是依赖于具体”。即采用xml文件的方式,配置好类与类之间的依赖关系。引入IOC(控制反转)与DI(依赖注入),让这些有依赖关系的类交给编写的另外程序实例化,并给关系赋值。
这样操作后,后面依赖的改动,就只需要修改配置文件即可,不再需要改具体的代码,即实现了依赖于抽象。
- 首先把存在具体依赖的部分都改为null
// FruitServiceImpl中的依赖
public class FruitServiceImpl implements FruitService{
private FruitDao fruitDao = null;
}
// FruitController中的依赖
public class FruitController{
private FruitService fruitService = null;
}
- 编写application.xml文件,这个配置文件描述了我需要的类,以及这些类的依赖关系
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id ="fruitDao" class="com.zhen.dao.FruitDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="fruitService" class="com.zhen.Service.FruitServiceImpl">
<!--property标签用来表示属性;name表示当前这个类需要的属性名,ref表示引用其他bean标签的id值所对应的类-->
<property name="fruitDao" ref="fruitDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="fruit" class="com.zhen.Controller.FruitController">
<property name="fruitService" ref="fruitService"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 编写BeanFactory接口,就是这个接口来控制类的实例化。
package com.zhen.ioc;
public interface BeanFactory {
public Object getBean(String id);
}
- 编写BeanFactory接口的实现类,根据我们配置的xml,实例化需要的类,以及设置好他们之间的依赖关系。
package com.zhen.ioc;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassPathXmlApplicationContext implements BeanFactory{
private Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
try{
// 读取解析xml文件
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("application.xml");
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 获得所有bean节点,IOC控制反转的代码
NodeList beanNodeList = document.getElementsByTagName("bean");
for (int i = 0; i < beanNodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
// 如果这个节点是元素节点
if (beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
// 获得id的值与全类名
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
String className = beanElement.getAttribute("class");
// 通过全类名反射进行初始化获得对应的实例
Object beanObj = Class.forName(className).newInstance();
// 放到map中
beanMap.put(beanId, beanObj);
}
}
// 注入bean之间的依赖关系,DI依赖注入的代码
for (int i = 0; i < beanNodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node beanNode = beanNodeList.item(i);
if (beanNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element beanElement = (Element) beanNode;
String beanId = beanElement.getAttribute("id");
NodeList childNodes = beanElement.getChildNodes();
for (int j = 0; j < childNodes.getLength(); j++) {
Node beanChildNode = childNodes.item(j);
// 找到property标签
if (beanChildNode.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE && "property".equals(beanChildNode.getNodeName())) {
Element propertyElement = (Element) beanChildNode;
// 获得property标签的两个属性值
String propertyName = propertyElement.getAttribute("name");
String propertyRef = propertyElement.getAttribute("ref");
// 将ref对应的类设置到当前对应实例的propertyName属性上去
Object refObj = beanMap.get(propertyRef);
Object beanObj = beanMap.get(beanId);
Field propertyField = beanObj.getClass().getDeclaredField(propertyName);
propertyField.setAccessible(true);
propertyField.set(beanObj,refObj);
}
}
}
}
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String id) {
return beanMap.get(id);
}
}
- 所以现在DispatcherServlet就不需要去实例化bean了,只要获取这个BeanFactory对象即可
package com.zhen.Controller;
import com.zhen.exception.DispatcherServletException;
import com.zhen.ioc.BeanFactory;
import com.zhen.ioc.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.zhen.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
@WebServlet("*.do")
public class DispatcherServlet extends ViewBaseServlet{
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
public DispatcherServlet() {
beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String servletPath = req.getServletPath();
servletPath = servletPath.substring(1);
int lastIndex = servletPath.lastIndexOf(".do");
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0,lastIndex);
// 通过fruit获得FruitController类的对象
Object controllerBeanObj = beanFactory.getBean(servletPath);
// 通过反射获取要调用的函数
String operate = req.getParameter("operate");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(operate)) {
operate = "index";
}
Method[] Methods = controllerBeanObj.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m: Methods) {
String name = m.getName();
if (operate.equals(name)) {
try {
// 获取对应函数需要的参数列表
Parameter[] parameters = m.getParameters();
Object[] parameterValues = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
Parameter parameter = parameters[i];
// 获得参数名
String parameterName = parameter.getName();
// 去req中获取,也有可能是需要req或是resp,特判一下
if ("req".equals(parameterName)) {
parameterValues[i] = req;
}else if ("resp".equals(parameterName)) {
parameterValues[i] = resp;
}else {
String parameterValue = req.getParameter(parameterName);
String typeName = parameter.getType().getName();
Object parameterObj = parameterValue;
if (parameterObj != null) {
// req中获取的值是String类型,根据参数的类型,不同的需要强转
if ("java.lang.Integer".equals(typeName)) {
parameterObj = Integer.parseInt(parameterValue);
}
}
parameterValues[i] = parameterObj;
}
}
// 调用Controller组件方法
m.setAccessible(true); // 让反射能调用私有方法
// 调用函数获取返回值
Object returnObj = m.invoke(controllerBeanObj,parameterValues);
String methodStr = (String) returnObj;
// 视图处理,根据返回的字符串,决定重定向或转发
if (methodStr.startsWith("redirect:")) {
String redirectStr = methodStr.substring("redirect:".length());
resp.sendRedirect(redirectStr);
}else {
super.processTemplate(methodStr,req,resp);
}
return;
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new DispatcherServletException("DispatcherServlet 出错了");
}
}
}
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!