题解 P5597【【XR-4】复读】
一道好题!挺对我脑回路的,于是秒掉了,来写个题解。
下文称执行一遍指令的过程为一个周期。例如指令是 LRU,那么 LRULRULRULRU 共执行了四个周期。
看到平方的数据范围,不难想到枚举第一个周期的终点。作为一台优秀的复读机,我们知道每个周期在树上发生的相对位移是相同的。
例如,如下的一棵树,如果第一周期从 移动到 ,那么第二周期一定从 移动到 :
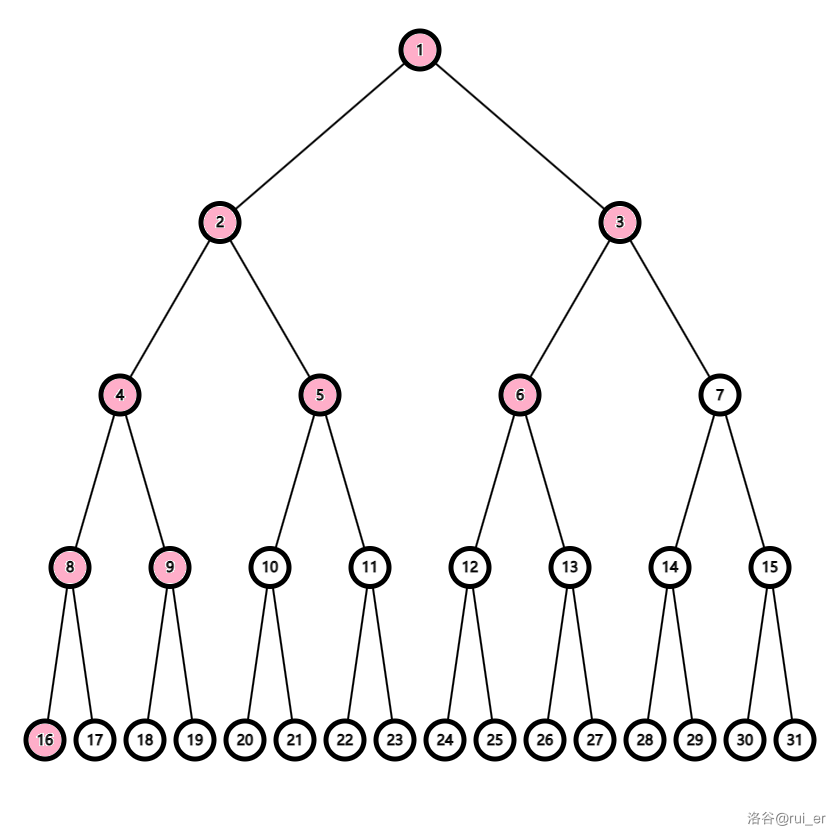
同时,因为在根节点的 U 操作非法,假设一个周期从 开始,那么途中一定一直在 的子树内,不可能到 上面。
依然假设第一周期从 移动到 ,那么根据这一点,我们第一周期中必须把所有在 子树内但不在 子树内的节点访问一遍,也就是 ,并最终停在 。同理,第二周期必须把 访问一遍并停在 ,第三周期必须把 访问一遍。
我们把 三棵子树取一个并(如下图所示),其中每个周期要从绿色的点出发,经过所有粉色的点,最终到达蓝色的点。
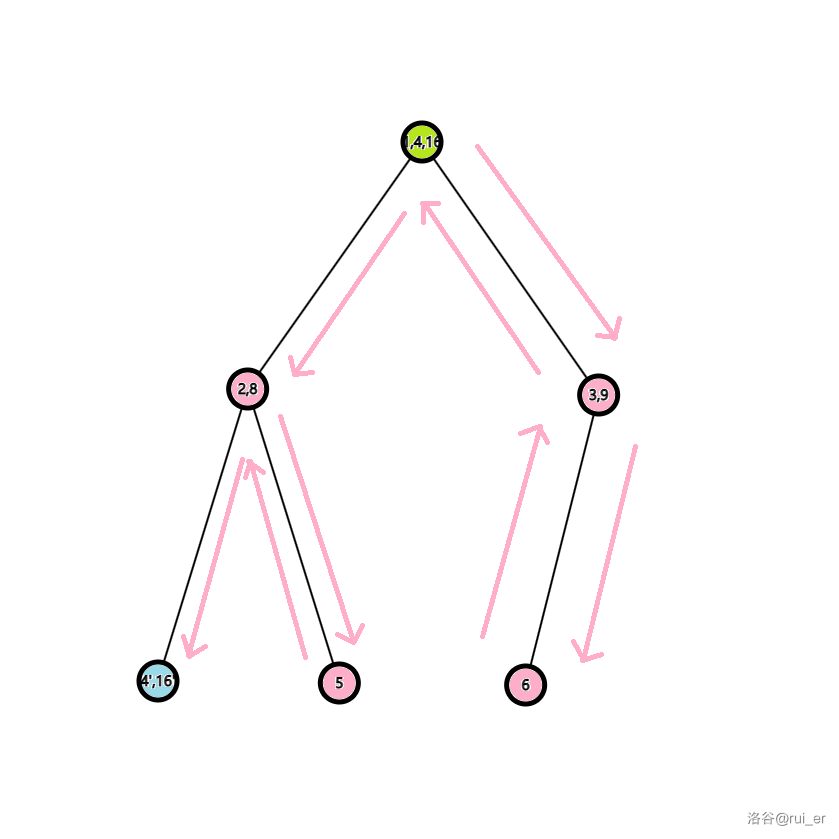
显而易见地,最少需要的指令数为 ,其中 为这棵树中的点数, 是起点和终点之间的边数。上图给出了一种构造,即 RLUULRUL。
枚举第一个周期的终点,然后求出所有这样的子树的并,最后根据上面公式统计最优解即可。
时间复杂度 。
//By: OIer rui_er
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(x,y,z) for(int x=(y);x<=(z);x++)
#define per(x,y,z) for(int x=(y);x>=(z);x--)
#define debug(format...) fprintf(stderr, format)
#define fileIO(s) do{freopen(s".in","r",stdin);freopen(s".out","w",stdout);}while(false)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
mt19937 rnd(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count());
int randint(int L, int R) {
uniform_int_distribution<int> dist(L, R);
return dist(rnd);
}
template<typename T> void chkmin(T& x, T y) {if(x > y) x = y;}
template<typename T> void chkmax(T& x, T y) {if(x < y) x = y;}
const int N = 2048;
struct BinaryTree {
int lc[N], rc[N], sz, rt;
BinaryTree() {
memset(lc, 0, sizeof(lc));
memset(rc, 0, sizeof(rc));
sz = rt = 0;
}
int read() {
int c = getchar() ^ 48, u = ++sz;
if(c & 1) lc[u] = read();
if(c & 2) rc[u] = read();
return u;
}
}T, TU; // original tree; the union of trees
void dfs_union(int u, int v, int root, int key) { // calculate the union
if(u == root || v == key) {
if(!key) key = v;
v = TU.rt;
}
if(T.lc[u]) {
if(!TU.lc[v]) TU.lc[v] = ++TU.sz;
dfs_union(T.lc[u], TU.lc[v], root, key);
}
if(T.rc[u]) {
if(!TU.rc[v]) TU.rc[v] = ++TU.sz;
dfs_union(T.rc[u], TU.rc[v], root, key);
}
}
int dfs_enum(int u, int d) { // enumerate the destination of round #1 moving
TU = BinaryTree();
TU.sz = TU.rt = 1;
dfs_union(T.rt, TU.rt, u, 0);
int ans = (TU.sz - 1) * 2 - d;
if(T.lc[u]) chkmin(ans, dfs_enum(T.lc[u], d+1));
if(T.rc[u]) chkmin(ans, dfs_enum(T.rc[u], d+1));
return ans;
}
int main() {
T.rt = T.read();
printf("%d\n", dfs_enum(T.rt, 0));
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!