异常
1.传统的异常处理方式
通过在原代码处设置各种条件判断校验
public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); int num1 = 0; if(sc.hasNextInt()) { num1 = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); int num2 = 0; if(sc.hasNextInt()) { num2 = sc.nextInt(); if(0 == num2) { System.out.println("除数不能为0!"); }else { int r = num1 / num2; System.out.println("num1/num2 = "+r); } }else { System.out.println("第二个数输入不是数字"); } }else { System.out.println("第一个数输入不是数字!"); } } }
传统方式具有的缺点:
【1】通过设置判断条件,影响执行的效率
【2】判断逻辑与业务逻辑混在一起,可维护性较差
2.异常
因为传统的异常处理不适应复杂的开发,所以系统设置了专门的一套异常处理机制。
下面我们认识一下什么是异常:
异常是指在程序执行过程中出现不正常的情况,中断了程序的运行。
java中的异常处理机制:专门制定一套为程序出现异常而处理,从而使程序不中断继续运行的机制。
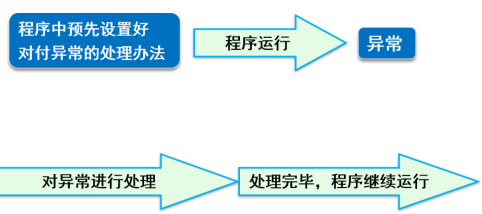
3.异常处理
涉及异常处理的关键字有try ... catch 、try .. . catch ......finally、throw、throws。
3.1try .. catch
try .. catch 语句:把有可能产生异常的语句放到try里面,而catch代码块负责捕获异常,并对异常进行处理。
【1】程序正常执行,没出现异常。

【2】出现异常,异常处理,然后正常结束。

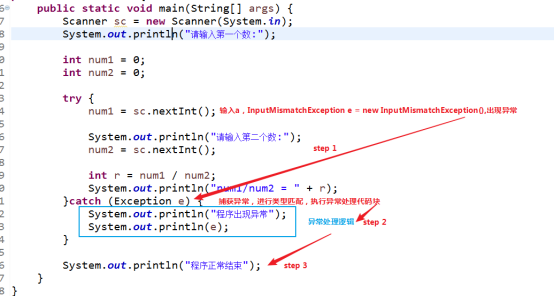
异常是一种特殊的对象,Exception是所有异常的父类或者间接父类。
异常的常见方法有:
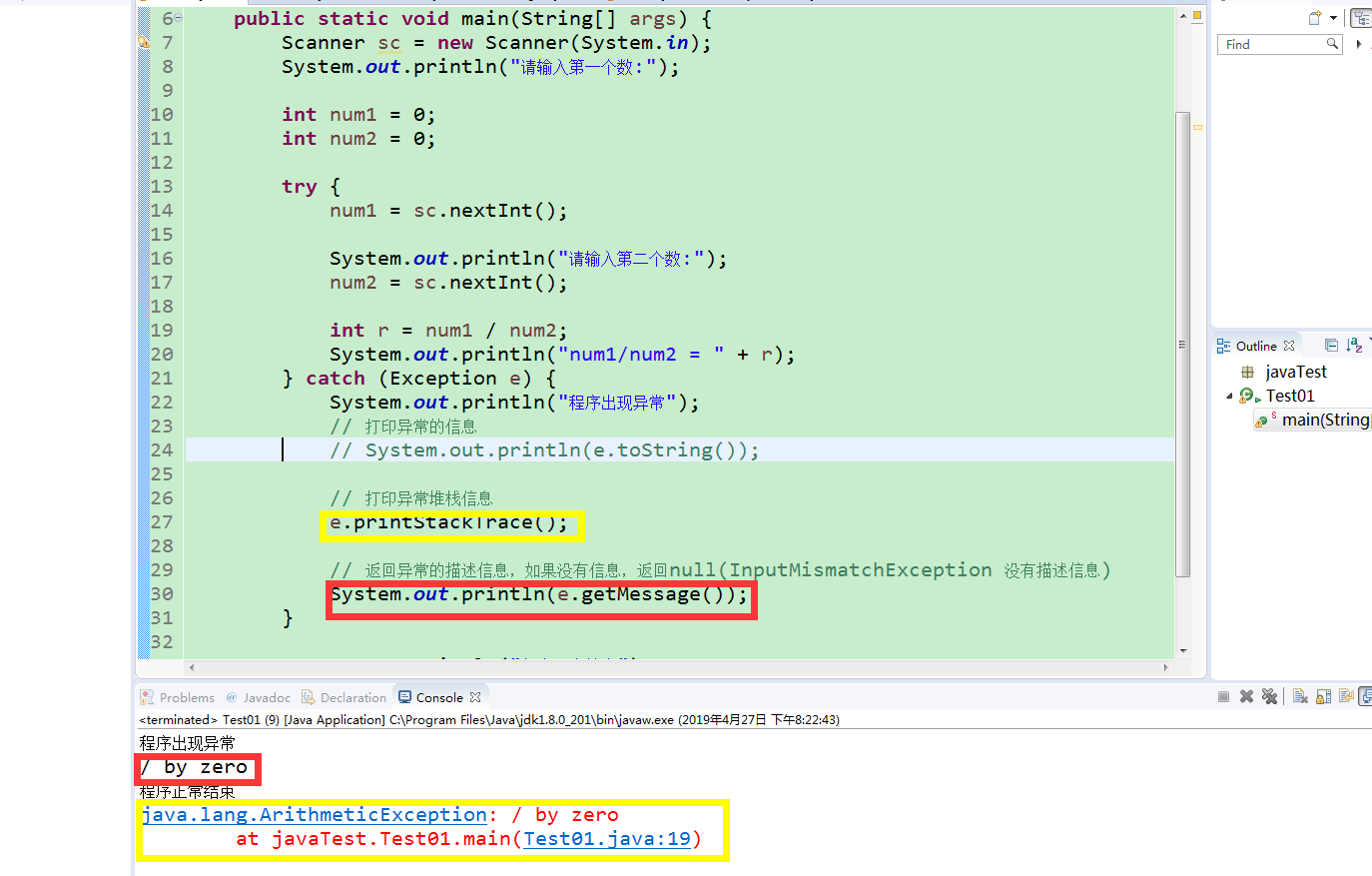
printstackTrace:打印异常处理的堆栈信息。

通常来说堆栈里面的信息有很多,
对于开发者来说,一般只需看明白第一行异常的简单、基本信息(异常的类型、异常的描述)
及最后一行:异常出现的位置(类——方法——行)
其堆栈信息在控制台输出的位置不固定
getmassage,返回异常处理的信息
【3】异常类型不匹配

【4】多重catch(个人认为不是很有必要,直接匹配Exception类型)
public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; try { num1 = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); num2 = sc.nextInt(); int r = num1 / num2; System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r); }catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("数学计算异常:"+e.getMessage()); }catch(InputMismatchException e) { System.out.println("输入不匹配异常:"+e.getMessage()); }catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("发送异常:"+e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("程序正常结束"); } }
3.2 try/catch/finally
把有可能产生异常的代码放到try中,catch负责匹配并处理异常,finally负责收尾工作(关闭数据库,关闭文件、释放内存等)。
public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; try { num1 = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入第二个数:"); num2 = sc.nextInt(); int r = num1 / num2; System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("程序出现异常"); } finally { System.out.println("不管是否出现异常,finally都执行"); } System.out.println("程序正常结束"); }
注:无论出现异常与否,finally总是执行
除特殊情况:
【1】System.exit(0)语句 退出jvm。
3.3存在return
总是最后会执行return语句
4.异常的分类

Throwable 类是 Java 语言中所有错误(Error)或异常(Exception)的父类,只有当对象是此类(或其子类之一)的实例时,才能通过 Java 虚拟机或者 Java throw 语句抛出。
Error 类表示错误类。仅靠程序本身无法恢复的严重错误。jvm内存耗尽、jvm崩溃等。
Exception 类表示异常类,可以通过java 异常处理机制处理。
Exception 根据是否处理分为两种情况。
RuntimeException:运行时异常。不要求程序必须做出处理。是所有运行时异常的父类。
CheckedException:检查时异常。要求程序必须处理,不处理编译不通过。
public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 运行时异常 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // runtime exception int r = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("r = "+ r); // 检查时异常 SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat(); try { Date date = df.parse("2019"); } catch (ParseException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
常见的运行时异常
ArithmeticException:数学计算异常。比如除数为0
InputMismatchException:输入不匹配异常
ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException:数组下标越界异常。
NullPointException:空指针异常,对象没有初始化就使用时,jvm会抛出该异常
IllegalArgumentException:非法参数异常。
ClassCastException:强制类型转换异常。
NumberFormatException:数字格式化异常。比如把“abc”格式化成数字。
常见的检查时异常:
ClassNotFoundException:类没有被发现异常。
SQLException:数据库相关异常
IOException:IO操作异常
ParseException:解析错误异常
运行时异常和检查时异常的区别
运行时异常:包括RuntimeException及其所有子类。不要求程序必须对它们作出处理,比如InputMismatchException、ArithmeticException、NullPointerException等。即使没有使用try-catch或throws进行处理,仍旧可以进行编译和运行。如果运行时发生异常,会输出异常的堆栈信息并中止程序执行。
Checked异常(非运行时异常):除了运行时异常外的其他异常类都是Checked异常。程序必须捕获或者声明抛出这种异常,否则出现编译错误,无法通过编译。处理方式包括两种:通过try-catch捕获异常,通过throws声明抛出异常从而交给上一级调用方法处理
FileNotFoundException:文件未发现异常。
5.声明异常
5.1throws关键字
当一个方法存在异常,而且自身有没有找到方法来解决,可以通过throws抛出异常交给上一级处理
public class Test01 { public static int div(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException{ int r = 0; r = a / b; return r; } public static void main(String[] args) { try { Test01.div(10, 0); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("除数不能为0"); } } }
开发者可以根据需要声明检查时异常(Exception或者非运行时异常)和运行时异常(RuntimeException或其子类)
如果调用处也不知道如何处理异常,可选择继续声明异常,我们把这个过程称为异常上抛
public class Test01 { public static int div(int a, int b) throws Exception{ int r = 0; r = a / b; return r; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //【1】 调用处知道如何处理! /* try { Test01.div(10, 0); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } */ // 【2】调用处也不知道如何处理 Test01.div(10, 0); } }
5.2异常和重载的关系
与其没有任何关系
方法的重载:
【1】方法名相同
【2】参数列表不同(类型、个数、顺序)
与返回值、修饰符声明异常无关
5.3异常和重写的关系
声明一个和方法重写有关系。
[1]父类方法声明了异常(检测时或运行时),子类可以不声明任何异常。
public class Father { public void showInfo() throws Exception{ } }
public class Son extends Father{ @Override public void showInfo(){ } }
可以认为:父类方法抛出异常,子类在重写过程中把该异常处理掉了,所以子类方法不用声明异常。
[2] 父类方法没有声明任何异常(检测时或运行时),子类也不能声明异常或者声明运行时异常。
[3] 父类声明了异常(检测时或运行时),子类声明完全一样的异常。
6.手动抛出异常
除了系统自动抛出异常外,有些问题需要开发者手动抛出异常。使用关键字throw
package cn.sxt02.exception06; public class Student { private String name; private String gender; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) throws Exception{ if(gender.equals("男") || gender.equals("女")) { this.gender = gender; }else { throw new Exception("性别不合法!"); } } public Student(String name, String gender) { super(); this.name = name; this.gender = gender; } public Student() { super(); } }
public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args){ Student stu = new Student(); stu.setName("二狗"); try { stu.setGender("xxx"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } }
7.自定义异常
如果开发者需要手动抛出的异常在系统不存在,可以自定义异常。
如果要自定义异常,首先要确定异常类型,如果异常是运行时异常,必须继承RuntimeException或其子类;如果异常是检查时异常,必须继承Exception或其子类。
异常的命名方式,参考系统命名方式,以Exception结尾。
public class AgeException extends Exception{ public AgeException() { super(); } public AgeException(String message) { super(message); } }

