1. at()方法 Array.prototype.at()
at() 方法接收一个整数值并返回该索引的项目,允许正数和负数。负整数从数组中的最后一个项目开始倒数。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
let index = 2;
console.log(array1.at(index));
// 2
index = -3;
console.log(array1.at(index));
//8
2. concat()方法 Array.prototype.concat()
concat() 方法用于合并两个或多个数组。此方法不会更改现有数组,而是返回一个新数组。
const array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
const array2 = ['d', 'e', 'f'];
const array3 = array1.concat(array2);
console.log(array3);
// expected output: Array ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"]
3. every()方法 Array.prototype.every()
every() 方法测试一个数组内的所有元素是否都能通过某个指定函数的测试。它返回一个布尔值。
const isBelowThreshold = (currentValue) => currentValue < 40;
const array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(array1.every(isBelowThreshold));
// expected output: true
4.fill()方法 Array.prototype.fill() 语法:fill(value, start, end)
fill() 方法用一个固定值填充一个数组中从起始索引到终止索引内的全部元素。不包括终止索引。
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
// fill with 0 from position 2 until position 4
console.log(array1.fill(0, 2, 4));
// expected output: [1, 2, 0, 0]
// fill with 5 from position 1
console.log(array1.fill(5, 1));
// expected output: [1, 5, 5, 5]
console.log(array1.fill(6));
// expected output: [6, 6, 6, 6]
5. filter() Array.prototype.filter()
filter() 方法创建一个新数组,其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素。
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result);
// expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
6. filter()方法 Array.prototype.filter()
filter() 方法创建一个新数组,其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素。
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result);
// expected output: Array ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
7.find()方法 Array.prototype.find()
find() 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的值。否则返回 undefined。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 8, 44];
const found = array1.find(element => element > 10);
console.log(found);
// expected output: 12
8. findIndex()方法 Array.prototype.findIndex()
findIndex()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。若没有找到对应元素则返回-1。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const isLargeNumber = (element) => element > 13;
console.log(array1.findIndex(isLargeNumber));
// expected output: 3
9.findLast() 方法 Array.prototype.findLast()
findLast() 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数条件的最后一个元素的值。如果没有找到对应元素,则返回 undefined。
const array1 = [5, 12, 50, 130, 44];
const found = array1.findLast((element) => element > 2);
if(found===undefined){
console.log("没有满足条件");
}else{
console.log(found);
}
//console.log(found);
// expected output: 44
10. forEach()方法 Array.prototype.forEach()
forEach() 方法对数组的每个元素执行一次给定的函数。
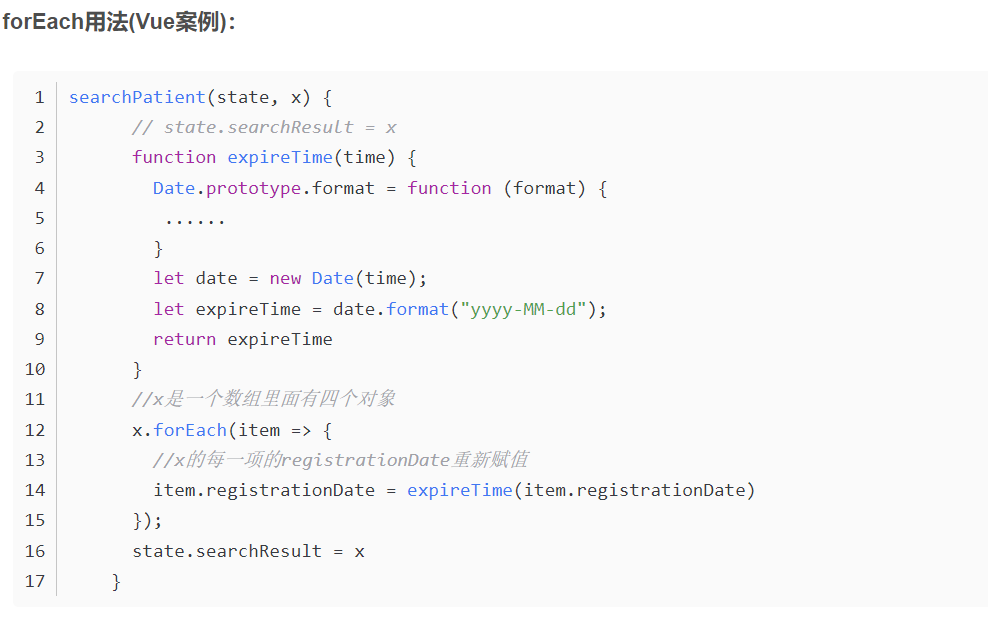
运用案例:
searchPatient(state, x) {
// state.searchResult = x
function expireTime(time) {
Date.prototype.format = function (format) {
......
}
let date = new Date(time);
let expireTime = date.format("yyyy-MM-dd");
return expireTime
}
//x是一个数组里面有四个对象
x.forEach(item => {
//x的每一项的registrationDate重新赋值
item.registrationDate = expireTime(item.registrationDate)
});
state.searchResult = x
}
//暂时先到这,后期再补一些。。 - .-



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号