简单数学刷题
P1414 又是毕业季II
把每个数的所有因数都枚举出来,假设因数为i,则让cnt[i]++。
根据选x+1个数的gcd小于等于选x个数的gcd
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)//先枚举选几个人
{
while (mx > 0 && cnt[mx] < i)//然后从最大的因数往小的枚举可以选出的情况
mx--;
cout << mx << endl;
}
一定能通过这样把所有i的情况找到:
如果极端情况所有数都是质数,由于cnt[1]==k,因此除了i=1会输出最大数以外,其他都会输出1.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int cnt[maxn];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n;
cin >> n;
int mx = 0;
for (int t = 1; t <= n; t++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
mx = max(x, mx);
for (int i = 1; i * i <= x; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
cnt[i]++;
if (i * i != x)
cnt[x / i]++;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
while (mx > 0 && cnt[mx] < i)
mx--;
cout << mx << endl;
}
return 0;
}
CF757B Bash's Big Day
同上,只不过要找cnt[i]不等于1的最大cnt[i]
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int cnt[maxn];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n;
cin >> n;
int mx = 0;
while (n--)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
mx = max(x, mx);
for (int i = 1; i * i <= x; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
cnt[i]++;
if (x / i != i)
cnt[x / i]++;
}
}
}
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= mx; i++)
ans = max(ans, cnt[i]);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
P1029 [NOIP2001 普及组] 最大公约数和最小公倍数问题
\(x0*y0=P*Q\)
直接暴力枚举即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main()
{
fastio;
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int c = a * b;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i * i <= c; i++)
{
if (c % i == 0)
{
int j = c / i;
if (gcd(i, j) == a)
{
ans++;
if (i * i != c)
ans++;
}
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
P1072 [NOIP2009 提高组] Hankson 的趣味题
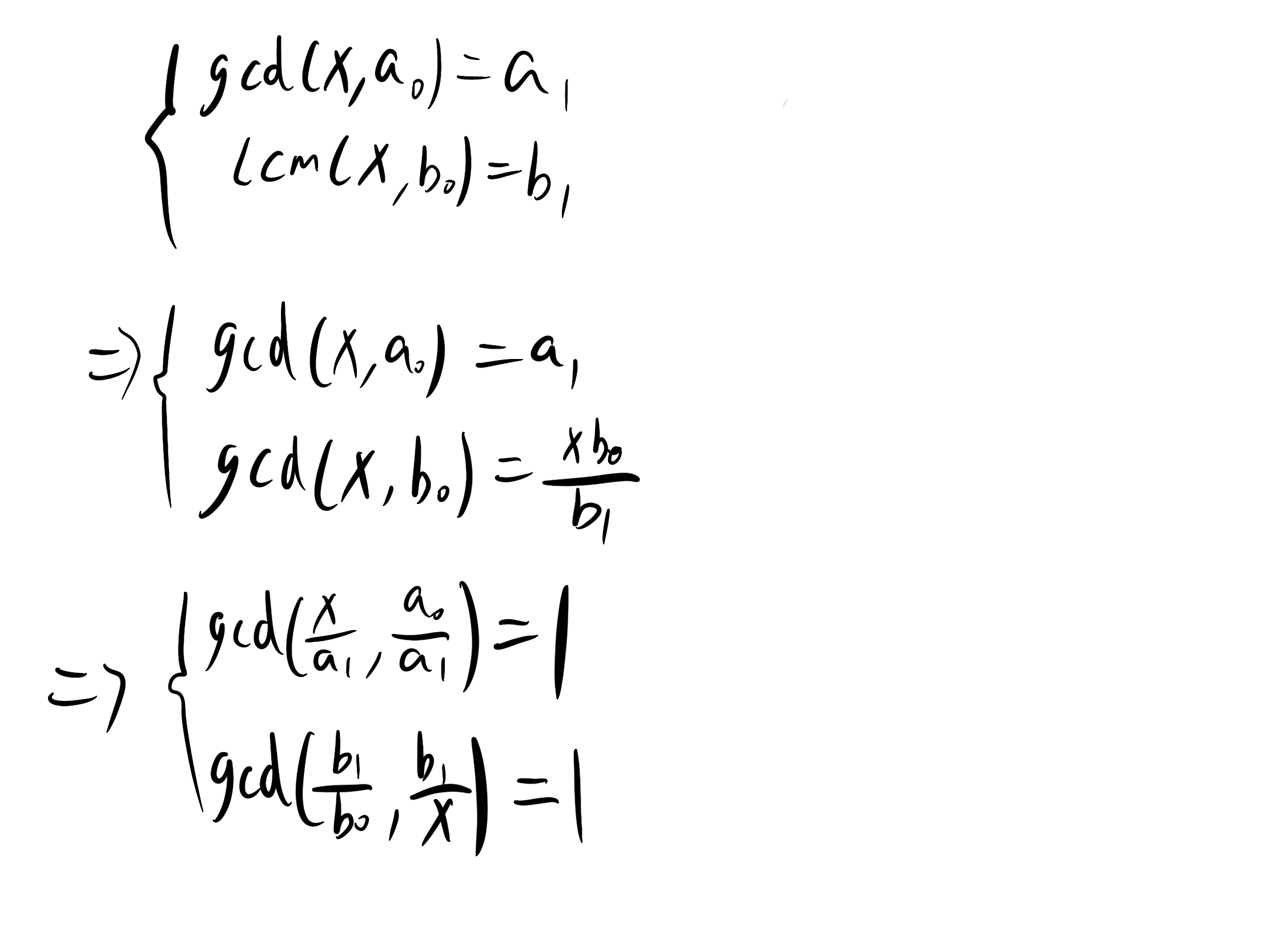
然后\(x|b_1\),枚举x即可,复杂度n*sqrt(b1)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main()
{
fastio;
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
ll a0, a1, b0, b1;
cin >> a0 >> a1 >> b0 >> b1;
if (b1 % b0 || a0 % a1) {
cout << 0 << "\n";
continue;
}
int ans = 0;
for (ll x = 1; x * x <= b1; x++)
if (b1 % x == 0)
{
if (x % a1 == 0 && gcd(x / a1, a0 / a1) == 1 && gcd(b1 / b0, b1 / x) == 1)
ans++;
ll y = b1 / x;
if (x == y|| y % a1)continue;
if (gcd(y / a1, a0 / a1) == 1 && gcd(b1 / b0, b1 / y) == 1)
ans++;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
CF687B Remainders Game
暴力做法,直接递推lcm取模:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b)
{
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
int main()
{
fastio;
ll n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
ll l = 1;
while (n--)
{
ll x;
cin >> x;
l = lcm(x, l) % k;
if (!l)
break;
}
if (l)
cout << "No";
else cout << "Yes";
return 0;
}
某个复杂做法:
由于\(lcm \% k==0\),只需要去check所有与k有相同质因子的数x中的每一个质因子:
假设这个质因子是p,去看是否cntx[p]>=cntk[p](x中p的个数是否大于k中p的个数),如果可以就凑出了k中的一种质因子(一定要一次全部凑出来,因为lcm的每个素因子个数等于所有数这个素因子个数的max)
最后看看k是不是1就知道能不能凑出k
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int v[maxn], p[maxn], cnt;
//bool v[maxn];卡常请把v改成1降低常数
void init_e()
{
memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));
cnt = 0;
}
void Euler_sieve(int n)
{
init_e();
cnt = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (v[i] == 0) { v[i] = i; p[++cnt] = i; }
for (int j = 1; j <= cnt; j++)
{
if (p[j] > v[i] || p[j] > n / i)break;
v[i * p[j]] = p[j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, k;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
Euler_sieve(1e6);
while (n--)
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x > 1)
{
int i = v[x];
int tmp = 1;
int flag = -1;
if (k % i == 0)flag = 0;
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
if (flag == 0)
{
tmp *= i;
if (k % tmp == 0 && k % (tmp * i))
{
k /= tmp;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
if (k > 1)
printf("No");
else printf("Yes");
return 0;
}
CF664A Complicated GCD
\(gcd(i,i+1)==1\),水题
CF762A k-th divisor
暴力分解
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
vector<ll>yz;
int main()
{
ll n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
ll lim = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= lim; i++)
{
if (n % i == 0)
yz.push_back(i);
}
for (int i=yz.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if (n / yz[i] != yz[i])
yz.push_back(n / yz[i]);
}
if (k > yz.size())
cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << yz[k - 1] << endl;
return 0;
}
CF776B Sherlock and his girlfriend
构造,素数涂1合数涂0
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int p[maxn], v[maxn], cnt = 0;
void elshai(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!v[i])
p[++cnt] = i, v[i] = i;
for (int j = 1; j <= cnt; j++)
{
if (p[j] > v[i] || p[j] > n / i)break;
v[i * p[j]] = p[j];
}
}
}
int col[maxn], ans = 0;
int main()
{
fastio;
elshai(1e6 + 5);
int n;
cin >> n;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
{
col[i] = (v[i] == i ? 1 : 2);
if (col[i] == 2)
ans = 2;
}
cout << ans << endl;
for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
cout << col[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
P5431 【模板】乘法逆元2
不算模版题。由于n<=5e6需要先预处理,把求和式子通分,然后求前缀后缀积,最后求逆元。(还要加个快读,数组也不能全ll,因为空间只有128MB)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 5e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int read()
{
int x = 0, f = 1;
char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c>'9') { if (c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + c - '0', c = getchar();
return f * x;
}
int qpow(int x, int y)
{
x %= mod;
ll res = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)res = res * x % mod;
x = 1ll * x * x % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return res%mod;
}
int inv(int x)
{
return qpow(x, mod - 2) % mod;
}
ll a[maxn];
int pre[maxn], suf[maxn], K[maxn];
int main()
{
//fastio;
ll n, k;
n = read(), mod = read(), k = read();
pre[0] = suf[n + 1] = K[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
a[i] = read();
pre[i] = pre[i - 1] * a[i] % mod;
K[i] = K[i - 1] * k % mod;
}
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
suf[i] = suf[i + 1] * a[i] % mod;
ll ans = 0;
ll und = inv(pre[n]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans = (ans + (K[i] * (1ll * pre[i - 1] * suf[i + 1] % mod) % mod) * und) % mod;
printf("%lld", ans);
return 0;
}
P3807 【模板】卢卡斯定理
套公式:\(C(n,m)=C(n/p,m/p)*C(n\%p,m\%p)\)
关于为什么不能线性求(因为数据很小)
因为递推fac的时候,p小于n+m,这时候fac[p]到fac[n+m]都会变成0,之后带有这些fac的项也都会变成0;
实际上C(n,m)=n!/m!/(n-m)!中fac中包含因子p的项可能会被消去,此时%p就不一定等于0了,但之前预处理的时候把这些项都标记成了0,这样答案就不对了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
#define pii pair<int,int>
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 5e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
ll qpow(ll x, ll y)
{
x %= mod;
ll res = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)res = res * x % mod;
x = x * x % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return res%mod;
}
ll inv(ll x)
{
return qpow(x, mod - 2) % mod;
}
ll a[maxn];
ll fac[maxn];
ll C(int n, int m)
{
if (n < m)return 0;
if (m == 0)return 1;
if (n < mod)
return fac[n] * inv(fac[m]) * inv(fac[n - m]) % mod;
return C(n / mod, m / mod) * C(n % mod, m % mod) % mod;
}
int main()
{
fastio;
int t;
cin >> t;
fac[0] = 1;
while (t--)
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m >> mod;
for (int i = 1; i < mod; i++)
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod;
cout << C(n + m, n)%mod << endl;
}
return 0;
}
CF632D Longest Subsequence
题意:给出n个数,要求选出尽可能多的数,满足它们的最小公倍数不大于m。允许数列里没数,此时这个数列的最小公倍数为1。
\(n,m<={10}^{6}, a_i <= {10}^{9}\)
两个数的lcm必然大于其中任意一个数
所以可以把\(a_i > m\)全部筛除;
剩下的a_i可以用类似埃筛的方法把所有可以整除a_i的小于等于m的数x的\(res[a[i]*j]+=cnt[a[i]]\)
最后从小到大枚举lcm,找到res[i]最大的第一个数就是可以凑出的最大lcm
结论:因为这个数是最小的一个可以被最多数整除的数,\(lcm(a_1,a_2,...,a_n)\)可以被其中任意一个\(a_i\)整除
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define fastio ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(NULL),cout.tie(NULL)
const int inf = 1e9 + 7;
const ll lnf = 1e18 + 7;
const int maxn = 5e6 + 10;
ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
double eps = 1e-6;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int cnt[maxn], res[maxn];
int main()
{
fastio;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
set<int>s;
vector<int>a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] > m)continue;
s.insert(a[i]);
cnt[a[i]]++;
}
for (auto i : s)
{
for (int j = i; j <= m; j += i)
res[j] += cnt[i];
}
int lcm = 1, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (res[i] > ans)
ans = res[i], lcm = i;
cout << lcm << " " << ans << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (lcm % a[i] == 0)
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}


