ARP Poisoning Attack and Mitigation Techniques ARP欺骗 中间人攻击 Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack 嗅探 防范 Can one MAC address have two different IP addresses within the network?
小结:
1、
ARP缓存投毒,窃听中毒者之间的通信;
2、
ARP Poisoning Attack and Mitigation Techniques - Cisco
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/catalyst-6500-series-switches/white_paper_c11_603839.html
ARP Poisoning (Man-in-the-Middle) Attack and Mitigation Techniques
A CSSTG SE Residency Program White Paper
Jeff King, CCIE 11873, CCSP, CISSP 80875
Kevin Lauerman, CCSP, CISSP 80877
Abstract
Security is at the forefront of most networks, and many companies implement a comprehensive security policy encompassing many of the OSI layers, from application layer all the way down to IP security. However, one area that is often left untouched is hardening Layer 2 and this can open the network to a variety of attacks and compromises.
This document will have a focus on understanding and preventing the ARP Poisoning (also known as the Man-In-The-Middle [MITM]) Layer 2 attack on the Cisco® Catalyst® 6500 switching series switch running Cisco IOS® Software. The Ettercap attack tool will be used to initiate Layer 2 attacks that you might encounter. Mitigation techniques to stop this attack are also covered.
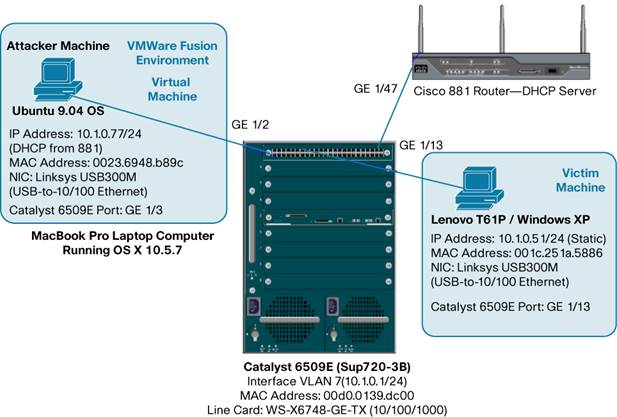
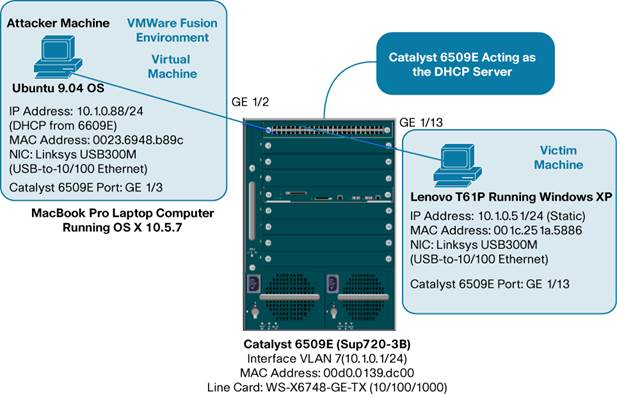
A MacBook Pro and a Lenovo T61P (laptops) was used for these test and acted as the attacker in some cases and the victim in others. Both computers also ran VMware.
Note that the attacks performed in this white paper were done in a controlled lab environment. We do not recommend that you perform this attack on your enterprise network.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Poisoning (MITM) Attack
A Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack is achieved when an attacker poisons the ARP cache of two devices with the (48-bit) MAC address of their Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card). Once the ARP cache has been successfully poisoned, each of the victim devices send all their packets to the attacker when communicating to the other device. This puts the attacker in the middle of the communications path between the two victim devices; hence the name Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack. It allows an attacker to easily monitor all communication between victim devices.
The objective of this MITM attack is to take over a session. The intent is to intercept and view the information being passed between the two victim devices.
Three (3) scenarios were used for the MITM attack. They were as follows:
|
Scenario |
Description |
|
1 |
Static IP Address on Attacker machine |
|
2 |
DHCP from 881 Router (DHCP Server) on Attacker machine |
|
3 |
DHCP from Cisco Catalyst 6509E DHCP Server on Attacker machine |
These (3) scenarios were chosen because they were all valid configurations that one might see in a customer's network; although scenario 2 and 3 are more likely in an enterprise network.
攻击步骤

Steps for the MITM (ARP Poisoning) Attack:
1. View initial ARP cache on the Victim PC (Windows XP)
2. View initial ARP cache on the Attacker PC (Ubuntu 9.04)
3. View initial MAC Address-Table on the Cisco Catalyst 6509E (Sup 720-3B)
4. Start Ettercap attack application on the Attacker PC (Ubuntu 9.04)
5. Configure Ettercap for “Unified Sniffing”
6. Select Interface (eth2) to sniff on Ubuntu 9.04 Attacker PC
7. Scan for host on wire
8. List hosts discovered and select targets for attack
9. Start sniffing
10. Start the MITM (ARP Poisoning) attack
11. Activate the “repoison_arp” plugin in Ettercap
12. Activate the “remote_browser” plugin in Ettercap
13. Open a Telnet session from the Victim to 10.1.0.1 (Int Vlan 7 on 6509E)
14. View “connections” in Ettercap for “active” connections (telnet session)
15. Select “active” session and then “view details”
16. View login and password between Victims (Windows XP and 6509E)
17. Perform “character injection” from Ettercap toward the 6509E (CLI)
18. Perform “character injection” from Ettercap toward Windows XP (Victim)
19. Open up web browser to from Windows XP Victim to CVDM on 6509E
20. Spawn browser on Attacker PC to view Victim's web pages being viewed
21. Scenario 2: DHCP from 881 Router (DHCP Server) on Attacker machine
22. Scenario 3: DHCP from Cisco Catalyst 6509E DHCP Server on Attacker machine
23. Mitigation of the MITM (ARP Poisoning) Attack
24. Summary
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARP_spoofing


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号