Java参数传递到底是值传递还是引用传递?
先来看看参数是如何传递的。
参数的传递
1.基本类型的参数传递
public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1; fun(a); } private static void fun(int x) { }
基本类型的参数传递,是直接将实参的值传递给形参。
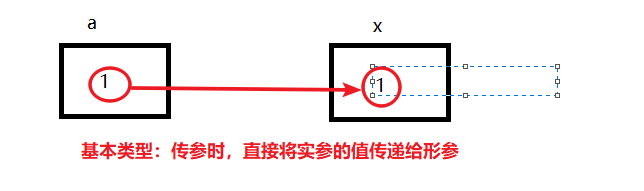
2.复杂类型的参数传递
public static void main(String[] args) { User user = new User(); fun(user); } private static void fun(User x) { }
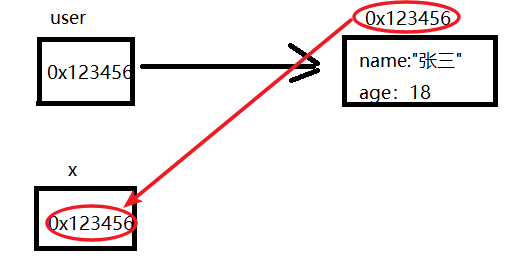
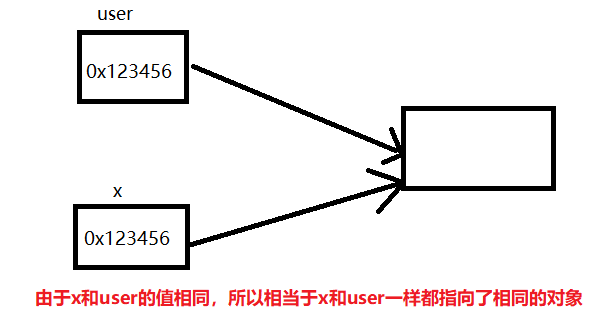
Java中参数的传递方式只有一种,那就是值传递。所谓值传递就是将实参值的副本传入方法内,而参数本身不会受到任何影响。
1.参数为基本类型
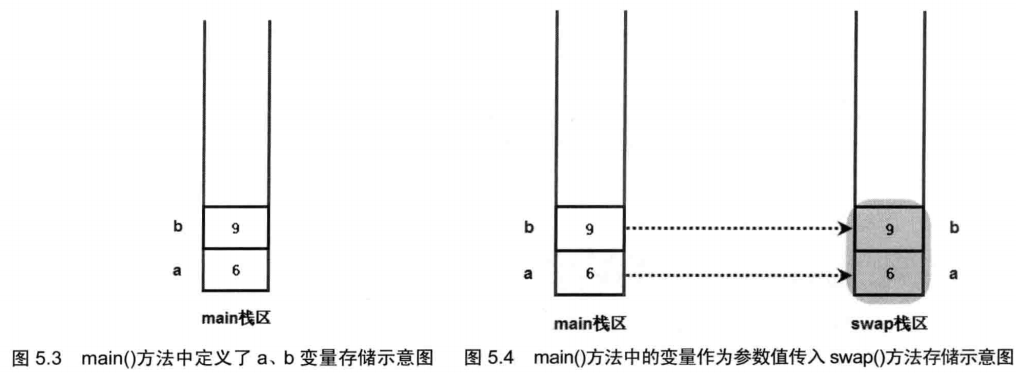
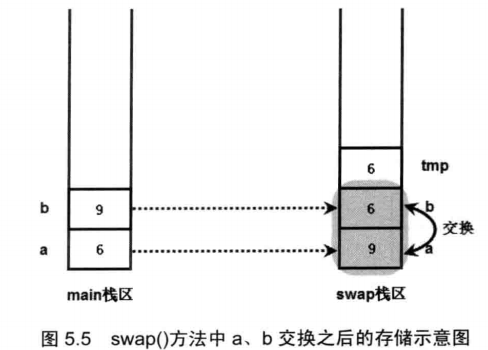
public class PassValue { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 6, b = 9; swap(a, b); System.out.println("交换后a=" + a + " b=" + b);// 6,9 } public static void swap(int a, int b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } }
下面是分析图:
2.参数为复杂类型
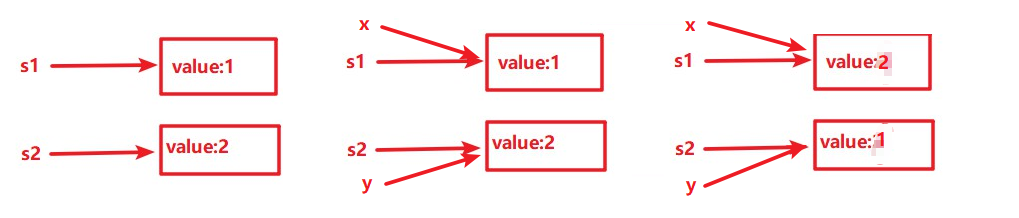
public class PassValue { public static void main(String[] args) { Swap s1 = new Swap(1); Swap s2 = new Swap(2); swap(s1, s2); System.out.println("交换后s1.value=" + s1.value + " s2.value=" + s2.value);//2,1 } public static void swap(Swap x, Swap y) { int temp = x.value; x.value = y.value; y.value = temp; } } class Swap { public int value; public Swap(int value) { this.value = value; } }
下面是分析过程:
面试题
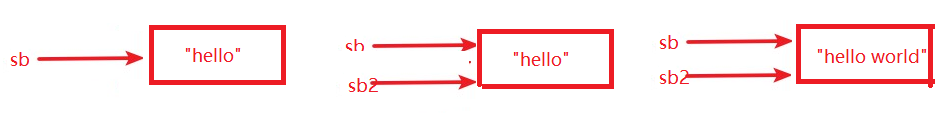
public class PassValue_string { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("hello"); change(sb); System.out.println(sb);//"hello world" } public static void change(StringBuffer sb) { sb.append(" world"); } }
分析如下:
不积跬步,无以至千里。不积小流,无以成江海!
