W2_python_module_list_tuple_dirct_file
w2_sys_os_list_tuple_dict
- 16、第02章节-Python3.5-模块初识
- 17、第03章节-Python3.5-模块初识2
- 18、第04章节-Python3.5-pyc是什么
- 19、第05章节-Python3.5-python数据类型
- 20、第06章节-Python3.5-bytes数据类型
- 21、第07章节-Python3.5-列表的使用
- 22、第08章节-Python3.5-列表的使用2
- 23、第09章节-Python3.5-元组与购物车程序练习
- 24、第10章节-Python3.5-购物车程序练习实例
- 25、第11章节-Python3.5-字符串常用操作
- 26.第12章节-Python3.5-字典的使用
16、第02章节-Python3.5-模块初识
sys模块
import sys
sys.path
print(sys.path)
打印环境变量
sys.argv
print(sys.argv)
返回列表:脚本相对路径,[以及传入参数]
print(sys.argv[1]) 表示打印传入的第一个参数值,依次类推
os模块
import os
os.system
result = os.system("ls")
print(result)
result可能的值为0或1,代表执行成功与否,不保存命令执行返回数据
os.popen
cmd_res = os.popen("dir").read()
cmd_res可以读取到命令执行的返回数据
os.mkdir
os.mkdir("new_dir")
创建一个目录
17、第03章节-Python3.5-模块初识2
18、第04章节-Python3.5-pyc是什么
检查源文件与pyc的时间,如果源文件更新,则预编译一次再执行
19、第05章节-Python3.5-python数据类型
int float complex(复数)
bool
20、第06章节-Python3.5-bytes数据类型
数据运算(略)
三元运算:
result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2
if 条件为真,则为值1
if 条件为假,则为值2
a,b,c = 1,3,5
d = a if a>b else c
print(d)
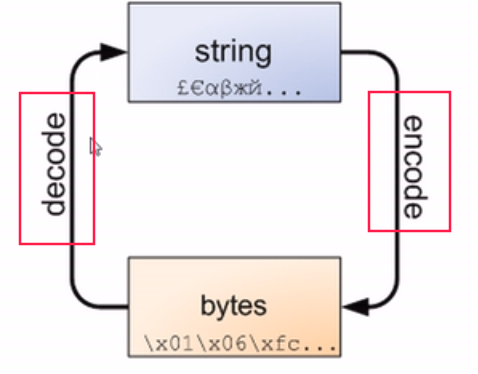
str与bytes
21、第07章节-Python3.5-列表的使用
列表与元组
列表
list_A = []
list_A.append("string")
list_A.insert(0,"string_A")
list_A[1] = "stringC"
list_A.remove("stringc")
del list_A[1]
list_A.pop()
list_A.pop(index)
list_A.clear() #清空列表
list_A.reverse() #顺序反转
list_A.sort() #排序
注:排序规则按accssic码规则排列
元组
元组可以看作是只读的列表。
只有count,index属性
练习:购物车程序
程序:购物车程序
需求:
1.启动程序后,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表
2.允许用户根据商品编号购买商品
3.用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒
4.可随时退出,退出时,打印已购买商品和余额
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
#Author:wu.
products = [
("手机",5000),
("电视",3000),
("空调",3500),
("冰箱",4000),
("微波炉",400),
("风扇",200),
("书",50),
("椅子", 1500)
]
shopping_list = []
while True:
salary = input("Input your salary:")
if salary.isdigit():
salary = int(salary)
balance = salary
break
else:
print("please input int number!")
while True:
for index,p_item in enumerate(products,1):
print(index,p_item)
user_choice = input("input product num to purchase or press \033[41m q \033[0m to quite\n\033[32m>>>\033[0m").strip()
if user_choice.isdigit():
user_choice = int(user_choice)
if int(user_choice) in range(len(products)+1):
p_item = products[user_choice - 1]
if balance > p_item[1]:
shopping_list.append(p_item)
balance = balance - p_item[1]
print("shopping cart list:",shopping_list)
print("your balance",balance)
continue
else:
print("\033[41m sorry, you don't have enough balance!\033[0m")
print("your balance \033[31m {balance} \033[0m".format(balance=balance))
continue
else:
print("Your choice out of range!")
continue
elif user_choice == 'q':
print("shopping cart list:", shopping_list)
print("total cost:", salary - balance)
print("your balance", balance)
exit()
else:
print("invalid input,please check!")
参考alex blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5717620.html
22、第08章节-Python3.5-列表的使用2
list_A.extend(list_B) #将list_B的元素扩展到list_A
尝试:列表的深copy,浅copy的区别
import copy
list_B = copy.deepcopy(list_A)

列表按步长取元素
print(list_A[0: -1:2]) #按步长为2,从0个元素取值到最后一个
print(list_A[::2]) #其中0和-1可以省略不写,与上一种等价
23、第09章节-Python3.5-元组与购物车程序练习
24、第10章节-Python3.5-购物车程序练习实例
25、第11章节-Python3.5-字符串常用操作
字符串操作
strings = 'Alex li'
print(list(strings))
strings.capitalize()
print(strings.count("l"))
strings.encode()
print(strings.endswith(' li')) #是否以指定字符结尾
strings = 'Alex \ li'
print(strings.expandtabs(tabsize=100)) #打印tab的个数
strings.format()
strings = 'Alex name li'
print(strings[strings.find("name"):9]) #找出以指定字符开始到第N个字符为止的中间字条串
print(strings[-1])
//# strings.format_map()
strings.isdigit()
print(strings.index('le'))
strings.isalnum() #包含所有的英文字符和阿拉伯数字
strings.isalpha() #包含纯英文字符
strings.isdecimal() #16进制
strings.isidentifier() #是否合格的变量名
strings.islower()
strings.isupper()
strings.isnumeric()
strings.isprintable()
strings.isspace()
strings.istitle()
strings = "+"
list_s = ["a","b","c"]
print(strings.join(list_s))
print(strings.ljust(50,"="))
//# strings.rjust()
strings = 'AAbbCC1ccbb'
print(strings.lower())
strings.upper()
strings.lstrip()
p = str.maketrans('abcdefg','1234567')
print("abcggg".translate(p))
en_string = "abcggg".translate(p)
d = str.maketrans('1234567','abcdefg')
print(en_string.translate(d))
print(strings.replace('bb','ZZ', 1))
strings.rfind('e') #从右边找
strings.split("l") #以指定字符分割
strings.splitlines() #以换行符分割
strings.swapcase() #大小写交换
26.第12章节-Python3.5-字典的使用
字典基本操作
dict = {key:value}
dict[key] #查询此key对应的value,此法不安全,如果此key无,则代码异常
dict.get(key) #查询此key对应的value,安全有效,代码无异常处理
dict[key] = "strings" #有此key,则修改,无此key则添加
del dict #删除整个字典
del dict[key] #删除此条键值对
dict.pop(key) #删除此条键值对
dict.popitem() #随机删除一个
print(key in info) #判断key是否在字典中,返回布尔值
多级字典的嵌套操作
dict.setdefult(key,new_value) #从dict中取key,如果key存在,则返回key对应的value,取不到,则创建该key,并把new_value作为值
dict_a = {key_a1:value_a1,key_a2:value:a2}
dict_b = {key_b1:value_b1,key_a2:value:a2}
dict_a.update(b) #update方法,可以将b中的key对应的值更新给dict_a中的相同key的值,如果dict_a中没有的key,则加入进去
25:00
dict.items() #将字典转为列表
dict.fromkeys([key1,key2,key3],value) #把列表中的数据作为keys,初始化一个字典,
尤其注意:以这种方式初始化的dict,value为列表时,更改任务一个key的value,所有的key的value都会改变
字典的循环
for key in dict: #最建议的循环方式
print(key,dict[key])
for k,v in dict.items(): #不建议的方式,因为数据大时,不够高效,因为items()是先将字典变成列表,再遍列
print(k,v)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号