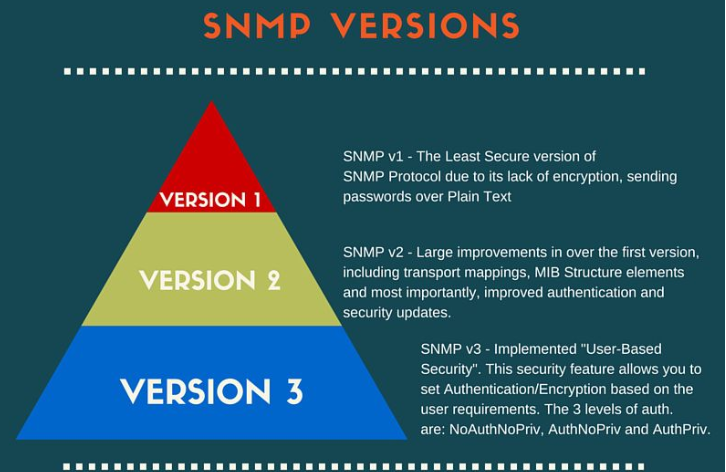
SNMP Introduction
Basic command of SNMP:
- GET: The GET operation is a request sent by the manager to the managed device. It is performed to retrieve one or more values from the managed device.
- GET NEXT: This operation is similar to the GET. The significant difference is that the GET NEXT operation retrieves the value of the next OID in the MIB tree.
- GET BULK: The GETBULK operation is used to retrieve voluminous data from large MIB table.
- SET: This operation is used by the managers to modify or assign the value of the Managed device.
- TRAPS: Unlike the above commands which are initiated from the SNMP Manager, TRAPS are initiated by the Agents. It is a signal to the SNMP Manager by the Agent on the occurrence of an event.
- INFORM: This command is similar to the TRAP initiated by the Agent, additionally INFORM includes confirmation from the SNMP manager on receiving the message.
- RESPONSE: It is the command used to carry back the value(s) or signal of actions directed by the SNMP Manager.
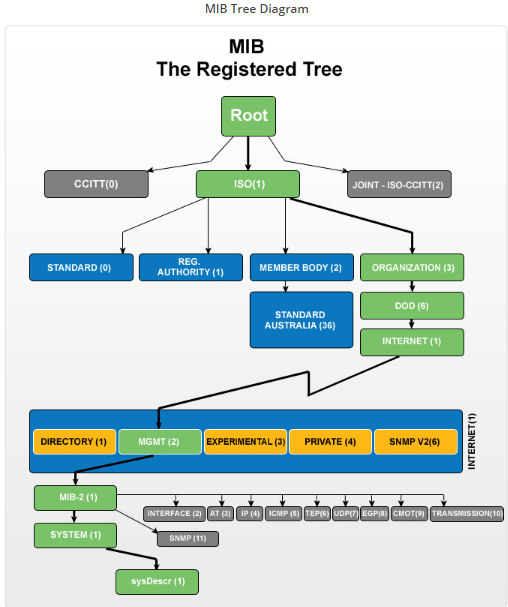
![(2)
org (3)
dod (6)
Internet (l )
experime
directory (I)
rWb-2 (1)
interfaces (2)
private (4)
enterprise (1)
microsoft
systn (I)
ip (4)
Cisco (9)
(311)
juniperMIB
(2636
OID Tree Example]()
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.1 - SNMP MIB-2 System
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.2 - SNMP MIB-2 Interfaces
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.3 - at
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.4 - ip
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.5 - icmp
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.6 - tcp
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.7 - udp
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.8 - egp
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.9 - cmot
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.10 - transmission
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.11 - snmp
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.14 - OSPF Version 2 MIB
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.15 - BGPv4
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.16 - Managed Objects for Bridges
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.17 - Bridge Mib
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.22 - rptrHealth
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.25 - HOST-RESOURCES-MIB, from RFC 1514
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.26 - Ethernet MAU mib
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.27 - Application MIB module
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.28 - MTA MIB module
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.29 - X.500 Directory MIB module
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.31 - ifMib
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.33 - upsMIB
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.34 - snaNode
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.38 - mdmMib
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.41 - sdlcStatus
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.43 - Printer-MIB
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.47 - entity-mib
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.69 - docsDev
- 1.3.6.1.2.1.92 - notificationLogMIB
OID:
This is a sample structure of OD:
Iso(1).org(3).dod(6).internet(1).private(4).transition(868).products(2).chassis(4).card(1).slotCps(2)-cpsSlotSummary(1).cpsModuleTable(1).cpsModuleEntry(1).cpsModuleModel(3).3562.3
or just:
1.3.6.1.4.868.2.4.1.2.1.1.1.3.3562.3
Private OID:
Many manufactures can supply custom MIB files for their hardware ,such as temperature , fan speed.
The MIB file is hard to read, they are only meant to be imported, or "compiled " by a Management Station.
Below is an example of Cisco MIB file for environment monitoring.
![计算机生成了可选文字:
S 2 iOOCISCOEnVMonVO ItagestatusEntry
0 日 ] ECT —TY P E 囗
SYNTAX
M × 一 C 匚 E 5 5 not—accessibleO
STAT 凵 5
C 凵 r r e nt 囗
凵 苁 n entry n the voltage S t at 凵 S
D E 5 匚 R I PT 10 N 囗
t 彐 匕 ] e , representing the S t at 凵 S 囗
Of the associated
testpoint maintained 匕 the environmentalO
{ CiSCOEnVMonV01tageStatuSIndex } 囗
m 囗 n ] t 囗 r 。
I N D EX
{ CiSCOEnVMonV01tageStatuSTab1e 1 } 囗 囗
SEQUENCE { 囗
Integer32 ( 0 . . 214 74 8 54 7 〕 , 囗
Displ aystring , 囗
dl_OW I e g e r 2 , 囗
ciscoEnVMonVOltageThresholdHigh I nt e g e r 2 ,
CiSCOEnVMonV01tageLaStShutdown I e g e r 2 , 囗
CiSCOEnVMonV01tageState
匚 ] S C 囗 E 囗 n St
CiSCOEnVMonV01tageStatuSIndex 0 日 ] ECT —TY P E 囗
SYNTAX
Integer32 ( 0 . . 21474H 547 〕 囗
STAT 凵 5
C 凵 r r e nt 囗
M × 一 C 匚 E 5 5 not—accessibleO
D E 5 匚 R I PT 10 N 囗
index for the testpoint being
This index S for 5 NM P purposes 囗 n ] , and has n 囗 囗
] nt r ] n S ] C m e 彐 n ] n 0 。 凵 囗](http://images2015.cnblogs.com/blog/541356/201610/541356-20161027132402531-436113165.png)
Cisco MIB information:
http://snmp.cloudapps.cisco.com/Support/SNMP/do/BrowseMIB.do?local=en&step=2
Load MIB file:
The files below is F5 MIB file.
We can use MIB Browser to load these file ,and you can see the F5 private OID in the picture.





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号