Iptables
There are three different chains : input , forward and output.
Input: This chain is used to control the behavior for incoming connections.
Forward: This chain is used for incoming connections that aren't actually being delivered locally. Think of a router -- data is always being sent to it but rarely actually destined for the router itself;
There is one sure-fire way to check whether or not your system uses the forward chain.

The screenshot above is of a server that's been running for a few months and has no restrictions on incoming or outgoing connections. As you can see, the output chain has processed 34M. The forward chain , on the other hand ,has processed 0GB. It means that this server isn't doing any kind of forwarding or being used as a pass-through device.
Output: this chain is used for outgoing connections. Iptables will check it's output chain to see what the rules are used before making a decision to allow or deny the connections attempt.
To see the default polices for the unmatched traffic.
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
Connection-specific Responses
Accept:
Drop:
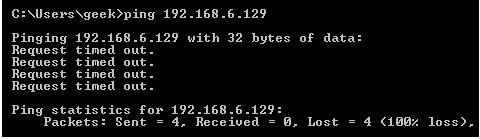
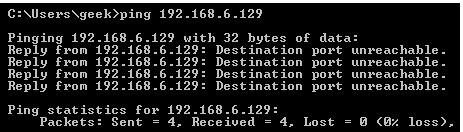
Reject: Don't allow the connection, but send back an error.
You can use iptables -A to append rules to the existing chain.
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.10.10.10 -j DROP
You can use netmask or standard slash notation to specify the range of IP addresses.
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.10.10.0/24 -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.10.10.0/255.255.255.0 -j DROP
Specific port
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport ssh -s 10.10.10.10 -j DROP
Connection States:
If you permit the SSH connections from 10.10.10.10, but SSH connections to 10.10.10.10 are not allowed.However, with the state ESTABLISHED ,the system is permitted to send back information over SSH as long as the session has already been established, which makes SSH communication possible between these two hosts.
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport ssh -s 10.10.10.10 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 22 -d 10.10.10.10 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
You should save the configuration
[root@localhost sysconfig]# /etc/init.d/iptables save
iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[ OK ]
The configuration file is /etc/sysconfig/iptables:
[root@localhost sysconfig]# more iptables
# Firewall configuration written by system-config-firewall
# Manual customization of this file is not recommended.
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号