享元模式
软件设计 石家庄铁道大学信息学院
实验13:享元模式
本次实验属于模仿型实验,通过本次实验学生将掌握以下内容:
1、理解享元模式的动机,掌握该模式的结构;
2、能够利用享元模式解决实际问题。
[实验任务一]:围棋
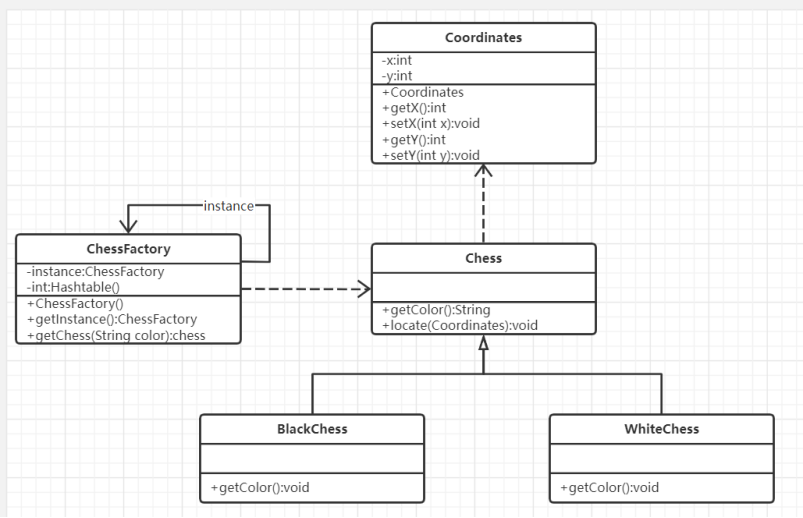
设计一个围棋软件,在系统中只存在一个白棋对象和一个黑棋对象,但是它们可以在棋盘的不同位置显示多次。
实验要求:
1. 提交类图;
2. 提交源代码;
3.注意编程规范;
4.要求用简单工厂模式和单例模式实现享元工厂类的设计。
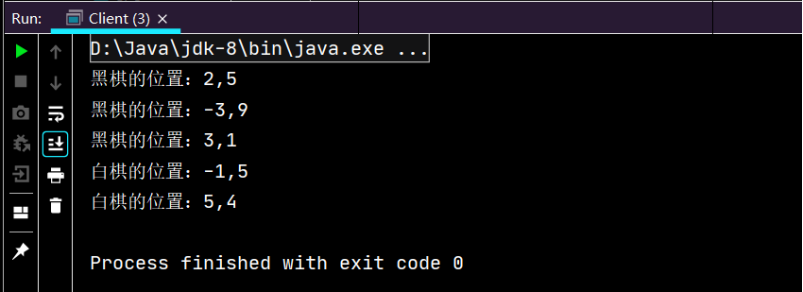
package test13; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Chess black1,black2,black3,white1,white2; ChessFactory factory; factory = ChessFactory.getInstance(); black1 = ChessFactory.getChess("b"); black2 = ChessFactory.getChess("b"); black3 = ChessFactory.getChess("b"); white1 = ChessFactory.getChess("w"); white2 = ChessFactory.getChess("w"); black1.locate(new Coordinates(2, 5)); black2.locate(new Coordinates(-3, 9)); black3.locate(new Coordinates(3, 1)); white1.locate(new Coordinates(-1, 5)); white2.locate(new Coordinates(5, 4)); } }
package test13; import java.util.Hashtable; public class ChessFactory { private static ChessFactory instance=new ChessFactory(); private static Hashtable ht; public ChessFactory() { ht=new Hashtable(); Chess black,white; black=new BlackChess(); ht.put("b", black); white=new WhiteChess(); ht.put("w", white); } public static ChessFactory getInstance() { return instance; } public static Chess getChess(String color) { return (Chess)ht.get(color) ; } }
package test13; class Coordinates { private int x; private int y; public Coordinates(int x,int y) { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub this.x = x; this.y = y; } public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } public int getY() { return y; } public void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } }
package test13; abstract class Chess { public abstract String getColor(); public void locate(Coordinates co){ System.out.println(this.getColor()+"棋的位置:"+co.getX()+","+co.getY()); } }
package test13; public class WhiteChess extends Chess { @Override public String getColor(){ return "白"; } }
package test13; public class BlackChess extends Chess { @Override public String getColor(){ return "黑"; } }
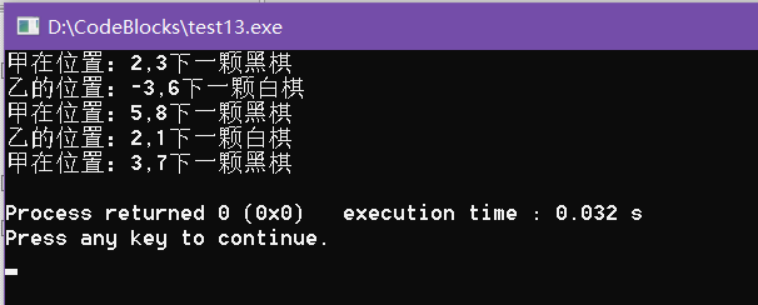
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<String> #include<vector> //棋子颜色 enum ChessColor { BLACK, WHITE }; //棋子位置 struct Coordinates { int x; int y; Coordinates(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) {} }; //棋子定义 class Chess { protected: ChessColor m_color; //颜色 public: Chess(ChessColor color) : m_color(color) {} ~Chess() {} virtual void Draw() {} }; class BlackChess : public Chess { public: BlackChess(ChessColor color) : Chess(color) {} ~BlackChess() {} void Draw() { cout << "下一颗黑棋"<<endl; } }; class WhiteChess : public Chess { public: WhiteChess(ChessColor color) : Chess(color) {} ~WhiteChess() {} void Draw() { cout << "下一颗白棋"<<endl; } }; class ChessFactory { private: vector<Coordinates> m_vecPos; //存放棋子的位置 Chess *m_blackChess; //黑棋棋子 Chess *m_whiteChess; //白棋棋子 string m_blackName; string m_whiteName; public: ChessFactory(string black, string white) : m_blackName(black), m_whiteName(white) { m_blackChess = NULL; m_whiteChess = NULL; } ~ChessFactory() { delete m_blackChess; delete m_whiteChess; } void setChess(ChessColor color, Coordinates pos) { if (color == BLACK) { if (m_blackChess == NULL) m_blackChess = new BlackChess(color); cout << m_blackName << "在位置:" << pos.x << ',' << pos.y ; m_blackChess->Draw(); } else { if (m_whiteChess == NULL) m_whiteChess = new WhiteChess(color); cout << m_whiteName << "的位置:" << pos.x << ',' << pos.y ; m_whiteChess->Draw(); } m_vecPos.push_back(pos); } }; //主函数 int main() { ChessFactory chessFactory("甲", "乙"); chessFactory.setChess(BLACK, Coordinates(2, 3)); chessFactory.setChess(WHITE, Coordinates(-3, 6)); chessFactory.setChess(BLACK, Coordinates(5, 8)); chessFactory.setChess(WHITE, Coordinates(2,1)); chessFactory.setChess(BLACK, Coordinates(3, 7)); }