Android 12(S) Binder(三)
学以致用,这一节来native binder实战!
android 12中的service用到的Bp、Bn文件多由aidl生成,所以实战中也用aidl来生成。
1、文件目录结构

文件目录结构如上,偷懒没有把头文件放到include目录当中去
2、aidl文件
package android.test; interface IHello { void sayHello(); void sayHelloTo(String people); String getName(); }
这里有要注意的地方,路径名文件名要对应包名,文件名对应接口名称,否则编译时会遇到错误。aidl文件的编写是用java来编写的。
有了aidl,要如何编译aidl呢?给个最简单的例子:
// test cc_library { name: "libhello", srcs:[ ":hello_aidl" ], shared_libs: [ "libbinder", "libutils", ], } filegroup { name: "hello_aidl", srcs: [ "binder/android/test/IHello.aidl" ], path: "binder" }
filegroup中的path对应的是src的第一级文件路径,如果没有的话会发生编译错误;如果我们的src路径直接是android/test/IHello.aidl,那就不需要path了。
编译完成之后就可以到out/soong/.intermediates 这个路径下的对应工程路径下找到生成文件了。
3、编写Bn实现
自己手写binder service需要写Ixxx,Bnxxx,Bpxxx等文件,用aidl会显得方便很多,因为编译器会帮我们生成这些文件,我们只要写一个类来继承Bn。
// IHello.h #pragma once #include <binder/IBinder.h> #include <binder/IInterface.h> #include <binder/Status.h> #include <utils/String16.h> #include <utils/StrongPointer.h> namespace android { namespace test { class IHello : public ::android::IInterface { public: DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(Hello) virtual ::android::binder::Status sayHello() = 0; virtual ::android::binder::Status sayHelloTo(const ::android::String16& people) = 0; virtual ::android::binder::Status getName(::android::String16* _aidl_return) = 0; }; // class IHello class IHelloDefault : public IHello { public: ::android::IBinder* onAsBinder() override { return nullptr; } ::android::binder::Status sayHello() override { return ::android::binder::Status::fromStatusT(::android::UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION); } ::android::binder::Status sayHelloTo(const ::android::String16&) override { return ::android::binder::Status::fromStatusT(::android::UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION); } ::android::binder::Status getName(::android::String16*) override { return ::android::binder::Status::fromStatusT(::android::UNKNOWN_TRANSACTION); } }; // class IHelloDefault } // namespace test } // namespace android
生成文件IHello.h中用的都是String16,定义在system/core/libutils/中,返回值都是状态Status,通过参数返回我们要的值。
下面看看Bn的实现:
#ifndef __HELLO_SERVICE_H__ #define __HELLO_SERVICE_H__ #include <android/test/BnHello.h> // HelloService.h class HelloService : public android::test::BnHello { public: HelloService(const char*); ~HelloService(); ::android::binder::Status sayHello() override; ::android::binder::Status sayHelloTo(const ::android::String16&) override; ::android::binder::Status getName(::android::String16*) override; private: const char* name; }; #endif
// HelloService.cpp #define LOG_TAG "HelloService" #include "HelloService.h" using ::android::binder::Status; HelloService::HelloService(const char* s) :name(s) { ALOGD("String16 = %s", ::android::String8(name_s).c_str()); } HelloService::~HelloService() { delete name; name = NULL; } Status HelloService::sayHello() { ALOGD("pid = %d, %s", getpid(), __func__); return Status::ok(); } Status HelloService::sayHelloTo(const ::android::String16& s) { ALOGD("pid = %d, %s, %s", getpid(), __func__, ::android::String8(s).c_str()); return Status::ok(); } Status HelloService::getName(::android::String16* aidl_return) { ALOGD("pid = %d, %s", getpid(), __func__); *aidl_return = ::android::String16(name);return Status::ok(); }
头文件中的函数直接从IHello.h中抄出来就好,要注意命名空间的使用!
4、Server端
// main_server.cpp #include "HelloService.h" #include "binder/IServiceManager.h" #include "binder/IPCThreadState.h" #include "binder/ProcessState.h" using namespace android; int main(int argc, char** argv) { sp<HelloService> hello = new HelloService("APLLE"); sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager(); sm->addService(String16("hello.service"), hello, false, IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT); ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool(); IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(); return 0; }
5、Client端
// main_client.cpp #define LOG_TAG "HelloService_Client" #include <android/test/IHello.h> #include "binder/IServiceManager.h" #include "binder/IPCThreadState.h" #include "binder/ProcessState.h" using namespace android::test; using namespace android; int main(int argc, char** argv) { sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager(); sp<IBinder> b = sm->getService(String16("hello.service")); sp<IHello> hello(interface_cast<IHello>(b)); ALOGD("pid = %d, sayHello", getpid()); hello->sayHello(); ALOGD("pid = %d, sayHelloTo ABC", getpid()); hello->sayHelloTo(String16("ABC")); ::android::String16 aidl_return; hello->getName(&aidl_return); ALOGD("pid = %d, name = %s", getpid(), ::android::String8(aidl_return).c_str()); return 0; }
6、Android.bp
// server cc_binary { name: "hello_server", srcs:[ "HelloService.cpp", "main_server.cpp" ], shared_libs: [ "libbinder", "libutils", "liblog", ], static_libs: [ "libhello", ], include_dirs: [ "frameworks/native/libs/binder/include", ], cflags: [ "-Wno-unused-parameter" ] } // client cc_binary { name: "hello_client", srcs:[ "main_client.cpp" ], shared_libs: [ "libbinder", "libutils", "liblog", ], static_libs: [ "libhello", ], include_dirs: [ "frameworks/native/libs/binder/include", ], cflags: [ "-Wno-unused-parameter" ], } // lib cc_library_static { name: "libhello", srcs: [ ":hello_aidl", ], shared_libs: [ "libbinder", "libutils", ], aidl: { export_aidl_headers: true, }, } filegroup { name: "hello_aidl", srcs: [ "binder/android/test/IHello.aidl" ], path: "binder" }
7、执行结果
执行时要关掉selinux,不然会找不到服务的
03-31 16:19:27.945 9325 9325 D HelloService: String16 = APLLE
03-31 16:19:27.945 9325 9325 D HelloService: pid = 9325, HelloService, name = APLLE, create HelloService 03-31 16:19:33.639 9327 9327 D HelloService_Client: pid = 9327, sayHello 03-31 16:19:33.640 9325 9326 D HelloService: pid = 9325, sayHello 03-31 16:19:33.640 9327 9327 D HelloService_Client: pid = 9327, sayHelloTo ABC 03-31 16:19:33.640 9325 9326 D HelloService: pid = 9325, sayHelloTo, ABC 03-31 16:19:33.640 9325 9326 D HelloService: pid = 9325, getName
03-31 16:19:33.640 9327 9327 D HelloService_Client: pid = 9327, name = APPLE
结果中可以看到server端的进程号为9325,client端进程号为9327,client端调用函数之后,server端执行的线程是9326。
binder如何传递自定义类,callback等也要再看看。
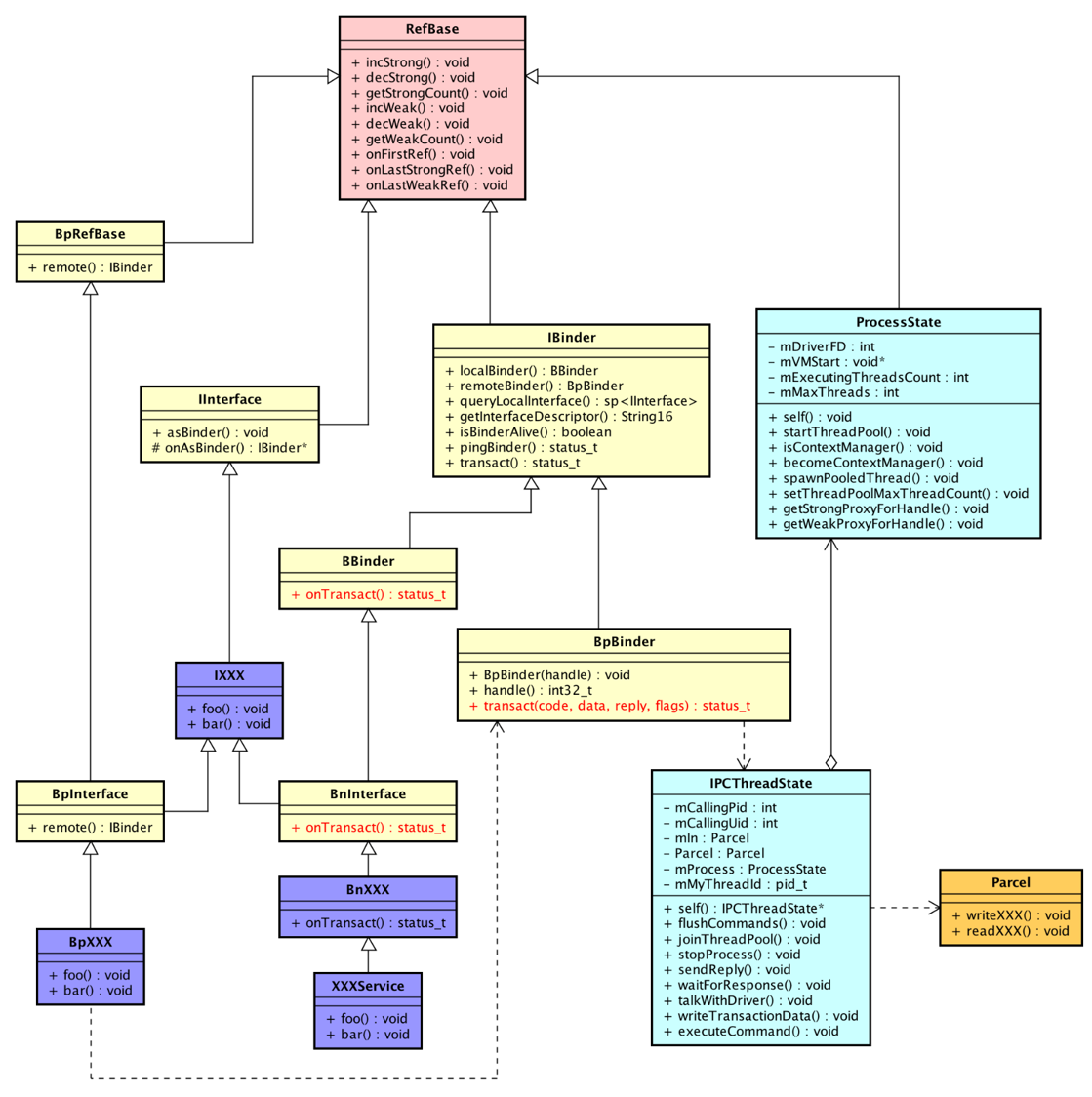
8、手写binder service
如果要手写binder其实也很简单,这里贴一张我们师兄画的UML类图,以及其博客主页 二的次方 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
按照这个类来写就好了,自己手写可以自由传参,就是封装到parcel中时比较麻烦一点



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号