堆(优先队列)
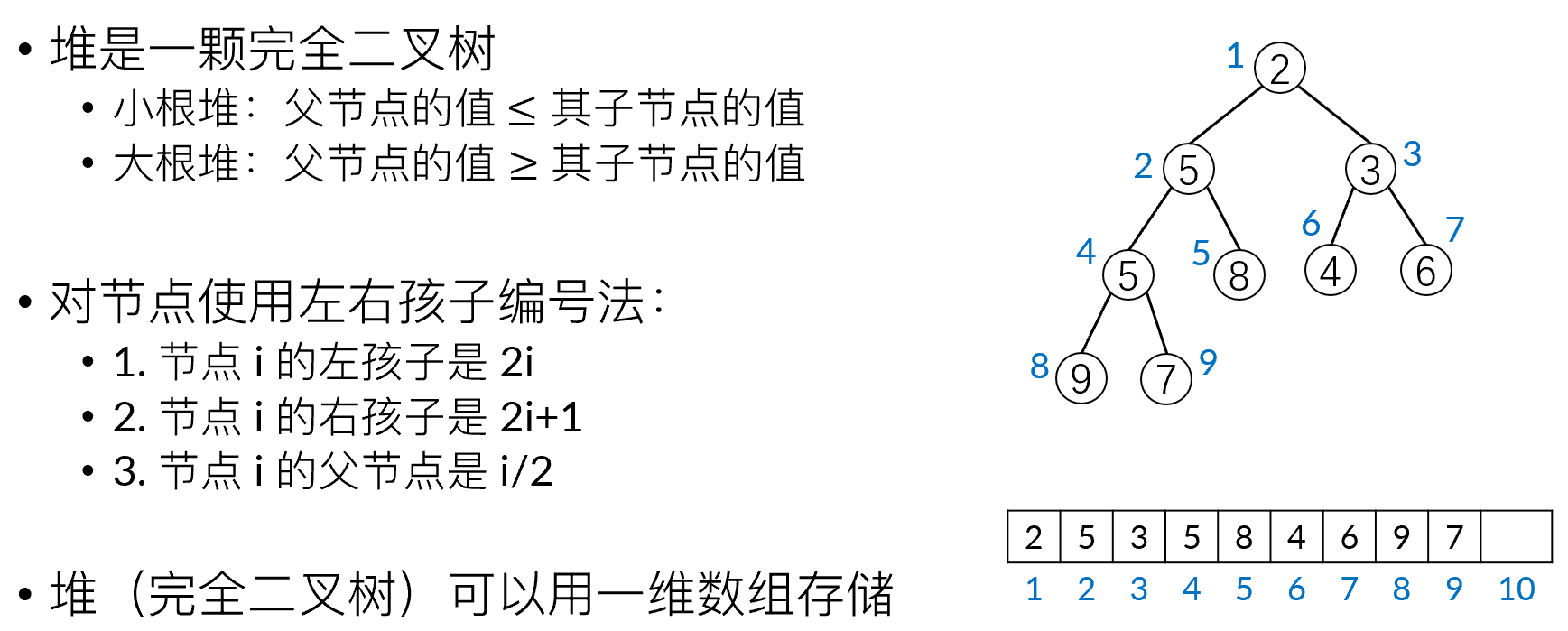
堆是一种树形结构,树的根是堆顶,堆顶始终保持为所有元素的最优值。有大根堆和小根堆,大根堆的根节点是最大值,小根堆的根节点是最小值。堆一般用二叉树实现,称为二叉堆。
堆的存储方式
堆的操作
empty
返回堆是否为空
top
直接返回根节点的值,时间复杂度 \(O(1)\)
push
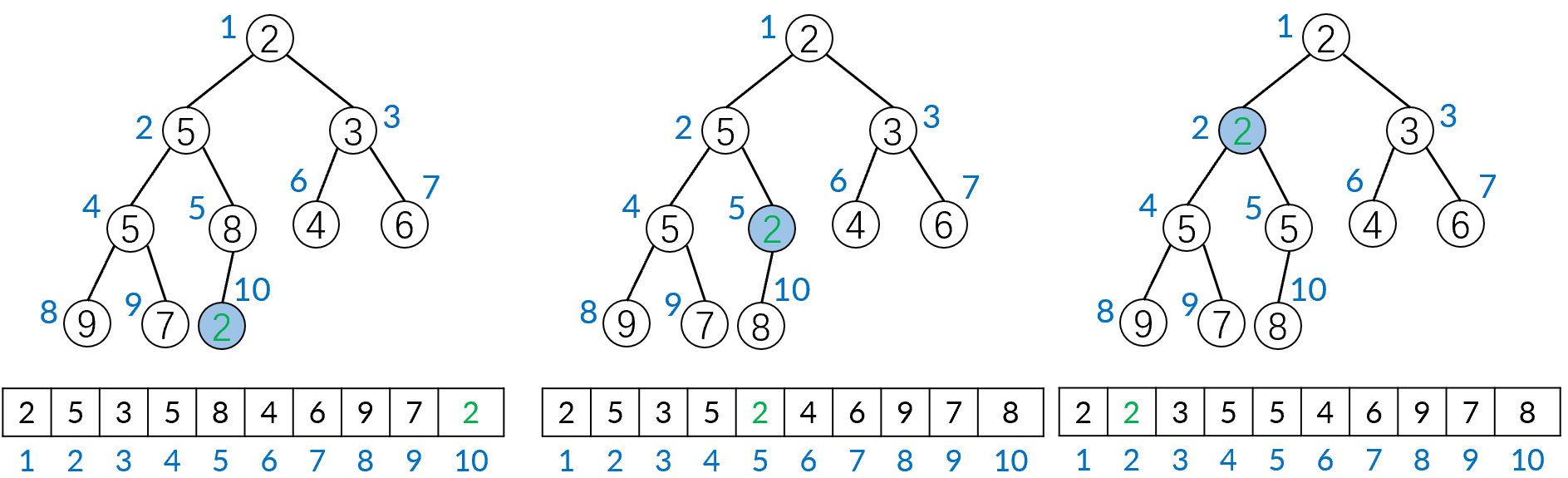
将新元素添加在数组最后面,若它比父节点小则不断与其父节点交换,使得堆重新满足父节点比子节点存储的数都要小(自下而上),时间复杂度 \(O(\log n)\)
pop
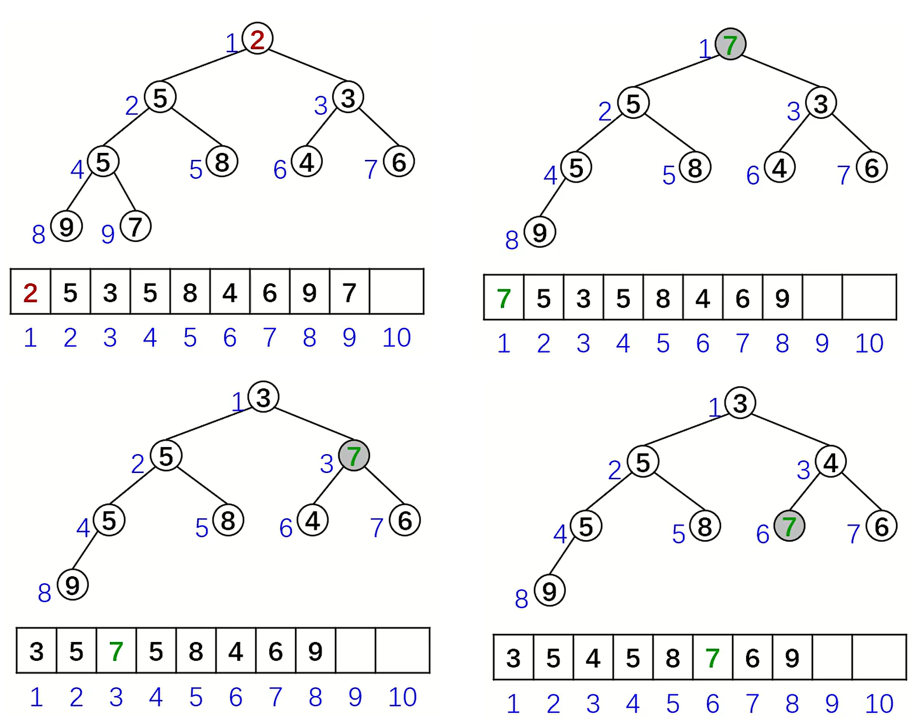
弹出根节点,并让堆依然符合原来的性质。首先交换根节点和数组中最后一个元素,再去掉最后一个元素。若新根节点比子节点大,则不断与较小子节点交换,直到重新满足条件(自上而下),时间复杂度 \(O(\log n)\)
例:P3378 【模板】堆
由此,给出二叉堆的模板实现:
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 5;
int heap[MAXN], len;
void push(int x) {
heap[++len] = x;
int i = len;
while (i > 1 && heap[i] < heap[i / 2]) {
swap(heap[i], heap[i / 2]);
i /= 2;
}
}
void pop() {
heap[1] = heap[len--];
int i = 1;
while (i * 2 <= len) {
int son = i * 2;
if (son < len && heap[son + 1] < heap[son]) son++;
if (heap[son] < heap[i]) {
swap(heap[son], heap[i]);
i = son;
} else break;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--) {
int op;
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
push(x);
} else if (op == 2) printf("%d\n", heap[1]);
else pop();
}
return 0;
}
例:P1177 【模板】排序
输入 \(n (n < 10^5)\) 个数字 \(a_i \ (a_i < 10^9)\),将其从小到大排序后输出。
分析:利用堆也是可以做排序的,先把所有的元素 push 进去,然后每次取出堆顶(最小值)输出并弹出堆顶,直到堆空为止,这种排序方法称为堆排序。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=100005;
struct Heap {
int a[MAXN],cnt;
void push(int x) { // 压入
a[++cnt]=x;
int i=cnt;
while (i>1 && a[i]<a[i/2]) {
swap(a[i/2],a[i]);
i/=2;
}
}
void pop() { // 删除
a[1]=a[cnt--];
int i=1;
while (i*2<=cnt) {
int son=i*2;
if (son<cnt && a[son+1]<a[son]) son++;
if (a[son]<a[i]) {
swap(a[son],a[i]);
i=son;
} else break;
}
}
int top() {
return a[1];
}
};
Heap h;
int main()
{
int n,x;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%d",&x);
h.push(x);
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
printf("%d ",h.top());
h.pop();
}
return 0;
}
堆排序整体的时间复杂度是 \(O(n \log n)\),空间复杂度为 \(O(n)\)。
选择题:以下排序方法中,哪个是不稳定的?
- A. 插入排序
- B. 冒泡排序
- C. 堆排序
- D. 归并排序
答案
C。
一个排序算法是稳定的,指的是如果待排序的序列中有两个或多个值相等的元素,在排序后,这些相等元素的相对位置不发生改变。反之,如果它们的相对位置可能发生改变,则称这个算法是不稳定的。
插入排序在插入一个新元素时,它会从后向前与已排序部分的元素进行比较。当遇到一个等于它的元素时,它会停止并将新元素插入到该元素后面。这保证了相等元素的原始相对顺序。因此,插入排序是稳定的。
冒泡排序只交换相邻且逆序的元素。如果两个相邻的元素相等,它不会进行交换,所以相等元素的相对顺序不会改变。因此,冒泡排序是稳定的。
归并排序在合并两个已排序的子数组时,如果来自左边子数组的元素和来自右边子数组的元素相等,总是优先选择左边子数组的元素。这确保了相等元素的相对顺序得以保持。因此,归并排序是稳定的。
堆排序在调整堆时,会将堆顶(最大/最小)元素与堆末尾的元素进行交换。这个末尾元素可能会跨越很长的距离被换到堆顶,这个过程完全不关心它与其他相等元素的原始相对顺序。正是这种大跨度的、不相邻的交换破坏了稳定性。
优先队列
C++ 提供了优先队列这个数据结构,也就是 STL 中的 priority_queue,底层就是由堆实现的。要使用优先队列,需要包含 queue 头文件,优先队列支持的基础操作如下:
priority_queue<int> q新建一个保存int型变量的优先队列q,默认是大根堆priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q新建一个小根堆q.top()优先队列查询最大值(或者是最小值)q.pop()将最大值(最小值)弹出队列q.push(x)将x加入优先队列
和大多数 STL 容器一样,可以使用 q.empty() 判断它是否为空,用 q.size() 获取它的大小。
例:P3378 【模板】堆
用 STL 的优先队列来写这道题代码更加简洁。
// STL 优先队列
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q; // 小根堆
int main()
{
int n; scanf("%d", &n); // 操作次数
while (n--) {
int op, x; scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1) { scanf("%d", &x); q.push(x); }
else if (op == 2) printf("%d\n", q.top());
else q.pop();
}
return 0;
}
例题:P2085 最小函数值
题目给定了若干个二次函数,由于 \(x\) 取的都是正整数,并且三个系数都为正整数,因此函数的取值单调递增且肯定大于 \(0\),要求这些函数生成的所有函数值中最小的 \(m\) 个。
朴素想法
暴力计算每个函数值
朴素的想法是对于每个函数都计算前 \(m\) 个取值,这样会得到 \(n \times m\) 个函数值,最小的 \(m\) 个函数值一定在这个范围内,用一个最大容量限定为 \(m\) 的小根堆始终维护最小的 \(m\) 个函数值,时间复杂度 \(O(nm \log m)\)
优化思路
注意函数的取值是单调递增的,因此实际上可以看作是给定 \(n\) 个排好序的数组,只不过数组并没有真正地存下来,而是给出了下标和值的对应关系。对于每个数组,它们的最小值所在的下标都是 \(1\),假设每个数组都有一个箭头指向 \(1\),需要在所有箭头指向的函数值中找到最小的那个,接下来最小的那个所处的数组的箭头向后移动,指向 \(2\),然后再和其他箭头关联的函数值比较,以此类推。这样一来箭头的后移只需要执行 \(m\) 次即可,而找最小函数值这个过程可以利用一个小根堆来提高效率,总体时间复杂度 \(O(m \log n)\)。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10005;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
struct Node {
int idx, x, f;
};
struct NodeCompare {
bool operator()(const Node &lhs, const Node &rhs) const {
return lhs.f > rhs.f;
}
};
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, NodeCompare> q;
int fn(int idx, int x) {
return a[idx] * x * x + b[idx] * x + c[idx];
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &a[i], &b[i], &c[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) q.push({i, 1, fn(i, 1)});
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Node t = q.top();
q.pop();
printf("%d ", t.f);
q.push({t.idx, t.x + 1, fn(t.idx, t.x + 1)});
}
return 0;
}
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10005;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
struct Node {
int idx, x, f;
bool operator<(const Node &other) const {
return f > other.f;
}
};
priority_queue<Node> q;
int fn(int idx, int x) {
return a[idx] * x * x + b[idx] * x + c[idx];
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &a[i], &b[i], &c[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) q.push({i, 1, fn(i, 1)});
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Node t = q.top();
q.pop();
printf("%d ", t.f);
q.push({t.idx, t.x + 1, fn(t.idx, t.x + 1)});
}
return 0;
}
习题:P6044 [POI 2018] Prawnicy
解题思路
题目的目标是从 \(n\) 个区间 \([l_i, r_i]\) 中选出 \(k\) 个区间,它们的公共交集 \([L,R]\) 的长度 \(R-L\) 最大。
对于任意选定的一组 \(k\) 个区间,它们的公共交集 \([L,R]\) 是由最晚的起始时间 \(L = \max \{ l_i \}\) 和最早的结束时间 \(R = \min \{ r_i \}\) 决定的,目标就是最大化 \(\max \{ r_i \} - \min \{ l_i \}\)。
一个关键的观察是,最优解的交集 \([L,R]\) 的左端点 \(L\),必然是某一个被选中区间的左端点 \(l_i\),因为如果 \(L\) 不是任何一个 \(l_i\),总可以稍微向左移动 \(L\) 直到它碰到某个 \(l_i\),这样不会使任何一个选中的区间失效,但可能会让交集变长。因此可以将所有区间的左端点 \(l_i\) 作为潜在的会议开始时间 \(L\),为了系统地处理,首先将所有 \(n\) 个区间按其左端点 \(l\) 从小到大排序。
从左到右遍历排好序的区间,当遍历到第 \(i\) 个区间 \([l_i,r_i]\) 时,将 \(l_i\) 作为当前会议的候选开始时间 \(L\)。此时,所有已经遍历过的区间(包括当前区间 \(i\))的左端点都 \(\le l_i\),这些区间都是可以在 \(l_i\) 这个时间点开始会议的候选者。目标是从这些候选者中,选出 \(k\) 个,使得它们的 \(\min \{ r \}\) 最大,这等价于选出那 \(k\) 个右端点 \(r\) 最大的区间。为了高效地维护这 \(k\) 个最大的右端点,可以使用一个小根堆,并使其大小始终保持不超过 \(k\)。当遍历到一个新的区间 \(i\) 时,将其右端点 \(r_i\) 加入小根堆。如果此时堆的大小超过了 \(k\),就弹出堆顶元素,因为是小根堆,弹出的总是当前堆中最小的那个右端点,这保证了队列里剩下的 \(k\) 个元素,一定是到目前为止遇到的所有候选区间中,右端点最大的那 \(k\) 个。当堆的大小恰好为 \(k\) 时,就找到了一个由 \(k\) 个区间组成的有效组合。这个组合的会议开始时间 \(L\) 是当前区间的左端点 \(l_i\)(因为按 \(l\) 排序,\(l_i\) 是这 \(k\) 个区间里最晚的开始时间)。这个组合的会议结束时间 \(R\) 是堆顶元素(因为堆顶是这 \(k\) 个最大右端点中的最小值,即 \(\min \{ r \}\))。计算当前长度 \(R-L\),并与已知的最大长度进行比较,如果更优则更新最大长度以及对应的 \([L,R]\)。
遍历完所有 \(n\) 个区间后,就得到了最大可能长度和对应的最优区间 \([L,R]\)。为了找到是哪 \(k\) 个律师,再遍历一次所有原始区间,任何一个满足 \(l_i \le L\) 并且 \(r_i \ge R\) 的区间,都是一个可以参与构成这个最优会议的有效律师,只需从中选出任意 \(k\) 个并输出他们的编号即可。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using std::priority_queue;
using std::vector;
using std::greater;
using std::sort;
using std::max;
const int N = 1000005;
// 定义区间结构体,包含左右端点和原始编号
struct Interval {
int id, l, r;
};
// 存储所有区间的数组
Interval a[N];
int main()
{
int n, k; scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
// 创建一个小根堆,用于存储区间的右端点 r
// 它会自动将最小的 r 放在堆顶
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
// 读取 n 个区间的信息,并存储其原始编号
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &a[i].l, &a[i].r);
a[i].id = i;
}
// 关键步骤:将所有区间按左端点 l 从小到大排序
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, [](const Interval &a, const Interval &b) {
return a.l < b.l;
});
// l, r 用于记录最优解区间的左右端点
int l = 0, r = -1; // 初始化为一个无效区间,保证任何有效解都比它长
// 遍历所有按左端点排好序的区间
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 将当前区间的右端点加入优先队列
pq.push(a[i].r);
// 维护优先队列的大小不超过 k
// 如果超过 k,就弹出最小的右端点,因为它最限制会议的结束时间。
while (pq.size() > k) pq.pop();
// 当队列大小恰好为 k 时,找到了一个由 k 个律师组成的有效会议方案
// 当前会议的开始时间 L = a[i].l (因为排序,这是 k 个区间中最晚的开始时间)
// 当前会议的结束时间 R = pq.top() (这是 k 个区间中最早的结束时间)
// 检查当前方案的长度是否优于已记录的最优解
if (pq.size() == k && pq.top() - a[i].l > r - l) {
// 如果更优,则更新最优解
l = a[i].l; r = pq.top();
}
}
// 输出最大会议时长
printf("%d\n", r - l);
// 第二次遍历,找出是哪些律师参与了最优会议
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 一个律师的区间 [a[i].l, a[i].r) 如果能参与构成最优会议 [l, r)
// 必须满足 a[i].l <= l 且 a[i].r >= r
if (a[i].l <= l && a[i].r >= r) {
printf("%d ", a[i].id); // 输出律师编号
k--; // 计数器减一
if (k == 0) break; // 找到 k 个后就停止
}
}
return 0;
}
例题:P1631 序列合并
可以发现,最小和一定是 \(A[1]+B[1]\),次小和是 \(\min (A[1]+B[2],A[2]+B[1])\),假设次小和是 \(A[2]+B[1]\),那么第三小和就是 \(A[1]+B[2],A[2]+B[2],A[3]+B[1]\) 三者之一。也就是说,当确定 \(A[i]+B[j]\) 为第 \(k\) 小和后,\(A[i+1]+B[j]\) 与 \(A[i]+B[j+1]\) 就加入了第 \(k+1\) 小和的备选答案集合。需要注意的是,\(A[1]+B[2]\) 与 \(A[2]+B[1]\) 都能产生 \(A[2]+B[2]\) 这个备选答案。
考虑到这一点,我们不妨把 \(A\) 和 \(B\) 两个序列的和看成 \(N\) 个有序数组,其中第一个数组为 \(A[1]+B[...]\),第二个数组为 \(A[2]+B[...]\),以此类推。这样一来,就相当于将这 \(N\) 个有序数组合并取出前 \(N\) 小的。因此可以先将 \(A[1]+B[1], A[2]+B[1], ..., A[N]+B[1]\) 这 \(N\) 种情况先加入堆中,若取出的堆顶元素来自于第 \(K\) 个数组,则将 \(A[K]+B[2]\) 这种情况继续放入堆中,直到取够前 \(N\) 种情况。时间复杂度 \(O(N \log N)\)。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100005;
int a[N], b[N], ans[N];
struct Index {
int x, y;
};
struct IndexCompare {
bool operator()(const Index& idx1, const Index& idx2) const {
return a[idx1.x] + b[idx1.y] > a[idx2.x] + b[idx2.y];
}
};
int main()
{
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
priority_queue<Index, vector<Index>, IndexCompare> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) q.push({i, 1});
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Index tmp = q.top(); q.pop();
ans[i] = a[tmp.x] + b[tmp.y];
q.push({tmp.x, tmp.y + 1});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d%c", ans[i], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');
return 0;
}
例题:P2859 [USACO06FEB] Stall Reservations S
按照开始吃草的时间对牛排序,依次对于每头牛,为其分配畜栏。畜栏可以分配给该头牛的条件是其是否被其他牛占用,因此可以维护每个畜栏中最后一头牛结束吃草的时间。如果不存在满足条件的畜栏,则为其新建一个。
可以用一个小根堆维护每个畜栏最后一头牛结束吃草的时间,尝试把当前的牛安排在堆顶(结束时间最早)的畜栏中,则时间复杂度为 \(O(N \log N)\)。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
using pi = pair<int, int>; // 使用 pair 来存储 {结束时间, 牛棚编号}
const int N = 50005;
// 定义 Cow 结构体,存储每头牛的开始时间 (l)、结束时间 (r) 以及原始输入顺序的id
struct Cow {
int l, r, id;
};
Cow c[N]; // 存储所有奶牛的信息
int ans[N]; // 用于存储最终每头牛分配到的牛棚编号,索引为原始id
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n); // 读取奶牛数量 N
// 读取每头奶牛的产奶时段,并记录其原始id
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &c[i].l, &c[i].r);
c[i].id = i; // 记录原始id,以便按原始输入顺序输出结果
}
// 贪心策略的关键第一步:将所有奶牛按开始时间 (l) 从小到大排序
// 这样做是为了确保总是先处理开始挤奶时间较早的奶牛
sort(c + 1, c + n + 1, [](Cow c1, Cow c2) {
return c1.l < c2.l;
});
// 最小优先队列(小根堆),用于管理正在使用的牛棚
// 队列中存储的 pair 格式为 {牛棚的当前占用结束时间, 牛棚的编号}
// 队列顶部 top() 总是结束时间最早的那个牛棚,即最快空闲的牛棚
priority_queue<pi, vector<pi>, greater<pi>> pq;
int cnt = 0; // 记录目前已分配的牛棚总数
// 遍历按开始时间排好序的奶牛
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 检查当前奶牛 c[i] 是否可以被分配到一个已有的牛棚
// 条件1: pq.empty() -> 优先队列为空,表示目前没有牛棚被占用,必须新建一个
// 条件2: pq.top().first >= c[i].l -> 堆顶牛棚(最早空闲的牛棚)的结束时间
// 仍然大于或等于当前奶牛的开始时间。
// 这意味着最早空闲的牛棚也来不及给当前奶牛使用,
// 所有其他牛棚的空闲时间会更晚,因此也无法使用。
// 所以,必须新建一个牛棚。
if (pq.empty() || pq.top().first >= c[i].l) {
cnt++; // 牛棚总数加一,分配一个新的牛棚
pq.push({c[i].r, cnt}); // 将新牛棚的信息(结束时间为当前奶牛的结束时间,编号为cnt)
// 放入优先队列,表示该牛棚已被占用
ans[c[i].id] = cnt; // 记录当前奶牛分配到的牛棚编号
} else {
// 否则 (即 pq 不为空且 pq.top().first < c[i].l),说明堆顶牛棚已经空闲了,可以复用
int t = c[i].r; // 当前奶牛的结束时间
int id = pq.top().second; // 获取即将被复用的牛棚的编号
pq.pop(); // 弹出旧的 {结束时间, 编号},表示该牛棚的旧占用结束
pq.push({t, id}); // 将牛棚的信息更新(新的结束时间为当前奶牛的结束时间,编号不变)
// 重新放入优先队列,表示该牛棚被当前奶牛占用
ans[c[i].id] = id; // 记录当前奶牛分配到的牛棚编号
}
}
// 输出结果
printf("%d\n", cnt); // 第一行输出所需的最小牛棚总数
// 接下来按原始输入顺序输出每头奶牛分配到的牛棚编号
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
对顶堆
如果把大根堆想成一个上宽下窄的三角形,把小根堆想成一个上窄下宽的三角形,那么对顶堆就可以具体地被想象成一个“陀螺”或者一个“沙漏”,通过这两个堆的上下组合,我们可以把一组数据分别加入到对顶堆中的大根堆和小根堆,以维护我们不同的需要。
根据数学中不等式的传递原理,假如一个集合 A 中的最小元素比另一个集合 B 中的最大元素还要大,那么就可以断定: A 中的所有元素都比 B 中元素大。所以,我们把小根堆“放在”大根堆“上面”,如果小根堆的堆顶元素比大根堆的堆顶元素大,那么小根堆的所有元素要比大根堆的所有元素大。
例如给定 \(N\) 个数字,求其前 \(i\) 个元素中第 \(K\) 小的那个元素(\(K\) 值可变)。
我们可以这样解决问题:把大根堆的元素个数限制成 \(K\) 个,由大根堆维护前 \(K\) 小的元素(包含第 \(K\) 个),小根堆维护比第 \(K\) 小的元素还要大的元素。
- 插入:若插入的元素小于大根堆堆顶元素,则将其插入大根堆,否则将其插入小根堆
- 维护:当大根堆的大小大于 \(K\) 时,不断将大根堆堆顶元素取出并插入小根堆,直到大根堆的大小等于 \(K\);当大根堆的大小小于 \(K\) 时,不断将小根堆堆顶元素取出并插入大根堆,直到大根堆的大小等于 \(K\)
- 查询第 \(K\) 小的元素:大根堆堆顶元素
- 删除第 \(K\) 小的元素:删除大根堆堆顶元素
同理,对顶堆还可以用于解决其他“第 \(K\) 小”的变形问题:比如求前 \(i\) 个元素的中位数等。
例题:P1168 中位数
使用两个堆,大根堆维护较小的数,小根堆维护较大的数。这样一来,小根堆的堆顶是较大的数中最小的,大根堆的堆顶是较小的数中最大的。
而求中位数只需要在保证两个堆中元素大小关系的同时,控制两个堆的大小尽可能平衡,这样其中一个堆的堆顶元素即为中位数。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
priority_queue<int> big;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> small;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
small.push(x);
if (i % 2 == 1) {
while (!big.empty() && small.top() < big.top()) {
int st = small.top();
small.pop();
int bt = big.top();
big.pop();
small.push(bt);
big.push(st);
}
int st = small.top();
small.pop();
big.push(st);
printf("%d\n", big.top());
}
}
return 0;
}
习题:P1801 黑匣子
解题思路
控制对顶堆中的大根堆的元素数目伴随着 \(i\) 的增长而增长。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200005;
int a[N];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> h;
priority_queue<int> ans;
int main()
{
int m, n;
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
int pre = 0;
int idx = 0;
while (n--) {
int u;
scanf("%d", &u);
for (int i = pre + 1; i <= u; i++)
ans.push(a[i]);
while (ans.size() > idx) {
h.push(ans.top());
ans.pop();
}
ans.push(h.top());
h.pop();
printf("%d\n", ans.top());
pre = u;
idx++;
}
return 0;
}
习题:P11289 【MX-S6-T1】「KDOI-11」打印
解题思路
题目的核心是模拟一个调度过程:当一个文件打印命令下达时,需要找到“等待时间最短”的打印机来执行任务。
整个过程是由一系列“文件打印命令下达”的事件驱动的,这些事件按其发生时间排序。因此,第一步就是将所有文件按照其下达时间从小到大进行排序,这样就可以按时间顺序处理每个文件。
在任何时刻,打印机都处于两种状态之一:空闲或工作中。需要一种高效的方式来找到“等待时间最短”的打印机。对于空闲的打印机,它们的等待时间都是 0,根据规则“如有多个,选择编号最小的”,应该选择编号最小的那台。对于工作中的打印机,它们的等待时间是打印机完成任务的时刻减去新文件下达的时刻,如果所有打印机都在工作,需要选择那个完成时刻最早的打印机。所以,需要两种不同的数据结构来管理这两种状态的打印机。
需要一个能快速提供“编号最小”的空闲打印机的数据结构,一个小根堆非常适合这个任务,把编号最小的打印机放在堆顶。需要一个能快速提供“完成任务时间最早”的打印机的数据结构,一个小根堆同样适用,但这个小根堆应当要将完成时刻早的打印机(若完成时刻相等,看编号小)放到堆顶,这需要自定义堆中元素的比较规则。
按时间顺序遍历每一个排好序的文件,在处理这个文件之前,先将本来处于工作中状态的打印机中完成时间在当下之前的弹出,并放入到空闲打印机中。接下来选择打印机,如果有空闲打印机,根据规则,应选择编号最小的空闲打印机,这正是空闲打印机的堆顶,取出之后,计算这台打印机新的完成时刻,再放入工作中打印机中。如果所有打印机都在工作,根据规则,应选择等待时间最短的,即完成时刻最早的那台,这正是工作中打印机的堆顶,取出之后计算它的新完成时刻(原来的完成时刻加上该文件打印时间)并重新加入到工作中打印机中。
在处理过程中记录每个打印机打印的文件编号,然后按格式输出。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using std::sort;
using std::priority_queue;
using std::vector;
using std::greater;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 200005;
// ready: 存放空闲打印机的编号,按编号构成小根堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> ready;
// tm[i]: 记录打印机 i 完成所有分配给它的任务的时刻
ll tm[N];
// 文件结构体
struct File {
int s, t, id; // s: 打印时间, t: 下达时刻, id: 原始编号
// 重载小于号,用于按 t 排序
bool operator<(const File &other) const {
return t < other.t;
}
};
File f[N];
// working 优先队列的自定义比较器
struct Compare {
bool operator()(const int lhs, const int rhs) const {
// 主要按完成时刻 tm 构建小根堆
// 如果完成时刻相同,按编号构建小根堆
return tm[lhs] != tm[rhs] ? tm[lhs] > tm[rhs] : lhs > rhs;
}
};
// working: 存放工作中的打印机编号,使用自定义比较器
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Compare> working;
// ans[i]: 存储打印机 i 打印的所有文件的编号
vector<int> ans[N];
int main()
{
int n, m; scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
// 读取文件信息
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &f[i].s, &f[i].t); f[i].id = i;
}
// 按文件下达时刻 t 排序
sort(f + 1, f + n + 1);
// 初始化:所有打印机都是空闲的,完成时刻为0
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
ready.push(i); tm[i] = 0;
}
// 按时间顺序处理每个文件
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 1. 更新状态:将已完成任务的打印机从 working 移到 ready
while (!working.empty() && tm[working.top()] <= f[i].t) {
ready.push(working.top()); working.pop();
}
// 2. 选择打印机并分配任务
if (ready.empty()) {
// Case A: 所有打印机都在忙
// 选择最早完成任务的打印机 (working.top())
int id = working.top();
working.pop();
// 任务在其原完成时间后排队,更新完成时间
tm[id] += f[i].s;
// 将更新后的打印机重新放入 working 中
working.push(id);
// 记录任务
ans[id].push_back(f[i].id);
} else {
// Case B: 有空闲打印机
// 选择编号最小的空闲打印机 (ready.top())
int id = ready.top();
ready.pop();
// 打印机从文件下达时刻 t 开始工作,更新完成时间
tm[id] = f[i].t + f[i].s;
// 将打印机移入 working 中
working.push(id);
// 记录任务
ans[id].push_back(f[i].id);
}
}
// 3. 输出结果
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
printf("%d", (int)ans[i].size()); // 打印文件数量
sort(ans[i].begin(), ans[i].end()); // 按要求对文件编号排序
for (int id : ans[i]) printf(" %d", id); // 打印文件编号
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
习题:P7913 [CSP-S 2021] 廊桥分配
解题思路
题目的核心是,将 \(n\) 个廊桥分配给国内区和国际区(例如,国内 \(i\) 个,国际 \(n-i\) 个),使得停靠廊桥的飞机总数最多。
一个直接的想法是枚举国内区的廊桥数量 \(i\)(从 \(0\) 到 \(n\)),然后对于每种分配方案,模拟一遍飞机的停靠过程,计算总数,最后取最大值。
题目的“先到先得”原则有一个非常重要的推论:一架飞机最终停靠在哪一个廊桥,与廊桥的具体编号无关,只与它抵达时空闲的廊桥的数量有关。更进一步,可以发现一个单调性:如果一架飞机在有 \(k\) 个廊桥时可以停靠,那么在有 \(k+1\) 个廊桥时,它也一定可以停靠。这意味着,给国内或者国际区增加一个廊桥(从 \(i\) 变为 \(i+1\)),不会导致原来能停靠的飞机变得不能停靠,只可能让一些原本不能停靠的飞机现在可以停靠了。因此,可以预先计算出:当国内区有 \(i\) 个廊桥时,能停靠多少架飞机,以及当国际区有 \(j\) 个廊桥时,能停靠多少架飞机。
以国内区为例,如何计算上述的结果?可以假设国内区有无限个廊桥,并按编号 \(1,2,3,\dots\) 排列。第一架抵达的飞机,停靠在 1 号廊桥。第二架抵达的飞机,如果 1 号廊桥空了,它也停 1 号;如果 1 号没空,它就停 2 号。这个过程遵循一个贪心策略:新抵达的飞机总是会选择编号较小的可用廊桥。通过这个过程,可以确定每一架飞机(如果能停靠的话)会停靠在几号廊桥。用 \(cnt_k\) 记录下在上述无限廊桥的假设下,恰好使用了 \(k\) 号廊桥的飞机数量。那么,如果实际只有 \(i\) 个廊桥,能停靠的飞机总数就是 \(cnt_1 + cnt_2 + \cdots + cnt_k\),这相当于一个前缀和。国际航班的处理计算过程同理。
如何高效地实现上述“分配到最小编号可用廊桥”的贪心策略?这需要同时管理“正在被占用的廊桥”和“已经空闲的廊桥”。可以使用一个小根堆存放正在被占用的廊桥,这个小根堆的堆顶应当是最先变回空闲的廊桥;使用另一个小根堆存放当前空闲的廊桥,它的堆顶是编号最小的。
将航班按抵达时间从小到大排序,依次处理每一架飞机。刚开始所有廊桥都是空闲的。处理每一架飞机时,先检查是否有廊桥在当前飞机抵达前就已经空闲了,如果有,将这些廊桥从占用廊桥中弹出,并加入到空闲廊桥中。此时,空闲廊桥堆中存放了所有当下可用的廊桥,取出堆顶的廊桥(编号最小的那个),分配给当前飞机,将这个廊桥的使用次数加一,然后将这个廊桥新的占用信息更新,推入占用廊桥堆。这个过程结束后,\(cnt\) 就计算好了。
根据 \(cnt\) 数组,计算出前缀和数组,国内区/国际区计算过程类似。
最后,枚举国内区的廊桥数量 \(i\)(从 \(0\) 到 \(n\)),此时国际区有 \(n-i\) 个廊桥,将两边预处理的结果加起来就是该分配方案下的总停靠数。遍历所有 \(i\),找出这个和的最大值,即为最终答案。
参考代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
// 飞机结构体
struct Flight {
int arr; // 抵达时间
int lv; // 离开时间
// 重载小于号,用于按抵达时间排序
bool operator<(const Flight& other) const {
return arr < other.arr;
}
};
Flight f1[N], f2[N]; // 分别存储国内和国际航班
int bri[N]; // bri[i] 记录廊桥 i 下一次变为空闲的时刻
int cnt[N]; // cnt[i] 记录在无限廊桥假设下,i 号廊桥停靠过的飞机总数
int ans1[N], ans2[N]; // 分别是国内/国际 cnt 数组的前缀和
// 自定义比较器,用于 occ 优先队列
// 堆顶是空闲时间 bri[i] 最小的廊桥
struct Compare {
bool operator()(int i, int j) {
return bri[i] > bri[j];
}
};
/**
* @brief 核心处理函数,模拟无限廊桥下的分配情况
* @param f 飞机数组 (已按抵达时间排序)
* @param n 总廊桥数 (用于初始化)
* @param m 飞机总数
*/
void process(Flight f[N], int n, int m) {
// 初始化 bri 和 cnt 数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
bri[i] = 0;
cnt[i] = 0;
}
// free: 存放空闲廊桥编号的小根堆,编号小的优先
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> free;
// occ: 存放被占用廊桥编号的小根,按空闲时间早的优先
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Compare> occ; // occupied
// 初始时,所有 n 个廊桥都是空闲的
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) free.push(i);
// 按抵达顺序处理每一架飞机
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
// 1. 释放廊桥:
// 将所有在当前飞机抵达前已经空闲的廊桥,从 occ 移到 free
while (!occ.empty() && bri[occ.top()] <= f[i].arr) {
free.push(occ.top());
occ.pop();
}
// 2. 分配廊桥:
// 如果有空闲廊桥
if (!free.empty()) {
// 取出编号最小的空闲廊桥 u
int u = free.top(); free.pop();
// 分配给当前飞机
bri[u] = f[i].lv; // 更新廊桥 u 的空闲时间
cnt[u]++; // 廊桥 u 的使用次数加一
// 将廊桥 u 放入被占用廊桥中
occ.push(u);
}
// 如果没有空闲廊桥,则该飞机停靠远机位,什么也不做
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m1, m2;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m1, &m2);
// 读取航班信息
for (int i = 1; i <= m1; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &f1[i].arr, &f1[i].lv);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m2; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &f2[i].arr, &f2[i].lv);
}
// 按抵达时间排序
sort(f1 + 1, f1 + m1 + 1);
sort(f2 + 1, f2 + m2 + 1);
// --- 预计算国内航班 ---
process(f1, n, m1);
// 计算前缀和:ans1[i] 表示有 i 个国内廊桥时能停靠的总数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans1[i] = ans1[i-1] + cnt[i];
}
// --- 预计算国际航班 ---
process(f2, n, m2);
// 计算前缀和:ans2[i] 表示有 i 个国际廊桥时能停靠的总数
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans2[i] = ans2[i-1] + cnt[i];
}
int ans = 0;
// --- 合并求解 ---
// 枚举分配给国内区的廊桥数 i (从 0 到 n)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int j = n - i;
// 给国内i个廊桥,给国际j个廊桥
// 计算总停靠数并更新最大值
ans = max(ans, ans1[i] + ans2[j]);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号