实体类
package com.example.pojo;
public class Account {
private Integer aid;
private String aname;
private String acontent;
}
数据访问层
package com.example.mapper;
import com.example.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountMapper {
int save (Account account) ;
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.AccountMapper" >
<!--
int save (Account account) ;
private Integer aid;
private String aname;
private String acontent
-->
<insert id="save" parameterType="account" >
insert into accounts values (#{aid}, #{aname}, #{acontent})
</insert>
</mapper>
业务逻辑层
package com.example.service;
import com.example.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountService {
int save (Account account) ;
}
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.mapper.AccountMapper;
import com.example.pojo.Account;
import com.example.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public int save (Account account) {
int num = accountMapper.save(account);
if (num == 1 ){
System.out.println("账户创建成功!" );
}else {
System.out.println("账户创建失败!" );
}
return num;
}
}
测试1
package com.example.test;
import com.example.pojo.Account;
import com.example.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestAccountSave {
@Test
public void testAccountSave () {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("applicationContext_service.xml" );
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl" );
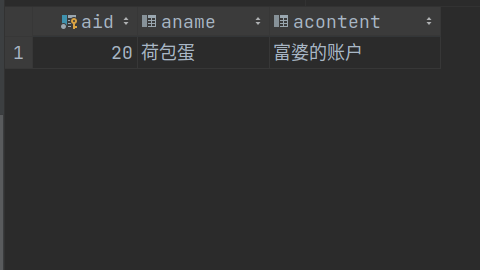
int num = accountService.save(new Account (20 , "荷包蛋" , "富婆的账户" ));
System.out.println("num: " + num);
}
测试输出
Logging initialized using 'class org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl' adapter.
Creating a new SqlSession
SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@5dbe30be] was not registered for synchronization because synchronization is not active
Aug 28 , 2022 3 :42 :05 PM com.alibaba.druid.support.logging.JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl info
INFO: {dataSource-1 } inited
JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@62c5bbdc] will not be managed by Spring
= => Preparing: insert into accounts values (?, ?, ?)
==> Parameters: 20 (Integer), 荷包蛋(String), 富婆的账户(String)
<== Updates: 1
Closing non transactional SqlSession [org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@5dbe30be]
账户创建成功!
num: 1
Process finished with exit code 0
测试2
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public int save (Account account) {
int num = accountMapper.save(account);
if (num == 1 ){
System.out.println("账户创建成功!" );
}else {
System.out.println("账户创建失败!" );
}
System.out.println(1 /0 );
return num;
}
}
测试输出
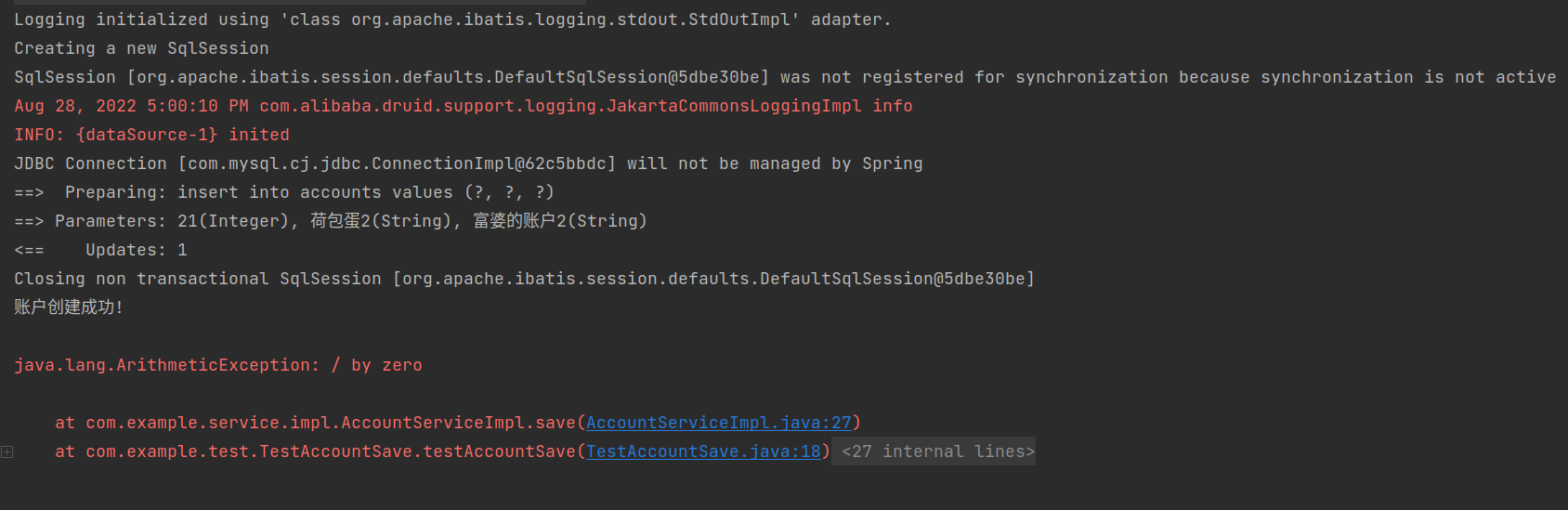
从控制台的输出可以看到,在出错前sql语句正常执行完毕,在出错后程序报错终止,此时不能确定新的账户信息有没有导入数据库
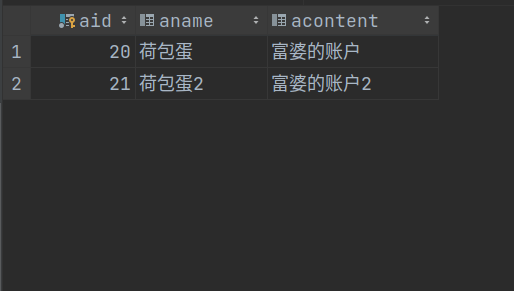
从数据表中可以确定,此时的SM框架没有开启自动回滚机制,虽然程序出错,但是在程序出错前导入到数据表中的数据是有效的,这显然不符合业务需求
applicationContext_service.xml
在业务逻辑层的配置文件applicationContext_service.xml中(也就是上一篇博文Spring 14: SM框架(Spring + MyBatis)初步整合中的该文件),添加sm框架的事务配置
<bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" />
</bean >
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" />
测试3
@Test
public void testAccountSave () {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("applicationContext_service.xml" );
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl" );
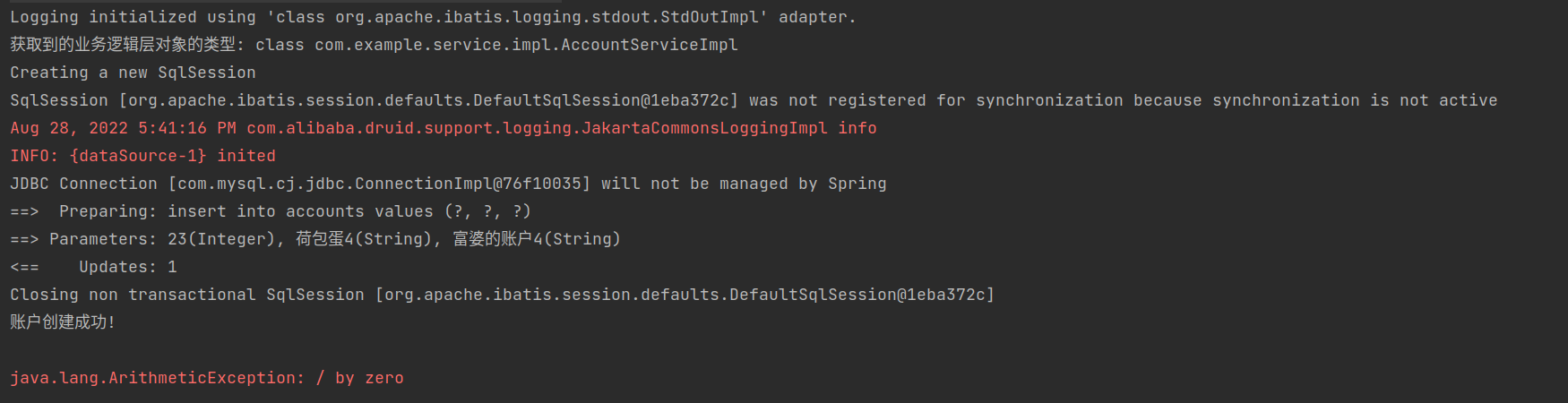
System.out.println("获取到的业务逻辑层对象的类型: " + accountService.getClass());
int num = accountService.save(new Account (23 , "荷包蛋4" , "富婆的账户4" ));
System.out.println("num: " + num);
}
测试输出
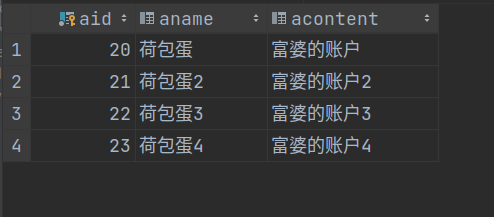
从控制台的输出可以看出,此时获取到的业务逻辑层对象的类型:class com.example.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl,不是jdk动态代理的类型,说明事务切面并没有真正开启
从数据表可以看出,虽然在applicationContext_service.xml中添加了事务机制,但是数据的回滚并没有成功
注意
上面虽然在SM框架中添加了事务配置,但是在添加了事务的注解驱动后,并没有在业务逻辑层的业务实现类中使用该注解,导致事务切面并没有真正切入
测试4
@Service
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
}
测试输出
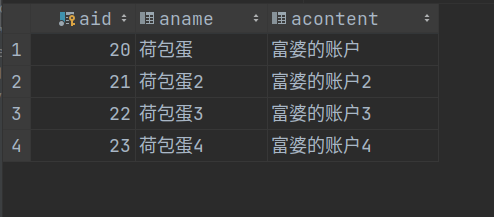
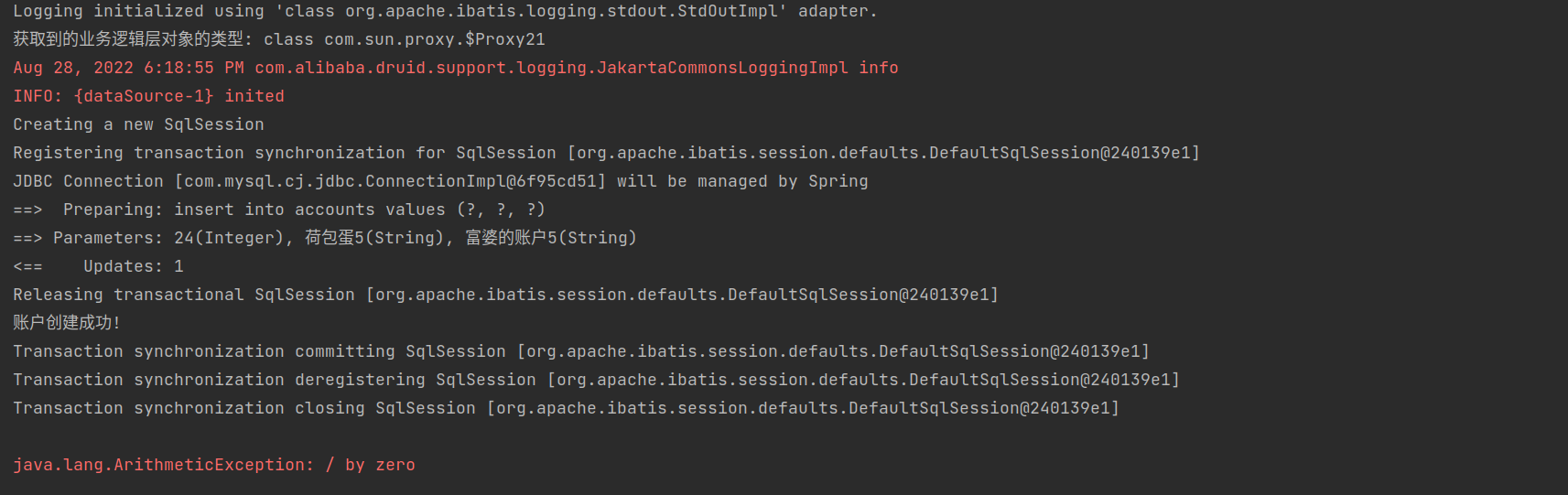
从控制台的输出可以看出,此时获取到的业务逻辑层对象的类型:class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy21,是jdk动态代理的类型,说明事务切面真正导入
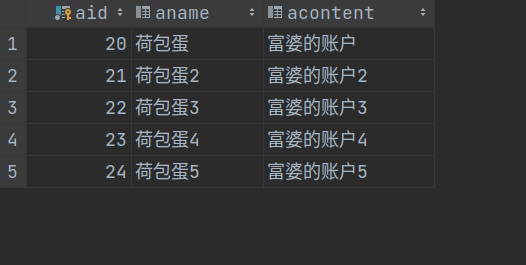
从数据表可以看出数据的回滚也确实执行成功,记录"24 荷包蛋5 富婆的账户5"在程序出错后成功回滚,并没有真正导入到数据表中
设置不回滚属性
上述事务的注解驱动还可以根据程序发生的异常名称,选择不回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, noRollbackForClassName = {"异常名称1", "异常名称2", "异常名称3"})
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, noRollbackForClassName = "异常名称1")
测试5
当设置:发生算术异常不回滚时,出现该种名称的错误时,已经导入到数据库中的数据,不会回滚
@Service
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, noRollbackForClassName = "ArithmeticException")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public int save (Account account) {
int num = accountMapper.save(account);
if (num == 1 ){
System.out.println("账户创建成功!" );
}else {
System.out.println("账户创建失败!" );
}
System.out.println(1 /0 );
return num;
}
}
测试输出
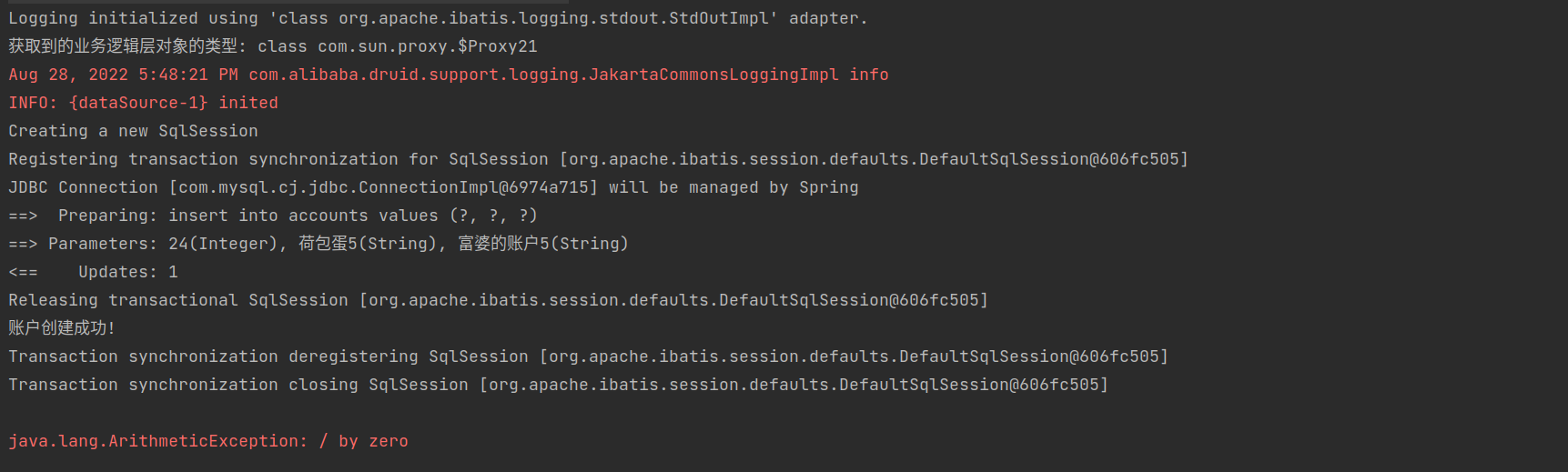
从控制台可以看出,程序出错前sql语句执行成功,之后程序终止,也可以看到jdk动态代理成功执行,事务切面成功导入
从数据表可以看到,该记录,成功导入数据表并有效,是因为我们回避了事务机制在遇到算术异常时的回滚机制,并未回滚已经导入的数据



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术