.Net Core微服务化ABP之五——IdentityServer4权限服务
架构图
设想中,客户端带有token的请求经由nginx,来到ocelot网关后,应先调用权限服务进行认证,认证成功后再往下游服务转发,所以本篇主要内容就是建立独立的权限服务,来完成认证以及授权的功能。
基于IdentityService4建立权限服务
最开始看到了ABP官方给出的文章 Identity Server,考虑到权限服务需要与数据库有关系,所以选择基于abp模板开始
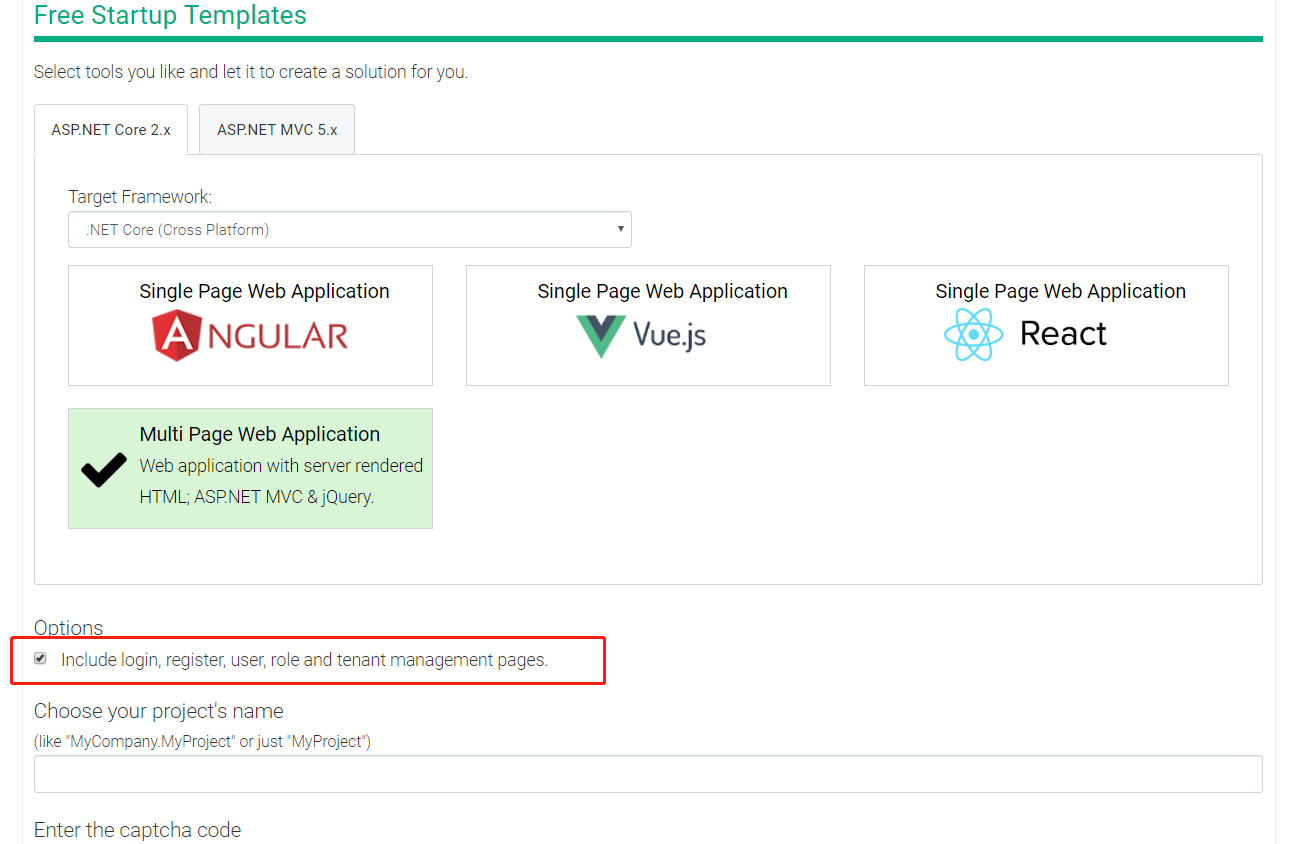
务必选择include login...,会包含部分必须的IdentityServer4依赖包
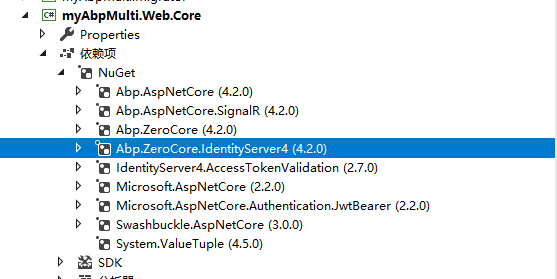
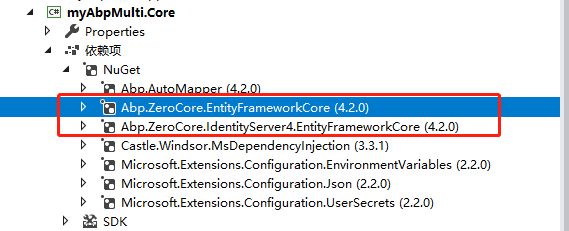
考虑到Mvc项目带有太多不相关的视图、静态资源,选择用Host项目,给Web.Core项目安装Abp.ZeroCore.IdentityServer4。因为EntityFrameworkCore项目依赖于Core项目,所以在Core项目安装Abp.ZeroCore.EntityFrameworkCore和Abp.ZeroCore.IdentityServer4.EntityFrameworkCore(仅用于演示功能实现,实际项目可能会有变化)
修改Core项目的myAbpMultiCoreModule
[DependsOn(typeof(AbpZeroCoreModule), typeof(AbpZeroCoreIdentityServerEntityFrameworkCoreModule))] public class myAbpMultiCoreModule : AbpModule { //... }
修改Starup.cs
using Abp.AspNetCore; using Abp.Castle.Logging.Log4Net; using Abp.Extensions; using Abp.IdentityServer4; using Castle.Facilities.Logging; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Cors.Internal; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using myAbpMulti.Authentication.JwtBearer; using myAbpMulti.Authorization.Users; using myAbpMulti.Configuration; using myAbpMulti.Identity; using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger; using System; using System.Linq; using System.Reflection; namespace myAbpMulti.Web.Host.Startup { public class Startup { private const string _defaultCorsPolicyName = "localhost"; private readonly IConfigurationRoot _appConfiguration; public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env) { _appConfiguration = env.GetAppConfiguration(); } public IServiceProvider ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // MVC services.AddMvc( options => options.Filters.Add(new CorsAuthorizationFilterFactory(_defaultCorsPolicyName)) ); IdentityRegistrar.Register(services); services.AddIdentityServer() .AddDeveloperSigningCredential() .AddInMemoryIdentityResources(IdentityServerConfig.GetIdentityResources()) .AddInMemoryApiResources(IdentityServerConfig.GetApiResources()) //.AddTestUsers(IdentityServerConfig.GetUsers().ToList()) .AddInMemoryClients(IdentityServerConfig.GetClients()) .AddAbpPersistedGrants<IAbpPersistedGrantDbContext>() .AddAbpIdentityServer<User>(); AuthConfigurer.Configure(services, _appConfiguration); //services.AddSignalR(); // Configure CORS for angular2 UI services.AddCors( options => options.AddPolicy( _defaultCorsPolicyName, builder => builder .WithOrigins( // App:CorsOrigins in appsettings.json can contain more than one address separated by comma. _appConfiguration["App:CorsOrigins"] .Split(",", StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries) .Select(o => o.RemovePostFix("/")) .ToArray() ) .AllowAnyHeader() .AllowAnyMethod() .AllowCredentials() ) ); // Swagger - Enable this line and the related lines in Configure method to enable swagger UI services.AddSwaggerGen(options => { options.SwaggerDoc("v1", new Info { Title = "myAbpMulti API", Version = "v1" }); options.DocInclusionPredicate((docName, description) => true); // Define the BearerAuth scheme that's in use options.AddSecurityDefinition("bearerAuth", new ApiKeyScheme() { Description = "JWT Authorization header using the Bearer scheme. Example: \"Authorization: Bearer {token}\"", Name = "Authorization", In = "header", Type = "apiKey" }); }); // Configure Abp and Dependency Injection return services.AddAbp<myAbpMultiWebHostModule>( // Configure Log4Net logging options => options.IocManager.IocContainer.AddFacility<LoggingFacility>( f => f.UseAbpLog4Net().WithConfig("log4net.config") ) ); } public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { app.UseAbp(options => { options.UseAbpRequestLocalization = false; }); // Initializes ABP framework. app.UseCors(_defaultCorsPolicyName); // Enable CORS! app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseJwtTokenMiddleware("IdentityBearer"); app.UseIdentityServer(); app.UseAbpRequestLocalization(); //app.UseSignalR(routes => //{ // routes.MapHub<AbpCommonHub>("/signalr"); //}); app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "defaultWithArea", template: "{area}/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); // Enable middleware to serve generated Swagger as a JSON endpoint app.UseSwagger(); // Enable middleware to serve swagger-ui assets (HTML, JS, CSS etc.) app.UseSwaggerUI(options => { options.SwaggerEndpoint(_appConfiguration["App:ServerRootAddress"].EnsureEndsWith('/') + "swagger/v1/swagger.json", "myAbpMulti API V1"); options.IndexStream = () => Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly() .GetManifestResourceStream("myAbpMulti.Web.Host.wwwroot.swagger.ui.index.html"); }); // URL: /swagger } } }
重点在于 IdentityRegistrar.Register(services) 之后的 services.AddIdentityServer(),以及app.UseAuthentication() 之后的两行。其中的IdentityServerConfig和IdentityRegistrar类放在了同一个文件,如下:
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Abp.IdentityServer4; using IdentityServer4.Models; using IdentityServer4.Test; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using myAbpMulti.Authorization; using myAbpMulti.Authorization.Roles; using myAbpMulti.Authorization.Users; using myAbpMulti.Editions; using myAbpMulti.MultiTenancy; namespace myAbpMulti.Identity { public static class IdentityRegistrar { public static IdentityBuilder Register(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddLogging(); return services.AddAbpIdentity<Tenant, User, Role>() .AddAbpTenantManager<TenantManager>() .AddAbpUserManager<UserManager>() .AddAbpRoleManager<RoleManager>() .AddAbpEditionManager<EditionManager>() .AddAbpUserStore<UserStore>() .AddAbpRoleStore<RoleStore>() .AddAbpLogInManager<LogInManager>() .AddAbpSignInManager<SignInManager>() .AddAbpSecurityStampValidator<SecurityStampValidator>() .AddAbpUserClaimsPrincipalFactory<UserClaimsPrincipalFactory>() .AddPermissionChecker<PermissionChecker>() .AddDefaultTokenProviders(); } } public static class IdentityServerConfig { public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("default-api", "Default (all) API") }; } public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources() { return new List<IdentityResource> { new IdentityResources.OpenId(), new IdentityResources.Profile(), new IdentityResources.Email(), new IdentityResources.Phone() }; } public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() { return new List<Client> { new Client { ClientId = "client", AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ClientCredentials.Union(GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword).ToList(), AllowedScopes = {"default-api"}, ClientSecrets = { new Secret("secret".Sha256()) } } }; } } }
因为我们将用户信息放在数据库中,所以还要修改DbContext
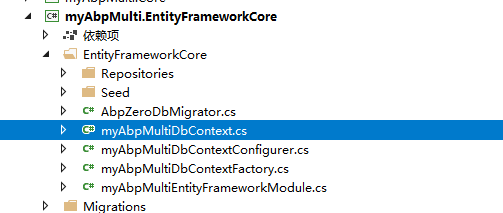
修改为:
using Abp.IdentityServer4; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Abp.Zero.EntityFrameworkCore; using myAbpMulti.Authorization.Roles; using myAbpMulti.Authorization.Users; using myAbpMulti.MultiTenancy; namespace myAbpMulti.EntityFrameworkCore { public class myAbpMultiDbContext : AbpZeroDbContext<Tenant, Role, User, myAbpMultiDbContext>, IAbpPersistedGrantDbContext { /* Define a DbSet for each entity of the application */ public DbSet<PersistedGrantEntity> PersistedGrants { get; set; } public myAbpMultiDbContext(DbContextOptions<myAbpMultiDbContext> options) : base(options) { } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); modelBuilder.ConfigurePersistedGrantEntity(); } } }
修改完成后需要更新数据库,执行Add-Migration "xxx" 和 Update-Database
至此IdentityServer的服务端配置完毕
根据IdentityServerConfig中填写的client_id,client_secret,grant_type 填写postman参数,username和password为数据表abpusers中存储的user信息
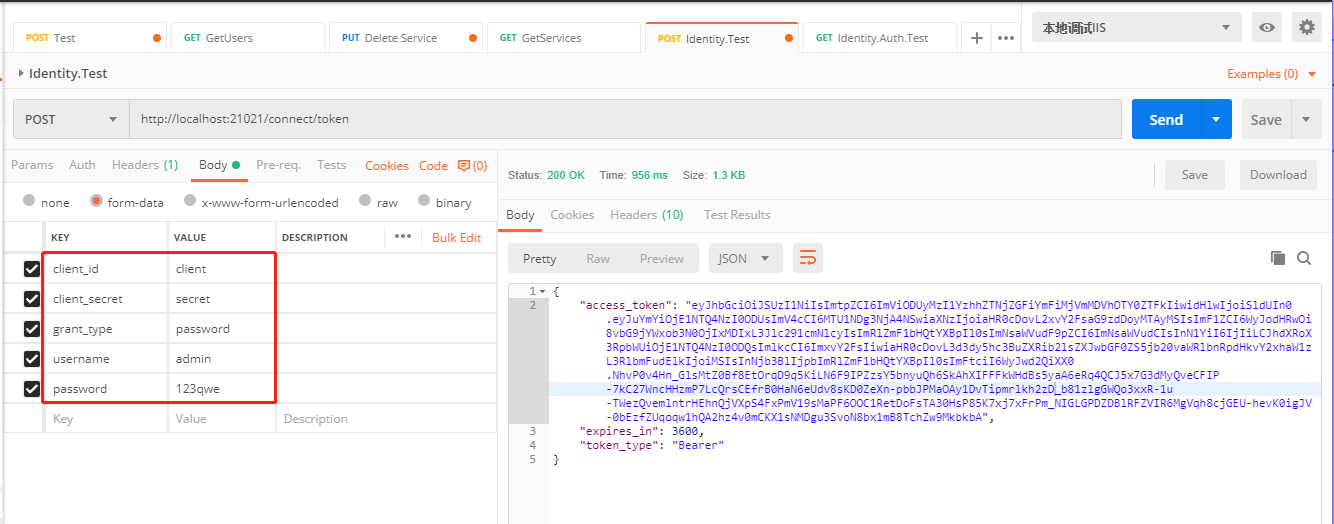
如果请求成功,可以在右侧获取到返回的token信息
向WebApi项目整合权限
在权限服务体系中,IdentityServer可以视作服务端,那其他所有需要权限验证的api服务,就全部属于客户端。
回到myAbpBasic.Web项目,在Core项目安装IdentityServer4.AccessTokenValidation
修改Startup.cs
public IServiceProvider ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { //Configure DbContext // Mvc // identity server services.AddMvcCore().AddAuthorization().AddJsonFormatters(); services.AddAuthentication("IdentityBearer").AddIdentityServerAuthentication("IdentityBearer", options => { options.Authority = "http://localhost:21021/"; options.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; options.ApiName = "default-api"; // match with configuration in IdentityServer }); // Swagger }
AddAuthentication后的参数,必须和权限服务中UseJwtTokenMiddleware名称一致。Authority自行改为权限服务地址。
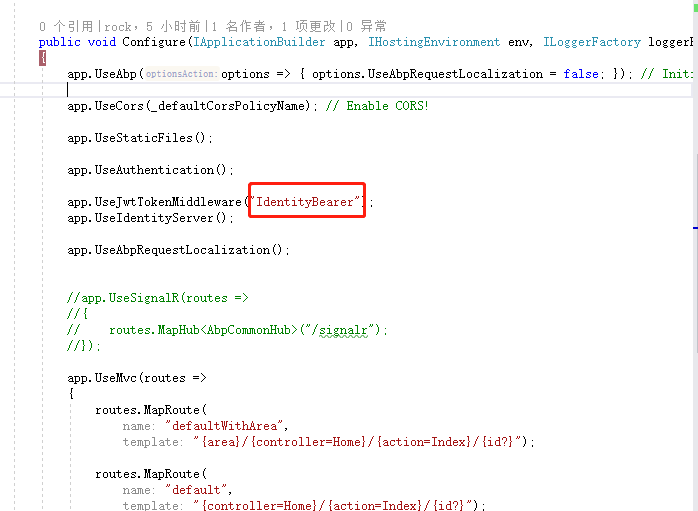
在app.UseMvc之前调用app.UseAuthentication()
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } // authentication app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseMvc(); // swagger ....... }
为了方便演示,给Default控制器Get方法增加Authorize特性,直接访问该api,会提示401
修改postman配置
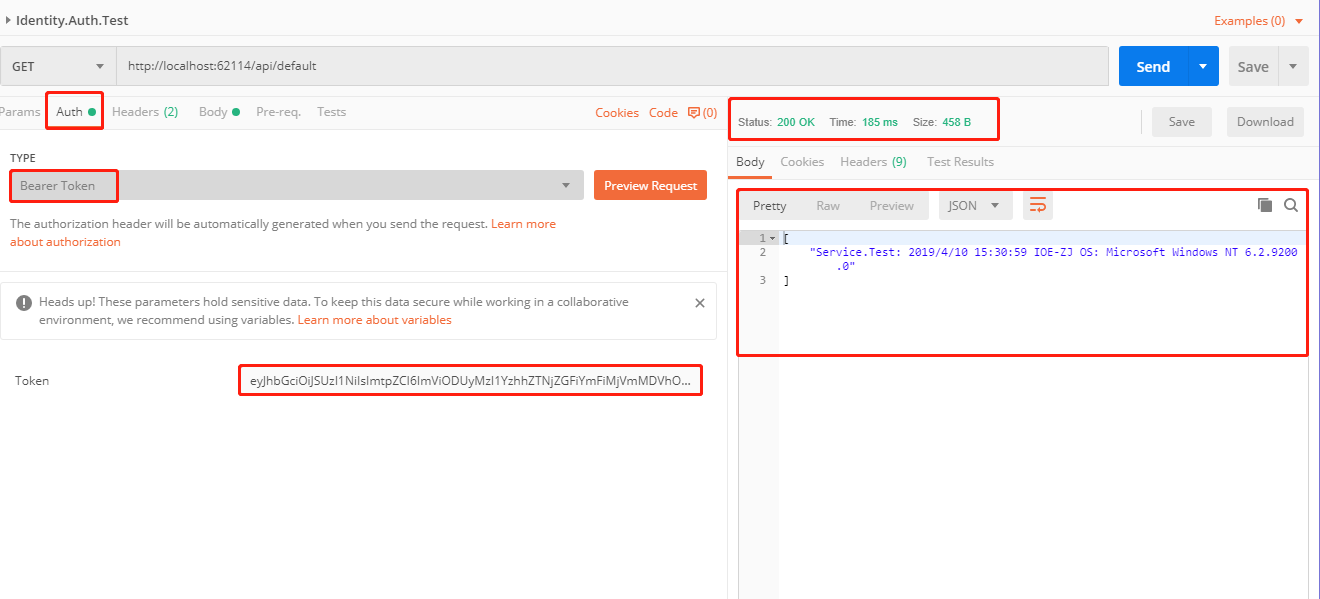
成功取得对应结果。
向MVC项目整合权限
暂缓,理论上mvc访问受权限保护的页面,会自动跳转到权限服务进行验证,成功后自动跳回原本页面,页面呈现后,左右的接口数据都需要直接从微服务获取了。不再经过mvc控制器。那么客户端需要拿到这个token才行。
权限角色区分
权限分为 系统角色权限和业务角色权限
系统角色是指整体平台的用户角色,大体上将app用户、网站用户、后台用户分开,分别拥有不同的接口权限。系统角色需要在每个api服务的每个接口进行标记。规划将系统角色分为以下几种
app_installer_user 师傅app
app_customer_user 商家app
web_customer_user 商家网站
web_admin_user 后台最高权限
web_manager_user 后台运维管理系统
web_business_user 后台业务配置系统
web_order_user 后台订单系统
业务角色是指业务子系统内部的权限划分。比如订单处理系统中就有订单查询、修改、派单、改派等权限,这个权限列表是固化在代码中的,业务系统中可以配置角色,以及每个角色拥有哪些权限。这部分权限不会出现在api服务中,而应该只在mvc客户端或api网关中出现,不涉及应用服务。mvc客户端可以轻松控制视图,但提交数据的接口应该是通过服务中心直接调用下游接口的,这部分就变得不可控。
本文涉及的是前者系统角色权限。用户登录验证后颁发token,同时该token也有对应的系统角色,一般而言,一个用户账号只对应一种客户端角色。基本上不存在一个账号既是商家,又是师傅的情况。
再次思考,identityserver中带的Claims-role控制不适合当前系统角色场景,因为它是用户-角色对应关系的,更像是业务角色。我们需要的是客户端-token-角色,也就是一类客户端同属一个角色,比如所有的商家版app客户端,都属于app_customer_user,那么显然可以简单地使用identityServer4自带的apiresource,clientid来控制。同时还允许一个账号(客户端)可能有多重权限的问题,admin_user有运维、业务、订单的所有权限。比如这样配置:
/// <summary> /// 允许使用认证服务的api列表 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("default-api", "Default (all) API"), new ApiResource("app_installer_user", "Default (all) API1"), new ApiResource("app_customer_user", "Default (all) API2"), new ApiResource("web_customer_user", "Default (all) API3"), new ApiResource("web_admin_user ", "Default (all) API4"), new ApiResource("web_manager_user ", "Default (all) API5"), new ApiResource("web_business_user ", "Default (all) API6"), new ApiResource("web_order_user ", "Default (all) API7") }; } /// <summary> /// 允许使用认证服务的应用客户端 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() { return new List<Client> { new Client { ClientId = "client", AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, AllowedScopes = {"default-api"}, ClientSecrets = new[]{ new Secret("secret".Sha256())} }, new Client { ClientId = "app_installer_client", AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, AllowedScopes = {"app_installer_user"}, ClientSecrets = new[]{ new Secret("secret".Sha256())} }, new Client { ClientId = "web_admin_client", AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, AllowedScopes = { "web_admin_user", "web_manager_user", "web_business_user", "web_order_user", }, ClientSecrets = new[]{ new Secret("secret".Sha256())} } }; }
2019-4-11 10:15:57 之前的理解完全错误,ApiResource指的是提供api服务,比如serviceorder,servicepartner,对我们来说client只需要设置一个default即可,因为暂时没有需要限制某种类型客户端只能访问几个服务。
public static class IdentityServerConfig { /// <summary> /// 允许使用认证服务的api列表 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("serviceorder", "Default (all) API"), new ApiResource("servicepartner", "Default (all) API1"), }; } /// <summary> /// /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources() { return new List<IdentityResource> { new IdentityResources.OpenId(), new IdentityResources.Profile(), new IdentityResources.Email(), new IdentityResources.Phone() }; } /// <summary> /// 允许使用认证服务的应用客户端 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() { return new List<Client> { new Client { ClientId = "default_client", AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, AllowedScopes = { "serviceorder", "servicepartner", }, ClientSecrets = new[]{ new Secret("secret".Sha256())} } }; } }
继续说这个权限体系,系统角色的实现好像有点困难。其实本质上是要限制api网关可以访问的api范围,可能用swagger的分组,为每个api网关单独配置swagger.json可以解决。每个网关只能看到自己有权限的api文档(不知道能不能限制权限),或者是本身网关程序上写的api接口。这样完美解决系统角色的问题。
继续看业务角色问题,业务角色权限为了和api服务解耦,个人觉得应该放在上层api网关处理。目前打算是将各个子系统独立开来,这样每个子系统的MVC程序(对应mpa应用)(or api网关程序,对应spa应用)就需要数据库来存储这些权限规则,考虑到每个应用都需要这个数据库,而且数据库结构是类似的,所以建立一个后台权限服务,考虑和基础服务合并。这个数据库包含后台用户表,后台角色表,角色用户表,角色权限表,用户的注册添加是在这个服务进行的,只不过注册成功的同时需要向sso(identityserver)注册新用户。子系统mvc程序读取所有权限列表,赋权给对应用户,并将角色-权限对应关系(增加字段,api网关名称)保存在数据库中,这步再具体开发应用时再实现,现在只需要控制apigateway项目的权限即可。
参考文章:
https://aspnetboilerplate.com/Pages/Documents/Zero/Identity-Server
https://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/identityserver4_foundation_and_quickstart_01.html
https://aspnetboilerplate.com/Pages/Documents/Authorization



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号