git push 原因以及问题!
$ git push ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git master // 把本地仓库提交到远程仓库的master分支中
$ git remote add origin ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git
$ git push origin master
这两个操作是等价的,第二个操作的第一行的意思是添加一个标记,让origin指向ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git,也就是说你操 作origin的时候,实际上就是在操作ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git。origin在这里完全可以理解为后者 的别名。
注意:需要说明的是,默认情况下这条语句等价于提交本地的master仓库到远程仓库,并作为远程的master分支。
如果想把本地的某个分支test提交到远程仓库,并作为远程仓库的master分支,或者作为另外一个名叫test的分支,那么可以这么做。
$ git push origin test:master // 提交本地test分支作为远程的master分支
$ git push origin test:test // 提交本地test分支作为远程的test分支
如果想删除远程的分支呢?类似于上面,如果:左边的分支为空,那么将删除:右边的远程的分支。
To prevent you from losing history, non-fast-forward updates were rejected
Merge the remote changes before pushing again. See the 'non-fast forward'
section of 'git push --help' for details.
This error can be a bit overwhelming at first, do not fear. Simply put, git cannot make the change on the remote without losing commits, so it refuses the push. Usually this is caused by another user pushing to the same branch. You can remedy this by fetching and merging the remote branch, or using pull to perform both at once.
In other cases this error is a result of destructive changes made locally by using commands like git commit --amend or git rebase. While you can override the remote by adding --force to the push command, you should only do so if you are absolutely certain this is what you want to do. Force-pushes can cause issues for other users that have fetched the remote branch, and is considered bad practice. When in doubt, don’t force-push.
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
$ git push origin :test // 刚提交到远程的test将被删除,但是本地还会保存的,不用担心。
$ git remote add origin ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git
$ git push origin master
这两个操作是等价的,第二个操作的第一行的意思是添加一个标记,让origin指向ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git,也就是说你操 作origin的时候,实际上就是在操作ssh://git@dev.lemote.com/rt4ls.git。origin在这里完全可以理解为后者 的别名。
注意:需要说明的是,默认情况下这条语句等价于提交本地的master仓库到远程仓库,并作为远程的master分支。
如果想把本地的某个分支test提交到远程仓库,并作为远程仓库的master分支,或者作为另外一个名叫test的分支,那么可以这么做。
$ git push origin test:master // 提交本地test分支作为远程的master分支
$ git push origin test:test // 提交本地test分支作为远程的test分支
如果想删除远程的分支呢?类似于上面,如果:左边的分支为空,那么将删除:右边的远程的分支。
当要push代码到git时,出现提示:
error:failed to push some refs to ...
Dealing with “non-fast-forward” errors
From time to time you may encounter this error while pushing:
- $ git push origin master
- To ../remote/
- ! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast forward)
- error: failed to push some refs to '../remote/'
Merge the remote changes before pushing again. See the 'non-fast forward'
section of 'git push --help' for details.
This error can be a bit overwhelming at first, do not fear. Simply put, git cannot make the change on the remote without losing commits, so it refuses the push. Usually this is caused by another user pushing to the same branch. You can remedy this by fetching and merging the remote branch, or using pull to perform both at once.
In other cases this error is a result of destructive changes made locally by using commands like git commit --amend or git rebase. While you can override the remote by adding --force to the push command, you should only do so if you are absolutely certain this is what you want to do. Force-pushes can cause issues for other users that have fetched the remote branch, and is considered bad practice. When in doubt, don’t force-push.
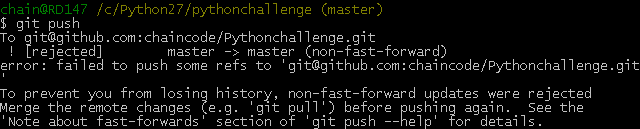
问题(Non-fast-forward)的出现原因在于:git仓库中已经有一部分代码,所以它不允许你直接把你的代码覆盖上去。于是你有2个选择方式:
1,强推,即利用强覆盖方式用你本地的代码替代git仓库内的内容
git push -f
2,先把git的东西fetch到你本地然后merge后再push
$ git fetch
$ git merge
这2句命令等价于- $ git pull
可是,这时候又出现了如下的问题:
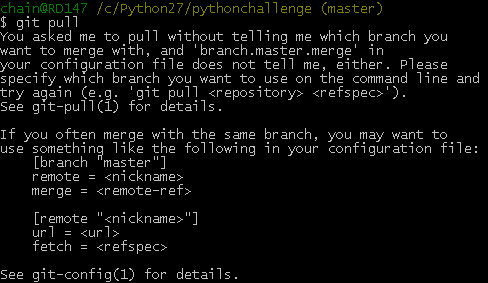
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/master
这等于告诉git2件事:1,当你处于master branch, 默认的remote就是origin。
2,当你在master branch上使用git pull时,没有指定remote和branch,那么git就会采用默认的remote(也就是origin)来merge在master branch上所有的改变如果不想或者不会编辑config文件的话,可以在bush上输入如下命令行:
- $ git config branch.master.remote origin
- $ git config branch.master.merge refs/heads/master
之后再重新git pull下。最后git push你的代码吧。it works now~
$ git push origin :test // 刚提交到远程的test将被删除,但是本地还会保存的,不用担心。



