Thymeleaf
简单说, Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。相较于其他的模板引擎,它有如下四个极吸引人的特点:
动静结合:Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
开箱即用:它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、改jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
多方言支持:Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
与SpringBoot完美整合:SpringBoot提供了Thymeleaf的默认配置,并且为Thymeleaf设置了视图解析器,我们可以像以前操作jsp一样来操作Thymeleaf。代码几乎没有任何区别,就是在模板语法上有区别。
快速入门:
1.创建工程,引入坐标
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
2.默认配置
不需要做任何配置,启动器已经帮我们把Thymeleaf的视图器配置完成,配置了模板文件(html)的位置,与jsp类似的前缀+ 视图名 + 后缀风格:
3.编写controller,控制视图跳转
@Controller public class HelloController { @GetMapping("show1") public String show1(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg", "Hello, Thymeleaf!"); return "hello"; } }
4.在 resources/templates/ 下新建一个html模板
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>hello</title> </head> <body> <h1 th:text="${msg}">大家好</h1> </body> </html>
@SpringBootApplication public class ThymeleafApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ThymeleafApplication.class, args); } }

语法:Thymeleaf的主要作用是把model中的数据渲染到html中,因此其语法主要是如何解析model中的数据
1.变量
例:在页面获取user数据:
<h1> 欢迎您:<span th:text="${user.name}">请登录</span> </h1>
动静结合:
Thymeleaf崇尚自然模板,意思就是模板是纯正的html代码,脱离模板引擎,在纯静态环境也可以直接运行。
如果我们直接在html中编写 ${} 这样的表达式,显然在静态环境下就会把表达式当成普通字符串,这不符合Thymeleaf的理念。
Thymeleaf中所有的表达式都需要写在 `指令` 中,指令是HTML5中的自定义属性,在Thymeleaf中所有指令都是以 `th:` 开头。因为表达式`${user.name}`是写在自定义属性中,因此在静态环境下,表达式的内容会被当做是普通字符串,浏览器会自动忽略这些指令,这样`span`的默认值`请登录`就会展现在页面。如果是在Thymeleaf环境下,`th`指令就会被识别和解析,而`th:text`的含义就是替换所在标签中的文本内容,于是`user.name`的值就替代了 `span`中默认的请登录。
指令的设计,正是Thymeleaf的高明之处,也是它优于其它模板引擎的原因。动静结合的设计,使得无论是前端开发人员还是后端开发人员可以完美契合。
如果浏览器不支持Html5,也就是不支持这种`th:`的命名空间写法,那么可以把`th:text`换成 `data-th-text`,Thymeleaf也可以兼容。
另外,`th:text`指令出于安全考虑,会把表达式读取到的值进行处理,防止html的注入。例如,`<p>你好</p>`将会被格式化输出为`$lt;p$gt;你好$lt;/p$lt;`。
如果想要不进行格式化输出,而是要输出原始内容,则使用`th:utext`来代替.
ognl表达式的语法糖:`${user.name}` 可以写作`${user['name']}
2.自定义变量
<h2> <p>Name: <span th:text="${user.name}">匿名</span>.</p> <p>Age: <span th:text="${user.age}">保密</span>.</p> <p>friend: <span th:text="${user.friend.name}">保密</span>.</p> </h2>
当数据量比较多的时候,频繁的写`user.`就会非常麻烦,因此,Thymeleaf提供了自定义变量来解决:
<h2 th:object="${user}"> <p>Name: <span th:text="*{name}">匿名</span>.</p> <p>Age: <span th:text="*{age}">保密</span>.</p> <p>friend: <span th:text="*{friend.name}">保密</span>.</p> </h2>
首先在 `h2`上 用 `th:object="${user}"`获取user的值,并且保存
然后,在`h2`内部的任意元素上,可以通过 `*{属性名}`的方式,来获取user中的属性,这样就省去了大量的`user.`前缀了
3.方法
ognl表达式中的方法调用:
<h2 th:object="${user}"> <p>FirstName: <span th:text="*{name.split(' ')[0]}">1</span>.</p> <p>LastName: <span th:text="*{name.split(' ')[1]}">2</span>.</p> </h2>
Thymeleaf内置对象:
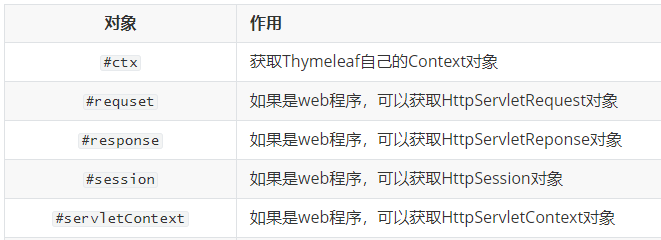
1.一些环境相关对象
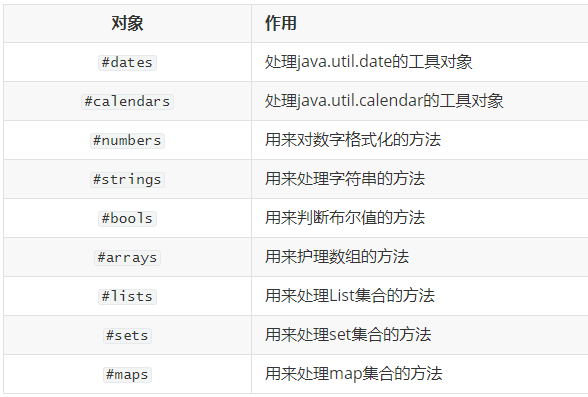
2.Thymeleaf提供的全局对象
model.addAttribute("today", new Date());
<p>今天是: <span th:text="${#dates.format(today,'yyyy-MM-dd')}">2020-01-01</span></p>
4.字面值
有的时候,我们需要在指令中填写基本类型如:字符串、数值、布尔等,并不希望被Thymeleaf解析为变量
字符串字面值:使用 ' 单引号引起来
<p>你正在观看 <span th:text="'thymeleaf'">template</span> 的字符串常量值.</p>
数字字面值:数字不需要任何特殊语法, 写的什么就是什么,而且可以直接进行算术运算
<p>今年是 <span th:text="2020">0000</span>.</p>
<p>两年后将会是 <span th:text="2020 + 2">0000</span>.</p>
布尔字面值:布尔类型的字面值是true或false:
<div th:if="true">你填的是true</div>
5.拼接
我们经常会用到普通字符串与表达式拼接的情况:
<span th:text="'欢迎您:' + ${user.name} + '!'"></span>
字符串字面值需要用`''`,拼接起来非常麻烦,Thymeleaf对此进行了简化,使用一对`|`即可:
<span th:text="|欢迎您:${user.name}!|"></span>
6.运算
需要注意:`${}`内部是通过OGNL表达式引擎解析的,外部的才是通过Thymeleaf的引擎解析,因此运算符尽量放在`${}`外进行。
算术运算:
支持的算术运算符:`+ - * / %`
<span th:text="${user.age} % 2 == 0">true or false</span>
比较运算:
支持的比较运算:`>`, `<`, `>=` and `<=` ,但是`>`, `<`不能直接使用,因为xml会解析为标签,要使用别名。
可以使用的别名:`gt (>), lt (<), ge (>=), le (<=), not (!), eq (==), neq/ne (!=)`
注意 `==` and `!=`不仅可以比较数值,还有类似于equals的功能。
条件运算:
三元运算
<span th:text="${user.sex} ? '男':'女'"></span>
三元运算符的三个部分:conditon ? then : else
condition:条件
then:条件成立的结果
else:不成立的结果
其中的每一个部分都可以是Thymeleaf中的任意表达式。
有的时候,我们取一个值可能为空,这个时候需要做非空判断,可以使用 表达式 ?: 默认值
注意:?:
<tr th:each="user : ${users}"> <td th:text="${user.name}">匿名</td> <td th:text="${user.age}">保密</td> </tr>
${users} 是要遍历的集合,可以是以下类型:
Iterable,实现了Iterable接口的类
Enumeration,枚举
Interator,迭代器
Map,遍历得到的是Map.Entry
Array,数组及其它一切符合数组结果的对象
在迭代的同时,我们也可以获取迭代的状态对象:
<tr th:each="user,status : ${users}"> <td th:text="${status.count}">序号</td> <td th:text="${user.name}">匿名</td> <td th:text="${user.age}">保密</td> </tr>
index,从0开始的角标
count,元素的个数,从1开始
size,总元素个数
current,当前遍历到的元素
even/odd,返回是否为奇偶,boolean值
first/last,返回是否为第一或最后,boolean值
8.逻辑判断
<span th:if="${user.age} < 24">小鲜肉</span>
9.分支控制switch
两个指令:`th:switch` 和 `th:case`
<div th:switch="${user.role}"> <p th:case="'admin'">用户是管理员</p> <p th:case="'manager'">用户是经理</p> <p th:case="*">用户是别的玩意</p> </div>
10.JS模板
模板引擎不仅可以渲染html,也可以对JS进行预处理。而且为了在纯静态环境下可以运行,其Thymeleaf代码可以被注释起来:
<script th:inline="javascript"> const user = /*[[${user}]]*/ {}; const age = /*[[${user.age}]]*/ 20; console.log(user); console.log(age) </script>