哈希表相关题目-python
栈&队列&哈希表&堆-python https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19446965/article/details/102982047
1、O(1)时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
设计一个支持在平均 时间复杂度 O(1) 下,执行以下操作的数据结构。
insert(val):当元素 val 不存在时,向集合中插入该项。
remove(val):元素 val 存在时,从集合中移除该项。
getRandom:随机返回现有集合中的一项。每个元素应该有相同的概率被返回。
示例 :
// 初始化一个空的集合。
RandomizedSet randomSet = new RandomizedSet();
// 向集合中插入 1 。返回 true 表示 1 被成功地插入。
randomSet.insert(1);
// 返回 false ,表示集合中不存在 2 。
randomSet.remove(2);
// 向集合中插入 2 。返回 true 。集合现在包含 [1,2] 。
randomSet.insert(2);
// getRandom 应随机返回 1 或 2 。
randomSet.getRandom();
// 从集合中移除 1 ,返回 true 。集合现在包含 [2] 。
randomSet.remove(1);
// 2 已在集合中,所以返回 false 。
randomSet.insert(2);
// 由于 2 是集合中唯一的数字,getRandom 总是返回 2 。
randomSet.getRandom();
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1
class RandomizedSet(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.nums = []
self.maps = {}
def insert(self, val):
"""
Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if val in self.maps:
return False
self.nums.append(val)
self.maps[val] = len(self.nums) - 1
return True
def remove(self, val):
"""
Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if val not in self.maps:
return False
# 将末尾的值移到待删除元素的位置
index = self.maps.get(val)
last_val = self.nums[-1]
self.nums[index] = last_val
self.maps[last_val] = index
# 删除最后一个元素
self.nums.pop()
# 删除被删除元素的index
del self.maps[val]
return True
def getRandom(self):
"""
Get a random element from the set.
:rtype: int
"""
return random.choice(self.nums)
2、O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复
示例:
// 初始化一个空的集合。
RandomizedCollection collection = new RandomizedCollection();
// 向集合中插入 1 。返回 true 表示集合不包含 1 。
collection.insert(1);
// 向集合中插入另一个 1 。返回 false 表示集合包含 1 。集合现在包含 [1,1] 。
collection.insert(1);
// 向集合中插入 2 ,返回 true 。集合现在包含 [1,1,2] 。
collection.insert(2);
// getRandom 应当有 2/3 的概率返回 1 ,1/3 的概率返回 2 。
collection.getRandom();
// 从集合中删除 1 ,返回 true 。集合现在包含 [1,2] 。
collection.remove(1);
// getRandom 应有相同概率返回 1 和 2 。
collection.getRandom();
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-delete-getrandom-o1-duplicates-allowed
1)把某个数在数组中出现的所有的位置用dict的形式存储下来
2)重复元素用set存下来,用于判断
3)删除一个数的时候,就是从这个 list 里随便拿走一个数(比如最后一个数)
class RandomizedCollection(object):
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.nums = []
self.maps = collections.defaultdict(set)
def insert(self, val):
"""
Inserts a value to the collection. Returns true if the collection did not already contain the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
self.nums.append(val)
self.maps[val].add(len(self.nums)-1)
return len(self.maps[val]) == 1
def remove(self, val):
"""
Removes a value from the collection. Returns true if the collection contained the specified element.
:type val: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not self.maps[val]:
return False
index = self.maps[val].pop()
self.nums[index] = None
return True
def getRandom(self):
"""
Get a random element from the collection.
:rtype: int
"""
x = None
while x is None: # 注意:这里不能写成while not x:
x = random.choice(self.nums)
return x
3、 复制带随机指针的链表
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
示例:
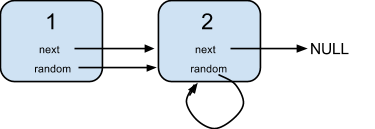
输入:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":{"$ref":"2"},"val":1}
解释:
节点 1 的值是 1,它的下一个指针和随机指针都指向节点 2 。
节点 2 的值是 2,它的下一个指针指向 null,随机指针指向它自己。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer
首先,先复习一下正常链表的拷贝:
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, next, random):
self.val = val
self.next = next
self.random = random
def copy_list(head):
if not head:
return None
new_head = Node(head.val)
p = head
q = new_head
while p:
if p.next:
q.next = Node(p.next.val)
else:
q.next = None
p = p.next
q = q.next
return new_head
此题还要存储一下random节点
class Solution(object):
def copyRandomList(self, head):
"""
:type head: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if head == None:
return None
maps = {}
new_head = Node(head.val, None, None)
maps[head] = new_head
p = head
q = new_head
while p:
q.random = p.random
if p.next:
q.next = Node(p.next.val, None, None)
maps[p.next] = q.next
else:
q.next = None
p = p.next
q = q.next
p = new_head
while p:
if p.random:
p.random = maps.get(p.random)
p = p.next
return new_head
4、 乱序字符串
给出一个字符串数组S,找到其中所有的乱序字符串(Anagram)。如果一个字符串是乱序字符串,那么他存在一个字母集合相同,但顺序不同的字符串也在S中。
所有的字符串都只包含小写字母
样例1:
输入:["lint", "intl", "inlt", "code"]
输出:["lint", "inlt", "intl"]
样例 2:
输入:["ab", "ba", "cd", "dc", "e"]
输出: ["ab", "ba", "cd", "dc"]什么是Anagram?
- 如果在更改字符顺序后它们可以相同,则两个字符串是anagram。
class Solution:
"""
@param strs: A list of strings
@return: A list of strings
"""
def anagrams(self, strs):
# write your code here
maps = collections.defaultdict(list)
for word in strs:
char_list = ''.join(sorted(word))
maps[char_list].append(word)
res = []
for word_list in maps.values():
if len(word_list) >= 2:
res += word_list
return res
5、最长连续序列
给定一个未排序的整数数组,找出最长连续序列的长度。
要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n)。
示例:
输入: [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2]
输出: 4
解释: 最长连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence
第一种:O(nlogn)
先排序,再统计
class Solution(object):
def longestConsecutive(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
if len(nums) <= 1:
return len(nums)
nums.sort()
length = 1
sum = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] - nums[i-1] == 0:
continue
if nums[i] - nums[i-1] == 1:
sum += 1
else:
if sum > length:
length = sum
sum = 1
if sum > length:
length = sum
return length
第二种:O(n)
HashSet 判断
class Solution(object):
def longestConsecutive(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
maps = set(nums)
length = 0
for num in nums:
if num in maps:
sum = 1
maps.remove(num)
l = num - 1
r = num + 1
while l in maps:
maps.remove(l)
l -= 1
sum += 1
while r in maps:
maps.remove(r)
r += 1
sum += 1
if length < sum:
length = sum
return length
参考:九章算法讲解 https://www.jiuzhang.com/solution/



