万能的搜索--之BFS(三)
接着(一)start
(二)广度优先搜索(BFS)
广度优先搜索(又称宽度优先搜索算法)是最简便的图的搜索算法之一,这一算法也是很多重要的图的算法的原型。 Dijkstra单源最短路径算法和Prim最小生成树算法都采用了和宽度优先搜索类似的思想。其别名又叫BFS,属于一种盲目搜寻法,目的是系统地展开并检查图中的所有节点,以找寻结果。换句话说,它并不考虑结果的可能位置,彻底地搜索整张图,直到找到结果为止。
广搜的核心思想就是:从初始结点开始,产生第一层节点,检查目标结点是否在这些后继结点之中,没有,就扩展第一层节点,若没有,用产生式规则得到第二层节点;检查目标结点是否在这些后继结点之中,没有,就扩展第 二层节点……像这样以此扩展节点、检查,直到发现目标结点为止。
优点:
找到的第一个解一定是最优解
缺点:
占用空间比较大
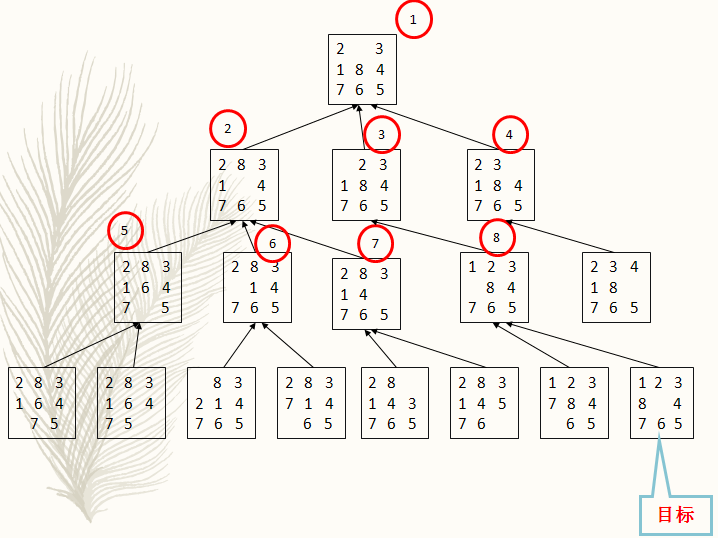
经典题:八数码问题、
在3×3的棋盘,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有1至8的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格,与空格相邻的棋子可以移到空格中。
给出一个初始状态和一个目标状态,找出一种从初始转变成目标状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。
伪代码:
初始状态加入队列
while 队列非空
获取当前队首状态
for 当前状态可能的下一状态st
if 该状态之前未被搜索到
if 该状态为目标状态
输出并退出
else
加入队尾
如何判重:
如何判断某一状态之前是否出现过?
将状态转换为一个数字(Hash)
举例
abac(字符串)转化为数字
0 * 26^3 + 1 * 26^2 + 0 * 26 + 2
矩阵转化为数字
具体代码实现:

#include<stdio.h> struct node { int xy[3][3]; int dir; }; struct node sh[102], end; int count = 1; void init() { printf("输入起始节点的位置:\n"); int i, j; for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) scanf("%d", &sh[0].xy[i][j]); sh[0].dir = -1; printf("输入目标节点的位置:\n"); for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) scanf("%d", &sh[101].xy[i][j]); sh[101].dir = -1; } //找出0的位置 int loction(int num) { int i; for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) if (sh[num].xy[i / 3][i % 3] == 0) return i; } //进行标记 long long sign(int num) { long long sum; sum = sh[num].xy[0][0]*100000000 + sh[num].xy[0][1]*10000000 + sh[num].xy[0][2]*1000000 + sh[num].xy[1][0]*100000 + sh[num].xy[1][1]*10000 + sh[num].xy[1][2]*1000 + sh[num].xy[2][0]*100 + sh[num].xy[2][1]*10 + sh[num].xy[2][2]; return sum; } void mobile(int num) { int temp; int loc; int up = 1, down = 1, left = 1, right = 1; loc = loction(num); int stand = sh[num].dir; //dir的0 1 2 3分别代表左 上 右 下 if (loc / 3 != 0 && stand != 1) { sh[count] = sh[num]; temp = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3] = sh[count].xy[loc / 3 - 1][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3 - 1][loc % 3] = temp; sh[count].dir = 3; count++; }; if (loc / 3 != 2 && stand != 3) { sh[count] = sh[num]; temp = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3] = sh[count].xy[loc / 3 + 1][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3 + 1][loc % 3] = temp; sh[count].dir = 1; count++; } if (loc % 3 != 0 && stand != 0) { sh[count] = sh[num]; temp = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3] = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3 - 1]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3 - 1] = temp; sh[count].dir = 2; count++; } if (loc % 3 != 2 && stand != 2) { sh[count] = sh[num]; temp = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3] = sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3 + 1]; sh[count].xy[loc / 3][loc % 3 + 1] = temp; sh[count].dir = 0; count++; } } void display(int num) { int i, j; for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) printf("%d ", sh[num].xy[i][j]); printf("\n"); } } int search() { int i = 0; while (1) { printf("\n"); display(i); printf("\n"); if (i == 100) { printf("超出了上限次数\n"); return 0; } if (sign(i) == sign(101)) { printf("在第%d次找到了", i); display(i); return i; } mobile(i); i++; } } int main() { init(); search(); return 0; }
未完.....
除特别注明外,本站所有文章均为Manjusaka丶梦寒原创,转载请注明来自出处



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号