Shiro入门学习之自定义Realm实现认证(四)
一、概述
Shirom默认使用自带的IniRealm,IniRealm从ini配置文件中读取用户的信息,而大部分情况下需要从系统数据库中读取用户信息,所以需要实现自定义Realm,Realm接口如下:
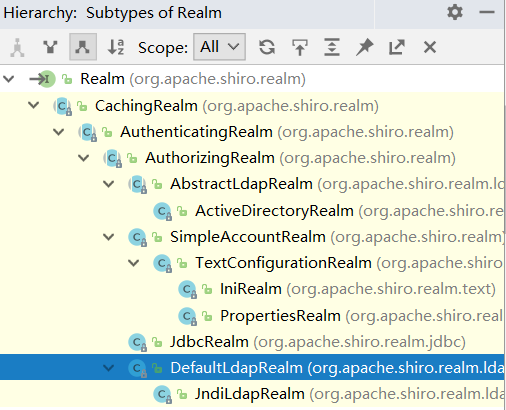
由此可以分析:
①CachingRealm:负责缓存处理
②AuthenticationRealm:负责认证
③AuthorizingRealm:负责授权
通常情况下,自定义的Realm继承AuthorizingRealm即可实现认证与授权
二、自定义Realm实现认证
1、新建module,添加如下pom依赖
<properties> <shiro.version>1.4.1</shiro.version> <loggingg.version>1.2</loggingg.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>${shiro.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>${loggingg.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2、自定义Realm类
public class UserRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm
{
private UserService userService= new UserServiceImpl();
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException
{
String username = token.getPrincipal().toString();
System.out.println("自定义Realm:"+username);
/**
* Shiro认证流程是根据用户名将用户对象查询出来,再做密码匹配
*/
User user = userService.queryUserByUserName(username);
if (user!=null)
{
/**
* 参数说明
* 参数1:可以传任意对象(可以通过subject.getPrincipal()获取该参数)
* 参数2:数据库中的用户密码
* 参数3:当前类名
*/
new SimpleAuthenticationInfo();
SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("fafafajsfjslkdfksdf", user.getPwd(), this.getName());
return info;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
}
3、test类
public class TestAuthenticationRealm { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.模拟前台传递的用户名和密码 String username = "zhangsan"; String password = "123456"; //2.创建安全管理器的工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //3.通过安全管理器工厂获取安全管理器 DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = (DefaultSecurityManager)factory.getInstance(); //4.创建自定义的Realm UserRealm userRealm = new UserRealm(); //5.设置自定义的Realm securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); //6.将安全管理器绑定到当前运行环境 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //7.从当前环境中获取Subject主体 Subject subject1 = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //8.调用主体的登录方法 try { subject1.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password)); System.out.println("登录成功~"); Object principal = subject1.getPrincipal(); System.out.println(principal); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { System.out.println("密码不正确"); }catch (UnknownAccountException e) { System.out.println("用户名不存在"); } } }
三、分析
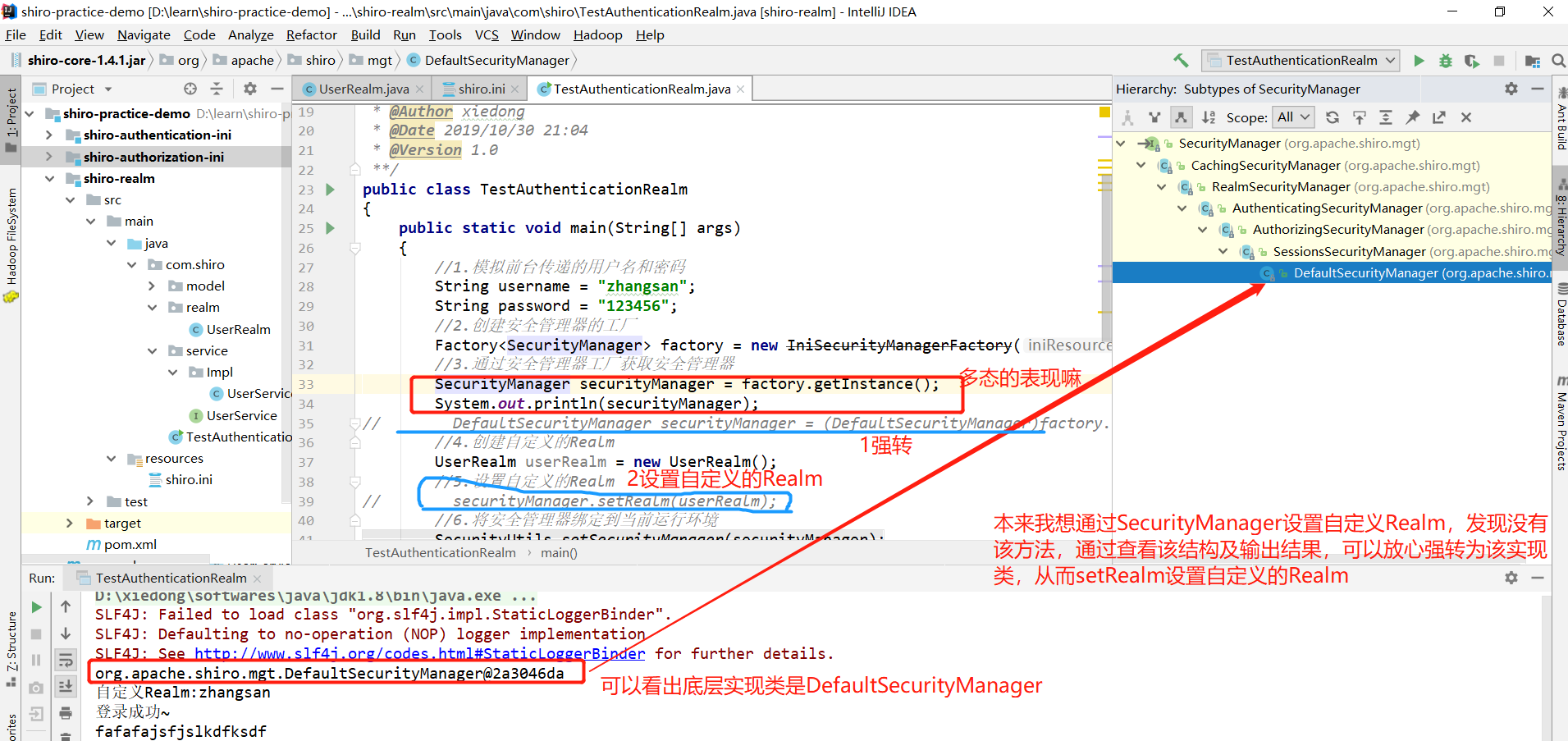
1、SecurityManager如何设置自定义的Realm?
SecurityManger不能直接setRealm,输出其结果发现默认实现类是DefaultSecurityManager,通过强转该类,调用setRealm方法设置自定义的Realm
2、自定义Realm的分析
参数1可以为任意参数,可以通过subject.getPrincipal()获取该参数
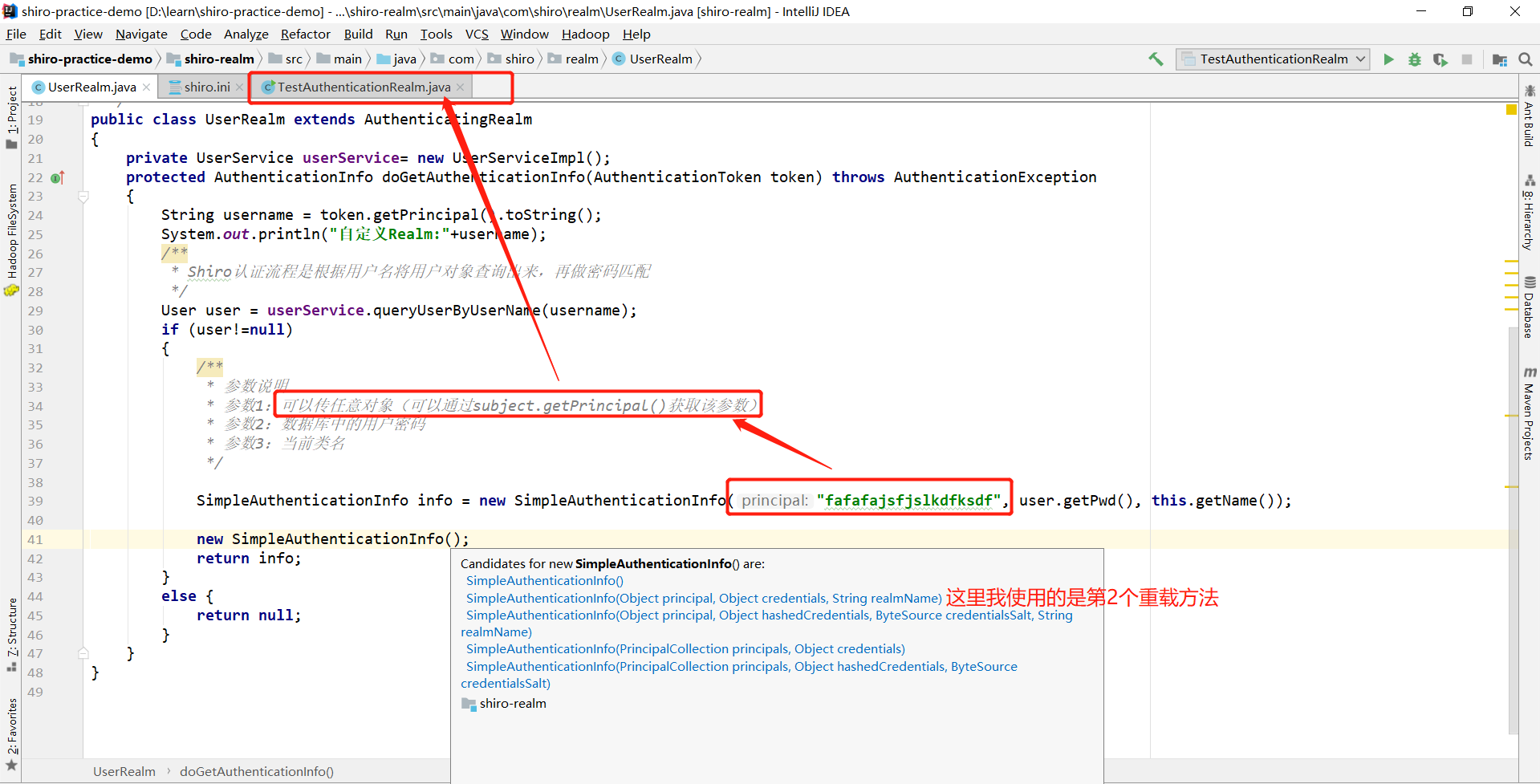
subject.getPrincipal()获取该参数

3、通过shiro.ini配置自定义的Realm
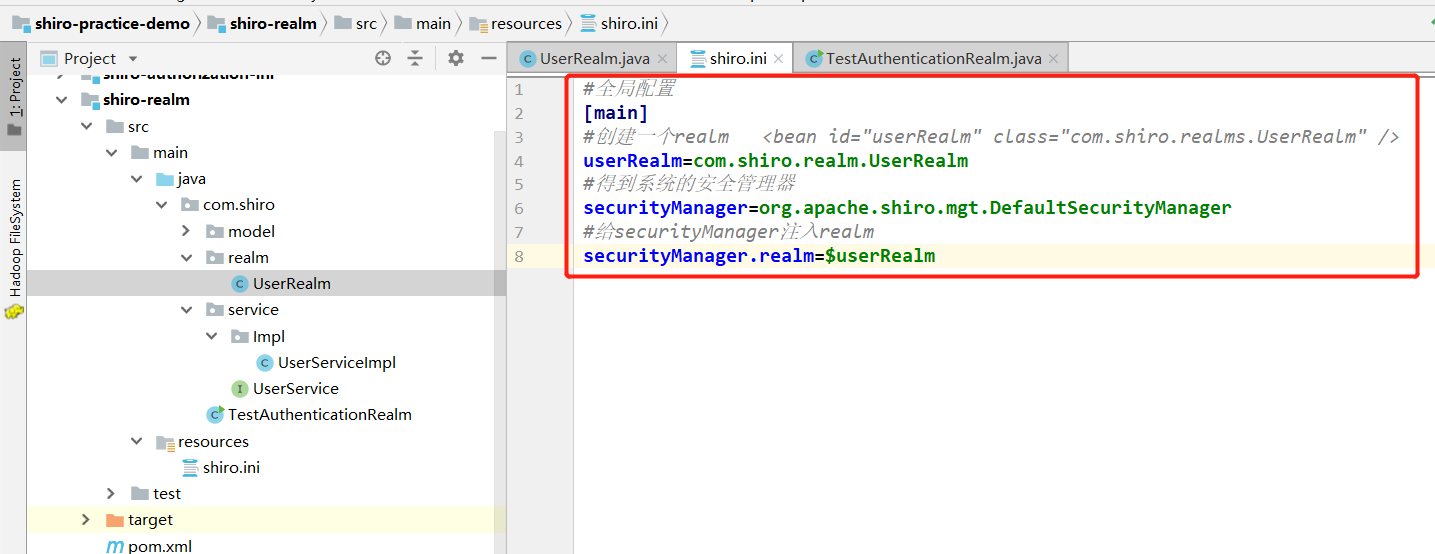
test类中需要注释以下2行:

四、总结
1、面向接口编程:可以发现处处是接口
2、SecurityManager接口的实现类是DefaultSecurityManager,通过该类的setRealm设置自定义的Realm
3、SimpleAuthenticationInfo的重载方法(参数1可以为任意对象,数据库查询密码,当前类名),可以通过subject.getPrincipal()获取参数1(很重要!)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号