15个Spring的核心注释示例
众所周知,Spring DI和Spring IOC是Spring Framework的核心概念。让我们从org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation和org.springframework.context.annotation包中探索一些Spring核心注释。我们经常将这些称为“Spring核心注释”,我们将在本文中对它们进行讲解。
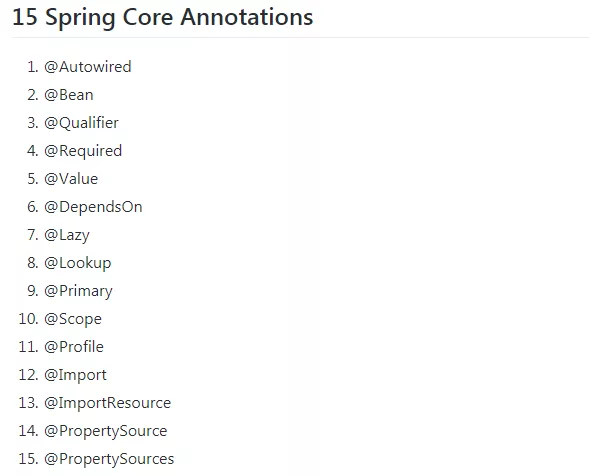
这是所有已知的Spring核心注释的列表。
@Autowired
我们可以使用@Autowired注释来标记Spring将要解析和注入的依赖关系。我们可以将这个注释与构造函数,setter或字段注入一起使用
- 构造器注入
@RestController public class CustomerController { private CustomerService customerService; @Autowired public CustomerController(CustomerService customerService) { this.customerService=customerService; } }
- setter注入
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class CustomerController { private CustomerService customerService; @Autowired public void setCustomerService(CustomerService customerService) { this.customerService=customerService; } }
- 领域注入
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class CustomerController { @Autowired private CustomerService customerService; }
@Bean
- @Bean是方法级注释,是XML元素的直接模拟。 注释支持一些提供的属性,例如init-method,destroy-method,auto-wiring和name。
- 您可以在
@Configuration注解或@Component注解类中使用@Bean批注 - 以下是方法声明的简单示例
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import com.companyname.projectname.customer.CustomerService; import com.companyname.projectname.order.OrderService; @Configuration public class Application { @Bean public CustomerService customerService() { return new CustomerService(); } @Bean public OrderService orderService() { return new OrderService(); } }
- 上述配置等效于以下Spring XML:
<beans> <bean id="customerService"class="com.companyname.projectname.CustomerService"/> <bean id="orderService" class="com.companyname.projectname.OrderService"/> </beans>
@Qualifier
此注释有助于微调基于注释的自动布线。 可能存在这样的情况:我们创建多个相同类型的bean,并且只想使用属性连接其中一个bean。 这可以使用@ Qualifier注释以及 @Autowired注释来控制。
示例:考虑使用EmailService和SMSService类来实现单个MessageService接口
- 为多个消息服务实现创建MessageService接口。
public interface MessageService { public void sendMsg(String message); }
- 接下来,创建实现:EmailService和SMSService。
public class SMSService implements MessageService { public void sendMsg(String message) { System.out.println(message); } } public class EmailService implements MessageService { public void sendMsg(Stringmessage) { System.out.println(message); } }
- 这时候该看看 @Qualifier注释的用法了
public interface MessageProcessor { public void processMsg(String message); } public class MessageProcessorImpl implements MessageProcessor { private MessageService messageService; // setter based DI @Autowired @Qualifier("emailService") public void setMessageService(MessageService messageService) { this.messageService=messageService; } // constructor based DI @Autowired public MessageProcessorImpl(@Qualifier("emailService")MessageService messageService) { this.messageService = messageService; } public void processMsg(String message) { messageService.sendMsg( message); } }
@Required
@Required 注释是一个方法级注释,并应用于bean的setter方法。此注释仅指示必须将setter方法配置为在配置时使用值依赖注入。
例如,对setter方法的 @Required标记了我们想要通过XML填充的依赖项:
@Required void setColor(String color){ this.color= color; } <bean class="com.javaguides.spring.Car"> <property name = "color" value="green"/> </bean>
否则,将抛出BeanInitializationException。
@Value
Spring @Value 注释用于为变量和方法参数指定默认值。我们可以使用@Value 注释来读取Spring环境变量以及系统变量 。Spring @Value 注释也支持SpEL。让我们看一下使用@Value 注释的一些示例 。
示例:我们可以使用@Value 注释为类属性指定默认值 。
@Value("Default DBConfiguration")
private String defaultName;
该 @Value 注释参数可以是只有字符串,但春天尝试将其转换为指定的类型。以下代码将正常工作,并将布尔值和整数值分配给变量。
@Value("true")
private boolean defaultBoolean;
@Value("10")
private int defaultInt;
这演示了Spring @Value - Spring环境变量
@Value("${APP_NAME_NOT_FOUND}")
private String defaultAppName;
接下来,使用 @Value 注释分配系统变量 。
@Value("${java.home}")
private String javaHome;
@Value("${HOME}")
private String homeDir;
Spring @Value – SpEL
@Value("#{systemProperties['java.home']}")
private String javaHome;
@DependsOn
该 @DependsOn 注释可以强制的Spring IoC容器中的bean,它是由注释之前初始化一个或多个bean @DependsOn 注释。
所述 @DependsOn 注释可以在直接或间接地注释与任何类使用 @Component 或与所述注解的方法 @Bean。
示例:让我们创建 FirstBean 和 SecondBean 类。在此示例中, SecondBean 在 bean之前初始化 FirstBean。
public class FirstBean{ @Autowired private SecondBean secondBean; } public class SecondBean { public SecondBean() { System.out.println("SecondBean Initialized via Constuctor"); } }
基于配置类在Java中声明上述bean。
@Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean("firstBean") @DependsOn(value={"secondBean"}) public FirstBean firstBean() { return new FirstBean(); } @Bean("secondBean") public SecondBean secondBean() { return new SecondBean(); } }
@Lazy
默认情况下,Spring IoC容器在应用程序启动时创建并初始化所有单例bean。我们可以通过使用 @Lazy 注释来防止单例bean的这种预初始化 。
所述 @Lazy 注释可以在任何类中使用,与直接或间接地注释 @Component 或与所述注解的方法 @Bean。
示例:考虑我们有两个bean - FirstBean 和 SecondBean。在此示例中,我们将FirstBean 使用 @Lazy注释显式加载。
public class FirstBean{ public void test() { System.out.println("Method of FirstBean Class"); } } public class SecondBean{ public void test(){ System.out.println("Method of SecondBean Class"); } }
基于配置类在Java中声明上述bean。
@Configuration public class AppConfig { @Lazy( value =true) @Bean public FirstBean firstBean() { return new FirstBean(); } @Bean public SecondBean secondBean() { return new SecondBean (); } }
我们可以看到,bean secondBean 由Spring容器初始化,而bean firstBean 则被显式初始化。
@Lookup
注释的方法 @Lookup 告诉Spring在我们调用它时返回方法返回类型的实例。
@Primary
我们使用 @Primary 当存在多个相同类型的bean时,我们使用它 给bean更高的优先级。
@Component @Primary class Car implements Vehicle {} @Component class Bike implements Vehicle {} @Component class Driver { @Autowired Vehicle vehicle; } @Component class Biker { @Autowired @Qualifier( "bike") Vehicle vehicle; }
@Scope
我们使用@ Scope注释来定义 @Component类的范围或 @Bean定义。 它可以是单例,原型,请求,会话,globalSession或某些自定义范围。 举个例子:
@Component @Scope(value= ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON) public class TwitterMessageService implements MessageService { } @Component @Scope(value =ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE) public class TwitterMessageService implements MessageService { }
@Profile
如果我们希望Spring仅在特定配置文件处于活动状态时使用 @Component类或 @Bean方法,我们可以使用 @Profile标记它。 我们可以使用注释的value参数配置配置文件的名称:
@Component @Profile("sportDay") class Bike implements Vehicle { }
@Import
该 @Import 注释指示一个或多个 @Configuration类进口。
例如:在基于Java的配置中,Spring提供了 @Import注释,允许从另一个配置类加载 @Bean定义。
@Configuration public class ConfigA { @Bean public A a() { return new A(); } } @Configuration @Import(ConfigA.class) public class ConfigB { @Bean public B b() { return new B (); } }
现在,在实例化上下文时,不需要同时指定ConfigA类和ConfigB类,只需要显式提供ConfigB。
@ImportResource
Spring提供了一个 @ImportResource注释,用于将 applicationContext.xml文件中的bean加载到ApplicationContext中。
例如:考虑我们在类路径上有 applicationContext.xmlSpring bean配置XML文件。
@Configuration @ImportResource( {"classpath*:applicationContext.xml"}) public class XmlConfiguration { }
@PropertySource
该 @PropertySource 注释提供了一种方便的声明性机制,用于添加 PropertySource Spring的Eenvironment以与@Configuration类一起使用 。
例如,我们从文件config.properties文件中读取数据库配置,并使用Environment 将这些属性值设置为 DataSourceConfig类。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; @Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:config.properties") public class ProperySourceDemo implements InitializingBean { @Autowired Environment env; @Override public void afterPropertiesSet()throws Exception { setDatabaseConfig(); } private void setDatabaseConfig() { DataSourceConfig config = new DataSourceConfig(); config.setDriver( env.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); config.setUrl(env.getProperty("jdbc.url")); config.setUsername(env.getProperty("jdbc.username")); config.setPassword(env.getProperty("jdbc.password")); System.out.println(config.toString()); } }
@PropertySources
我们可以使用此批注指定多个 @PropertySource配置:
@PropertySources( { @PropertySource("classpath:config.properties"), @PropertySource("classpath:db.properties") }) public class AppConfig { //... }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号