有时预定义的SAPUI5类型不够灵活,您希望在视图中执行简单的计算或格式化——这正是表达式真正有用的地方。我们使用它们根据数据模型中的当前数字格式化价格。
Preview
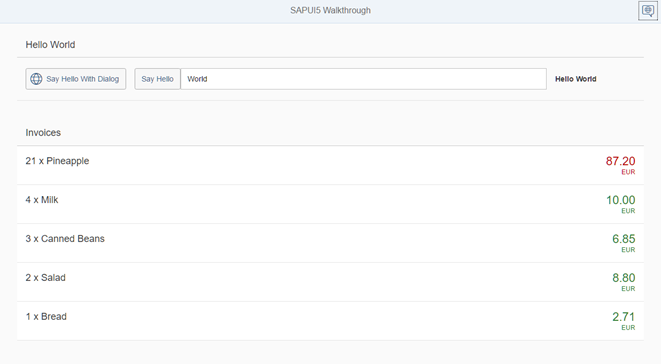
The price is now formatted according to its number
Coding
You can view and download all files at Walkthrough - Step 22.
webapp/view/InvoiceList.view.xml
<mvc:View controllerName="sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.InvoiceList" xmlns="sap.m" xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc"> <List headerText="{i18n>invoiceListTitle}" class="sapUiResponsiveMargin" width="auto" items="{invoice>/Invoices}" > <items> <ObjectListItem title="{invoice>Quantity} x {invoice>ProductName}" number="{ parts: [{path: 'invoice>ExtendedPrice'}, {path: 'view>/currency'}], type: 'sap.ui.model.type.Currency', formatOptions: { showMeasure: false } }" numberUnit="{view>/currency}" numberState="{= ${invoice>ExtendedPrice} > 50 ? 'Error' : 'Success' }"/> </items> </List> </mvc:View>
操作符的条件是来自我们的数据模型的值。表达式绑定中的模型绑定必须使用$符号转义,正如您在代码中看到的那样。如果价格高于50,我们将状态设置为“Error”(数字将显示为红色),否则设置为“Success”(数字将显示为绿色)。我们在声明性视图中添加了属性numberState,并引入了一个新的绑定语法,该语法从括号中的=开始。这个符号用于初始化新的绑定语法,它被称为表达式,可以执行简单的计算逻辑,如这里所示的三元运算符。
表达式仅限于帮助格式化数据(如数学表达式、比较等)的一组特定操作。您可以在文档中查找可能的操作。
Conventions
只对简单的计算使用表达式绑定。
Parent topic: Walkthrough
Previous: Step 21: Data Types
Next: Step 23: Custom Formatters
Related Information


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号