vagrant构建centos虚拟环境
vagrant搭建centos
什么是vagrant
Vagrant 是一个简单易用的部署工具,用英文说应该是 Orchestration Tool 。它能帮助开发人员迅速的构建一个开发环境,帮助测试人员构建测试环境,Vagrant 基于 Ruby 开发,使用开源 VirtualBox 作为虚拟化支持,可以轻松的跨平台部署。
如何使用
1、构建本地的目录
/Users/yj/vagrant/centos7
2、官方下载对应的镜像文件,官方下载地址
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ wget https://github.com/CommanderK5/packer-centos-template/releases/download/0.7.2/vagrant-centos-7.2.box
3、导入刚刚下载的镜像(box文件)
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ vagrant box add centos7.2 /Users/yj/vagrant/centos7/vagrant-centos-7.2.box
==> vagrant: A new version of Vagrant is available: 2.2.15 (installed version: 2.2.14)!
==> vagrant: To upgrade visit: https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html
==> box: Box file was not detected as metadata. Adding it directly...
==> box: Adding box 'centos7.2' (v0) for provider:
box: Unpacking necessary files from: file:///Users/yj/vagrant/centos7/vagrant-centos-7.2.box
==> box: Successfully added box 'centos7.2' (v0) for 'virtualbox'!
4、初始化
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ vagrant init
这时候当前目录会生成一个Vagrantfile文件
5、修改Vagrantfile中的box名称
config.vm.box = "centos7-1"
6、启动
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Importing base box 'centos7-1'...
==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> default: Setting the name of the VM: centos7_default_1619487768038_36727
==> default: Fixed port collision for 22 => 2222. Now on port 2200.
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2200 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2200
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
default: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
default: Warning: Connection reset. Retrying...
default:
default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace
default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security.
default:
default: Inserting generated public key within guest...
default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it's present...
default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key...
==> default: Machine booted and ready!
==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM...
default: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
default: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
default: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
default: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
default: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
default: your host and reload your VM.
default:
default: Guest Additions Version: 5.0.14
default: VirtualBox Version: 6.1
==> default: Mounting shared folders...
default: /vagrant => /Users/yj/vagrant/centos7
7、登入
可直接只用vagrant ssh登入
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ vagrant ssh
Last failed login: Mon Apr 26 22:52:26 BRT 2021 from 10.0.2.2 on ssh:notty
There were 5 failed login attempts since the last successful login.
Last login: Mon Apr 26 22:50:07 2021 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@localhost ~]$
也可以使用ssh
$ ssh -p 2200 root@127.0.0.1
上面启动的时候已经告诉我们地址和端口了
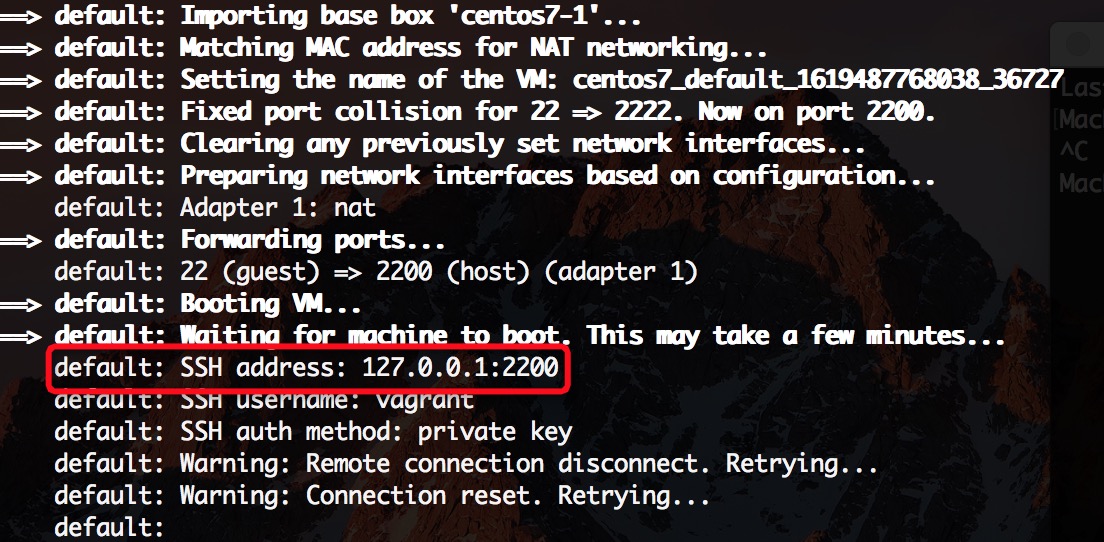
账号:root
密码:vagrant
同时构建多台
修改Vagrantfile
修改之前产生的Vagrantfile文件为
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.define "centos7-1" do |vb|
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.memory = 1024
v.cpus = 1
end
vb.vm.host_name = "centos7-1"
vb.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.111"
vb.vm.box = "centos7.2"
end
config.vm.define "centos7-2" do |vb1|
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.memory = 1024
v.cpus = 1
end
vb1.vm.host_name = "centos7-2"
vb1.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.112"
vb1.vm.box = "centos7.2"
end
config.vm.define "centos7-3" do |vb2|
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.memory = 1024
v.cpus = 1
end
vb2.vm.host_name = "centos7-3"
vb2.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.113"
vb2.vm.box = "centos7.2"
end
end
网络使用的是私有网络,私有网络和公有网络区别可以看下文
启动
MacBook-Pro-3:centos7 yj$ vagrant up
默认的账号还是root,密码还是vagrant
这里设置了静态的ip,我们就可以通过静态ip直接访问虚拟机了
$ ssh root@192.168.44.113
vagrant中的网络
私有网络
private_network
私有网络,对应于virtualbox的host-only网络模型,这种模型下,虚拟机之间和宿主机(的虚拟网卡)之间可以互相通信,但不在该网络内的设备无法访问虚拟机
如果私有网络的虚机不在一个网络,vagrant为这些private_network网络配置的IP地址并不在同一个网段。vagrant会自动为不同网段创建对应的host-only网络。
所以使用private_network如果没有外部机器(虚拟机宿主机之外的机器)连接,使用这种方式设置的静态ip,能够摆脱主机网络变换的限制。
PS:比如public_network如果更换了wefi连接,之前设置的静态ip可能就不可用了,因为网段不一样了。
vb1.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.56.112"
公有网络
public_network
公有网络,对应于virtualbox的桥接模式,这种模式下,虚拟机的网络和宿主机的物理网卡是平等的,它们在同一个网络内,虚拟机可以访问外网,外界网络(特指能访问物理网卡的设备)也能访问虚拟机
vagrant为virtualbox配置的public_network,其本质是将虚拟机加入到了virtualbox的桥接网络内。
vagrant在将虚拟机的网卡加入桥接网络时,默认会交互式地询问用户要和哪个宿主机上的网卡进行桥接,一般来说,应该选择可以上外网的物理设备进行桥接。
由于需要非交互式选择或者需要先指定要桥接的设备名,而且不同用户的网络环境不一样,因此如非必要,一般不在vagrant中为虚拟机配置public_network。
公有网络的iP网络要和主机的网段一致。
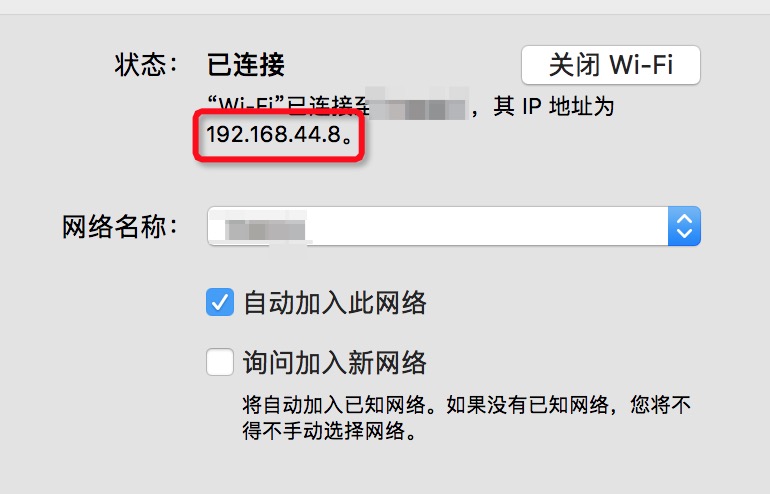
vb.vm.network "public_network", ip: "192.168.44.111",bridge: "en0: Wi-Fi (AirPort)"
常用的命令
| 子命令 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| box | 管理box镜像(box是创建虚拟机的模板) |
| init | 初始化项目目录,将在当前目录下生成Vagrantfile文件 |
| up | 启动虚拟机,第一次执行将创建并初始化并启动虚拟机 |
| reload | 重启虚拟机 |
| halt | 将虚拟机关机 |
| destroy | 删除虚拟机(包括虚拟机文件) |
| suspend | 暂停(休眠、挂起)虚拟机 |
| resume | 恢复已暂停(休眠、挂起)的虚拟机 |
| snapshot | 管理虚拟机快照(hyperv中叫检查点) |
| status | 列出当前目录(Vagrantfile所在目录)下安装的虚拟机列表及它们的状态 |
| global-status | 列出全局已安装虚拟机列表及它们的状态 |
| ssh | 通过ssh连接虚拟机 |
| ssh-config | 输出ssh连接虚拟机时使用的配置项 |
| port | 查看各虚拟机映射的端口列表(hyperv不支持该功能) |
参考
【熟练使用vagrant(11):vagrant配置虚拟机网络】https://www.junmajinlong.com/virtual/vagrant/vagrant_network/
【一个好用的Vagrantfile】https://github.com/boilingfrog/vagrant-provider-script/tree/master/virtualbox


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号