java第一次作业
一,前言
经过几周的学习,我们先后完成了三次pta的作业,每次的作业都能收获不同的知识要点。
在第一次作业中,我们练习巩固了如何创建,编译和运行非常基础的java程序,比如如何利用基本数据类型,变量,常量,操作符,表达式以及输入输出来进行基本的程序设计。同时训练了各种循环,选择语句。题量较大,难度适中,有个别题目难度加大。但是对于我这个新手菜鸟来说,做起来非常吃力。知识点包括变量类型的强制转换,字符串的比较,转换等一系列基础操作。
第二次作业,题量一如既往的大,难度相较于第一次作业有较大上升,例如二进制数值的提取以及求下一天的运算,对我来说都有很大难度。学习了变量保留小数的方法,进行了选择结构的进一步学习,绝对值函数的使用等。
第三次作业,只有四道题目,看似题量变少了,其实难度直线上升。我们需要自学类与对象以及方法的使用。包括定义方法,调用方法,以及其作用域的范围,如何定义类和创建对象等多个知识点的学习。
二,设计与分析
第一次作业:
(1)计算快递运费
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String args[]){ Scanner myscanner=new Scanner(System.in); double w=myscanner.nextDouble(); double x=0; if(w<1){ x=12; System.out.print(x); } else if(w<20){ x=12+2*(w-1); System.out.print((int) (x+0.5)); } else if(w<60){ x=39+1.9*(w-20); System.out.print((int) (x+0.5)); } else if(w>=60){ x=115+1.3*(w-60); System.out.print((int) (x+0.5)); } } }
解析:先输入快递的重量并申明价格为x,然后通过多个判断语句确定重量所属范围内关于价格的表达式,最后计算得出总价格并输出。
知识点:四舍五入保留整数的方法为
(int) (x+0.5)
第二次作业:
(1)巴比伦发求平方根近似值
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner myscanner = new Scanner(System.in); float a = myscanner.nextFloat(); float b = myscanner.nextFloat(); float n = 0; if (a <= 0 || b <= 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { n = (b + a / b) / 2; while (Math.abs(n - b) >0.00001) { b = n; n = (b + a/b) / 2; } System.out.println(b); } } }
解析:输入n和lastGuess最初的猜测值,先通过一个if语句判断两个数是否符合要求,然后利用whil语句,当由公式求得的nextGuess和lastGuess相差较大时,把nextGuess的值赋给lastGuess,继续以上过程,直至nextGuess和lastGuess几乎相同,此时lastGuess或者nextGuess就是平方根的近似值。最后输出答案。
知识点:绝对值函数的使用
Math.abs(n - b)
第三次作业:
(1)定义日期类
Date结构图: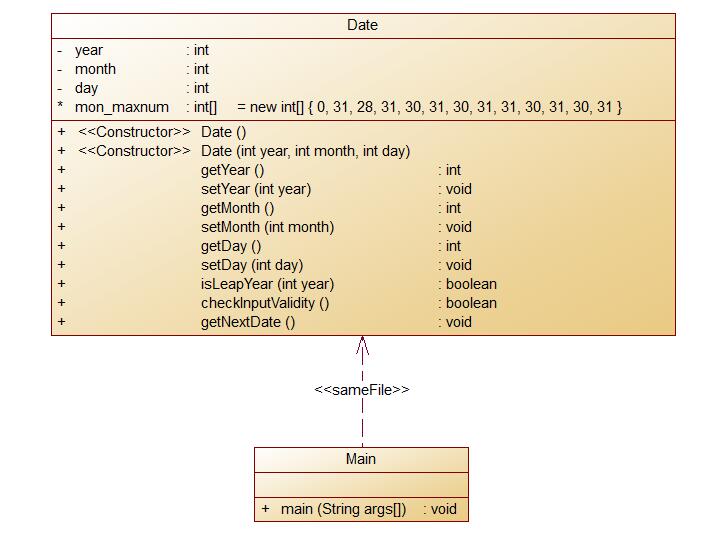
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(System.in); int year = myScanner.nextInt(); int month = myScanner.nextInt(); int day = myScanner.nextInt(); Date date = new Date(year, month, day); date.nextDate(); } } class Date { private int year; private int month; private int day; public Date(int year, int month, int day) { this.year = year; this.month = month; this.day = day; } public int getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(int year) { this.year = year; } public int getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(int month) { this.month = month; } public int getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } public boolean isLeapYear() { return (this.year%4 == 0&&this.year % 100 != 0)||this.year % 400 == 0; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { int[] a = new int[]{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; if (isLeapYear()) { a[2] = 29; } return (this.year >= 1900 && this.year <= 2000 && this.month > 0 && this.month <= 12 && this.day <= a[this.month] && this.day > 0); } public void nextDate() { int[] a = new int[]{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; int d = 0, m = 0; if (isLeapYear()) { a[2] = 29; } if (checkInputValidity()) { if (this.month == 12) { if (this.day == a[this.month]) { this.year = this.year + 1; m = 1; d = 1; } else { m = this.month; d = this.day + 1; } } else { if (this.day == a[this.month]) { m = this.month + 1; d = 1; } else { m = this.month; d = this.day + 1; } } System.out.println("Next day is:"+this.year+"-"+ m + "-" + d); } else { System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong"); } } }
解析:
- 程序首先导入了java.util.Scanner包,用于读取用户输入。
- 然后定义了一个Public类Main,其中包含了一个main方法。在main方法中,通过Scanner类读取用户输入的年月日,并将其存储在变量year, month, day中。
- 接下来定义了一个Date类,包括了构造函数和一些方法,用于存储和计算日期信息。构造函数用于初始化Date对象的年月日属性,同时定义了get和set方法,用于对对象的属性进行操作。
- 在Date类中还定义了isLeapYear方法,用于判断当前年份是否为闰年;checkInputValidity方法,用于检查输入的日期是否合法;以及nextDate方法,用于计算输入日期的下一天日期。
- nextDate方法中,首先根据当前年份是否为闰年,确定每个月的天数,然后判断输入日期是否合法。如果合法,根据输入日期的月份和天数计算出下一天的日期,并输出结果。如果不合法,则输出错误提示信息。
- 最后在main方法中,创建了一个Date对象,并调用了它的nextDate方法,输出结果。 整个程序主要用于练习面向对象编程思想,封装了日期计算的功能,提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
知识点:
- 类的定义和使用:定义了一个Date类,包括年月日的私有属性和构造方法,以及获取和设置属性的方法、判断是否为闰年的方法、检查输入日期是否合法的方法、计算下一天日期并输出的方法。
- 条件语句的使用:在nextDate方法中,通过if语句判断当前日期是否为当年最后一天或当月最后一天,从而计算下一天的日期。
- 数组的使用:定义了一个长度为13的整型数组a,并在checkInputValidity和nextDate方法中根据是否为闰年对数组的第二个元素进行修改,即2月的天数。
- 逻辑运算符的使用:在isLeapYear方法中,通过&&和||逻辑运算符判断是否为闰年。
(2)日期类设计
要求: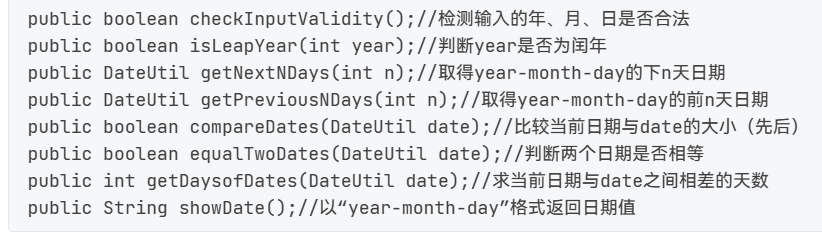
类图: 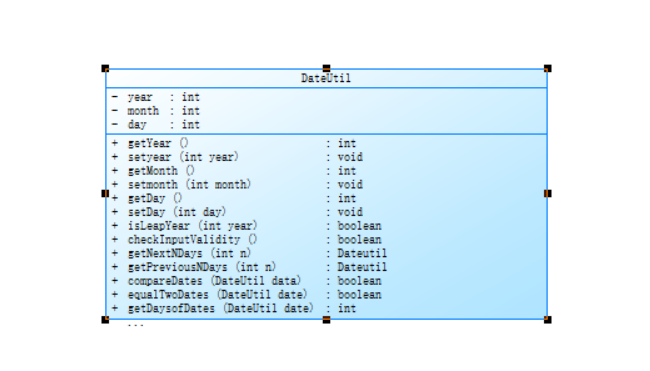
代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int year = 0; int month = 0; int day = 0; int choice = input.nextInt(); if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method int m = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } m = input.nextInt(); if (m < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method int n = 0; year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } n = input.nextInt(); if (n < 0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.print( date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class DateUtil { private int year; private int month; private int day; int[] mon_maxnum = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; DateUtil(int year, int month, int day){ this.year = year; this.month = month; this.day = day; } int getYear() { return year; } void setyear(int year) { this.year = year; } int getMonth() { return month; } void setmonth(int month) { this.month = month; } int getDay() { return day; } void setDay(int day) { this.day = day; } public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { if (year % 400 == 0 || year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) return true; else return false; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { if(month > 0 && month <=12) { if (mon_maxnum[month] >= day && month != 2 && year >= 1820 && year <= 2020 && day >=1) return true; else if (isLeapYear(year) && month == 2 && day <= 29 && day > 0) return true; else if (!isLeapYear(year) && month == 2 && day <= 28 && day > 0) return true; else return false; } else return false; } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { int year1 = this.year; int month1 = this.month; int day1 = this.day; while(n > 366) { if (!isLeapYear(year1)) { n -= 365; year1++; } else { n -= 366; year1++; } } while(n > mon_maxnum[month1]) {//算出跨越了几年几月后剩余几天 if (!isLeapYear(year1)) {//非闰年情况 while(n > mon_maxnum[month1]) { n -= mon_maxnum[month1]; month1++; if(month1 > 12) { year1 += 1; month1 = 1; break; } } } else if (isLeapYear(year1)) {//闰年情况 if(month1 != 2) { while (n > mon_maxnum[month1]) { if (month1 == 2) n -= 29; else n -= mon_maxnum[month1]; month1++; if(month1 > 12) { month1 = 1; year1 += 1; break; } } } else if(month1 == 2 && n > 29) { month1++; n -= 29; } } } if (isLeapYear(year1)) { if (day1 + n > 29 && month1 == 2) { day1 = n - 29; month1++; } } else if (day1 + n > mon_maxnum[month1]) { n = n-(mon_maxnum[month1] - day1); day1 = 0; month1++; day1 = n + day1; } else day1 += n; if (month1 == 13) month1 = 1; DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); return date1; } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { int year1 = this.year; int month1 = this.month; int day1 = this.day; int flag = 0; while(n != 0) { if (day1 > n) { day1 -= n; flag++; } else { n = n - day1; month1 -= 1; if (month1 == 0) { month1 = 12; year1 -= 1; } if (month1 == 2 && isLeapYear(year1)) day1 = 29; else day1 = mon_maxnum[month1]; } for (int i = month1; n > mon_maxnum[i]; i--) { if (i == 2 && isLeapYear(year1)) n -= 29; else n -= mon_maxnum[i]; month1 -= 1; if (month1 == 0) { month1 = 12; year1 -= 1; i = 13; } if (month1 == 2 && isLeapYear(year1)) day1 = 29; else day1 = mon_maxnum[month1]; } if (day1 > n && flag != 1) { day1 -= n; n = 0; } if (flag == 1) n = 0; } DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(year1, month1, day1); return date1; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if (this.year > date.year) return true; else if (this.year == date.year && this.month > date.month) return true; else if (this.year == date.year && this.month == date.month && this.day > date.day) return true; else return false; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { if (this.year == date.year && this.month == date.month && this.day == date.day) return false; else return false; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { int days,t; days = 0; if(!compareDates(date)) { t = this.year; this.year = date.year; date.year = t; t = this.month; this.month = date.month; date.month = t; t = this.day; this.day = date.day; date.day = t; } if (compareDates(date)) { if (this.year > date.year) { this.year -= 1; date.year += 1; if (this.year == date.year && isLeapYear(this.year)) days = 366; else if (this.year == date.year && !isLeapYear(this.year)) days = 365; else { this.year += 1; date.year -= 1; days = (this.year - date.year-1) * 365; } for (int i = date.month + 1; i <= 12; i++) { if(isLeapYear(date.year) && i == 2) days += 29; else days += mon_maxnum[i]; } for (int i = 1; i < this.month; i++) { if (isLeapYear(this.year) && i == 2) days += 29; else days += mon_maxnum[i]; } if (date.month == 2 && isLeapYear(date.year)) days = days + 29 - date.day + this.day; else days = days + mon_maxnum[date.month] - date.day + this.day; } else if (this.year == date.year && this.month > date.month) { days = this.day; if (isLeapYear(date.year) && date.month == 2) days = days + 29 - date.day; else days = days + mon_maxnum[date.month] - date.day; date.month += 1; for (int i = date.month; i < this.month; i++) if (isLeapYear(i)) { if (i == 2) days += 29; else days += mon_maxnum[i]; } } else days = this.day - date.day; for (int i = date.year + 1; i < this.year; i++) { if (isLeapYear(i)) days++; } } return days; } public String showDate() { return this.year+"-"+this.month+"-"+this.day; } }
解析:
判断日期是否合法
判断是否是闰年
判断当下日期是否为2月或12月
之后计算最终日期
心得:
这道题还未完全掌握,存在部分错误,是第二次作业的进阶版,需反复练习。
三,踩坑心得
(1)舍入错误
Symtm.out.print("1.0 - 0 1 - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1 - 0.1");
显示0.5000000000000001而不是0.5
(2)判断符的使用
错误:else if(year<=3&year>1){
}
正确:else if(year<=3&&year>1){
}
(3)多使用eclipse进行代码的输入,规范好代码的格式,做到更贴合企业的要求。
四,改进建议
在做题之前需看清题目的要求。在敲代码时注意格式,做到符合阿里的代码格式要求。看到题目后分析并画图,接下来一步一步完成内容。遇到不会的问题多去翻书,这本教材可以基本解决我们的所有问题,把不会的知识点记录下来,逐一攻克。
五,总结
经过这三次pta的练习,我已经大致熟悉基本java程序的书写。在之后的学习中,还需要加大类与对象的使用的练习,多去了解eclipse这个软件的使用方法。加油!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号