Copy List with Random Pointer
Question: There is a doubly linked list with next pointer and random pointer (points to an arbitrary node in list). You have to make a copy of the linked list and return. In the end original list shouldn't be modified. Time complexity should be O(n).
这个是微软经典list题目之一: 铁索连舟. 本来是想自己写一篇总结的, 但是网上那篇英文的是在是写的太好了, 干脆就直接来一篇翻译算了, 原文链接: 《Copy A Linked List With Next And Random Pointer》
问题描述: 有一个双向链表, 链表的每一个节点都有两个指针, 一个是next指向下一个节点, 另一个是random指针, 可以指向该链表的任意一个节点或者NULL. 要求你复制这个双向链表并且不得修改原来的那个链表, 时间复杂度要求O(n).
链表的结构体:
1 |
struct Node { |
2 |
int val; |
3 |
Node *next; |
4 |
Node *random; |
5 |
}; |
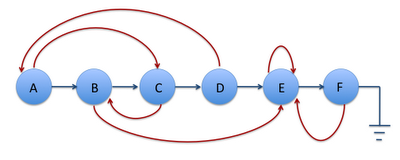
例子: 下图中的蓝色指针就是 next指针,红色指针是我们的 random 指针.
算法(答案):
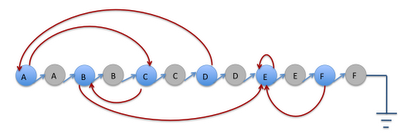
1) 将原链表中的每个节点都复制一遍并且将复制的节点插入到对应的原节点和该原节点下一个节点之间. 比如下面:
- 复制A(蓝色)得到A的copy(灰色) 插入到A(蓝色)和B(蓝色)之间
- 复制B(蓝色)得到B的copy(灰色) 插入到B(蓝色)和C(蓝色)之间
- 一直重复这个过程直到得到第N个个节点(原链表的最后一个节点)的copy
对应的第一幅图, 在第一个1)以后, 就能得到下图:
2) 第二步按照两个两个的次序(A, A’, B, B’……), 我们用A’代表A(蓝色)的复制, 复制那个random指针如下:
original->next->random = original->random->next;
可以这样做是因为 original->next 是我们的复制的节点(A’)而且original->random->next是原链表中的那个random指针的复制. 自己比划一下就能理解了. 所以original->next->random = original->random->next;的意思就是把复制链表中的节点的random指针赋值, 赋的值就是对应原链表中的相同位置上的节点(这个节点是在赋值链表上的而不是原链表的节点). 这里也可以看出来第一步1)的目的其实就是利用A–>A’–>B–>B’…这样的结构充分提供出了在复制链表中的random指针应该正确指向哪个节点的信息(也是这个题目的难点和关键).
3) 重建原链表已经抽离复制链表. 其实就是打断原链表和复制链表的指针连接:
original->next = original->next->next;
copy->next = copy->next->next;
特别小心以及注意最后节点的next = NULL
这个方法的时间复杂度是 O(n) time, 空间复杂度是O(1).
1 struct Node { 2 int val; 3 Node *next; 4 Node *random; 5 }; 6 7 //copy the linked list with head root (with random pointer) 8 Node* copy_list(Node* root) 9 { 10 Node *res; 11 12 Node* cur = root; 13 Node *next, *tmp; 14 15 //(1) Create the copy of every node in the list and insert 16 //it in original list between current and next node. 17 while(cur) 18 { 19 tmp = new Node(); 20 tmp->val = cur->val; 21 tmp->random = NULL; 22 tmp->next = cur->next; 23 next = cur->next; 24 cur->next = tmp; 25 cur = next; 26 } 27 28 //save result pointer 29 res = root->next; //A' 30 31 //(2) make the random pointer: Copy the arbitrary link for result 32 cur = root; 33 while(cur) 34 { 35 cur->next->random = cur->random->next; 36 cur = cur->next->next; //move 2 nodes at a time 37 } 38 39 //(3) 抽离复制链表以及重建原始链表: restore the original and copy linked lists 40 cur = root; 41 tmp = root->next; 42 while(cur && tmp) 43 { 44 cur->next = cur->next->next; 45 cur = cur->next; 46 if (tmp->next){ 47 //这里要小心注意判断, 也就是当复制链表到了最后一个node的时候, 例子中的F节点 48 //这F'(灰色)已经完整了, 而curr则需要cur->next = cur->next->next;来设置list tail的null 49 tmp->next = tmp->next->next; 50 tmp = tmp->next; 51 } 52 } 53 54 return res; 55 }
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer. 3 * class RandomListNode { 4 * int label; 5 * RandomListNode next, random; 6 * RandomListNode(int x) { this.label = x; } 7 * }; 8 */ 9 public class Solution { 10 public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { 11 // Note: The Solution object is instantiated only once and is reused by each test case. 12 if(head == null) return head; 13 RandomListNode old = head; 14 while(old != null){ 15 RandomListNode cpy =new RandomListNode(old.label); 16 cpy.next = old.next; 17 old.next = cpy; 18 old = cpy.next; 19 } 20 old = head; 21 while(old != null){ 22 old.next.random =(old.random != null ? old.random.next : null);23 old = old.next.next; 24 } 25 old = head; 26 RandomListNode newhead = head.next; 27 RandomListNode newcur = head.next; 28 while(old != null && newcur != null){ 29 old.next = old.next.next; 30 old = old.next; 31 if(newcur.next != null){ 32 newcur.next = newcur.next.next; 33 newcur = newcur.next; 34 } 35 } 36 return newhead; 37 } 38 }
posted on 2013-10-11 08:25 Step-BY-Step 阅读(938) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报