VAD(Virtual Address Descriptor)虚拟地址描述符
VAD树#
应用层进程会通过调用VirtualAlloc分配多个内存块,每个内存块包含1个或多个内存页。windows操作系统为了有效的管理这些内存块构建了一个AVL二叉树,这个AVL树就是VAD树。应用层的每一个内存块(包含VirtualAlloc申请的私有的和Mapping共享的)都对应一个VAD树结点(结构体类型为_MMVAD)。
//win7 32位
typedef struct _MMVAD
{
ULONG u1; //包含父结点
struct _MMVAD* LeftChild; //左子树
struct _MMVAD* RightChild; //右子树
ULONG StartingVpn; //内存块起始地址的页帧
ULONG EndingVpn; //内存块结束地址的页帧(对于4kb(0x1000)的页而言,内存块地址就是StartingVpn*0x1000~EndingVpn*0x1000+0xfff)
ULONG u; //_MMVAD_FLAGS类型的指针,包含了内存块的一些属性位
EX_PUSH_LOCK PushLock;
ULONG u5; //_MMVAD_FLAGS3类型的指针,包含了内存块的一些属性位
ULONG u2; //_MMVAD_FLAGS2类型的指针,包含了内存块的一些属性位
struct _SUBSECTION* Subsection; //包含了_CONTROL_AREA结构和_SEGMENT结构,含有更多的详细信息
struct _MSUBSECTION* MappedSubsection;
struct _MMPTE* FirstPrototypePte; //原型PTE,对于Mapped共享的内存块有意义(private私有内存块无意义)。第一个原型PTE
struct _MMPTE* LastContiguousPte; //原型PTE,对于Mapped共享的内存块有意义(private私有内存块无意义)。最后一个原型PTE
struct _LIST_ENTRY ViewLinks;
struct _EPROCESS* VadsProcess;
}MMVAD;
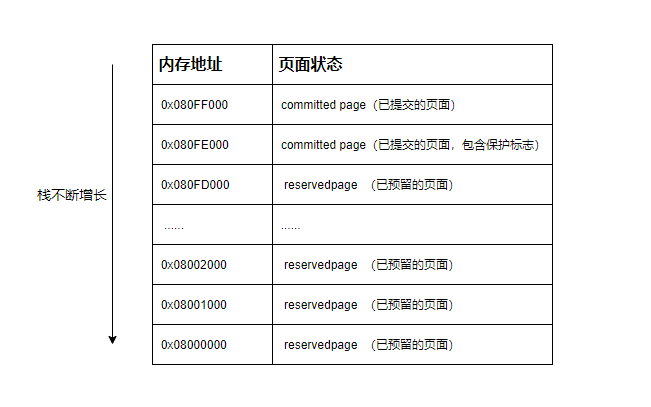
当我们调用VirtualAlloc时如果传入的参数flAllocationType的值为reserved保留,这时windows操作系统也会构造并增加一个VAD结点来描述这块内存块。但是因为只是预留了一块虚拟地址,操作系统并未为其映射实际的物理内存,所以此时此VAD结点是没有实际意义的。但是这样做的好处是通过较小的开销(VAD结点构造)来预留一块虚拟地址待需要使用再分配PTE页表等结构为其映射实际的物理内存。(线程栈就是这样做的,当线程栈首先预留一块较大的虚拟内存,随着线程栈的增长不断提交新的虚拟内存块,映射到实际的物理内存中)
与VAD有关的结构#
nt!_MMADDRESS_NODE
+0x000 u1 : <unnamed-tag>
+0x004 LeftChild : Ptr32 _MMADDRESS_NODE
+0x008 RightChild : Ptr32 _MMADDRESS_NODE
+0x00c StartingVpn : Uint4B
+0x010 EndingVpn : Uint4B
kd> dt _MMVAD_SHORT
nt!_MMVAD_SHORT
+0x000 u1 : <unnamed-tag>
+0x004 LeftChild : Ptr32 _MMVAD
+0x008 RightChild : Ptr32 _MMVAD
+0x00c StartingVpn : Uint4B
+0x010 EndingVpn : Uint4B
+0x014 u : <unnamed-tag>
+0x018 PushLock : _EX_PUSH_LOCK
+0x01c u5 : <unnamed-tag>
kd> DT _MMVAD
nt!_MMVAD
+0x000 u1 : <unnamed-tag>
+0x004 LeftChild : Ptr32 _MMVAD
+0x008 RightChild : Ptr32 _MMVAD
+0x00c StartingVpn : Uint4B
+0x010 EndingVpn : Uint4B
+0x014 u : <unnamed-tag>
+0x018 PushLock : _EX_PUSH_LOCK
+0x01c u5 : <unnamed-tag>
+0x020 u2 : <unnamed-tag>
+0x024 Subsection : Ptr32 _SUBSECTION
+0x024 MappedSubsection : Ptr32 _MSUBSECTION
+0x028 FirstPrototypePte : Ptr32 _MMPTE
+0x02c LastContiguousPte : Ptr32 _MMPTE
+0x030 ViewLinks : _LIST_ENTRY
+0x038 VadsProcess : Ptr32 _EPROCESS
_MMADDRESS_NODE, _MMVAD_SHORT与 _MMVAD三个结构很相似,_MMVAD_SHORT是_MMADDRESS_NODE的扩展,_MMVAD又是_MMVAD_SHORT和_MMADDRESS_NODE的扩展。因为对于Private私有内存来说并不涉及到section对象,所以其对应的VAD树结点应该是_MMVAD_SHORT类型,至于其余扩展字段对于Private私有内存块是没有意义的。_MMVAD扩展的结构是用来描述Section对象(Mapped内存)的。
nt!_MMVAD_FLAGS
+0x000 CommitCharge : Pos 0, 19 Bits //实际提交的页数
+0x000 NoChange : Pos 19, 1 Bit //是否允许应用层修改对应内存页的保护属性(置1的话,应用层调用VirtualProtect无法改变内存页的保护属性)
+0x000 VadType : Pos 20, 3 Bits //置1时表示此内存块为Exe的Mapped
+0x000 MemCommit : Pos 23, 1 Bit //提交状态(置1为已提交)
+0x000 Protection : Pos 24, 5 Bits //对应内存块的保护属性
+0x000 Spare : Pos 29, 2 Bits
+0x000 PrivateMemory : Pos 31, 1 Bit //私有内存块,调用VirtualAlloc申请的(置1为私有内存块Private,置0为映射Mapped(DLL/Exe))
kd> dt _MMVAD_FLAGS2
nt!_MMVAD_FLAGS2
+0x000 FileOffset : Pos 0, 24 Bits
+0x000 SecNoChange : Pos 24, 1 Bit
+0x000 OneSecured : Pos 25, 1 Bit
+0x000 MultipleSecured : Pos 26, 1 Bit
+0x000 Spare : Pos 27, 1 Bit
+0x000 LongVad : Pos 28, 1 Bit
+0x000 ExtendableFile : Pos 29, 1 Bit
+0x000 Inherit : Pos 30, 1 Bit
+0x000 CopyOnWrite : Pos 31, 1 Bit //写拷贝属性(置1为写拷贝)
_MMVAD的u成员对应的是_MMVAD_FLAGS结构体,u2成员对应的是_MMVAD_FLAGS2结构体,包含了对应内存块的属性信息。
typedef struct _SUBSECTION
{
struct _CONTROL_AREA* ControlArea;
struct _MMPTE* SubsectionBase;
struct _SUBSECTION* NextSubsection;
ULONG PtesInSubsection;
ULONG UnusedPtes;
struct _MM_AVL_TABLE* GlobalPerSessionHead; //此链表将所有Mapped类型并且需要映射到每一个进程中虚拟地址都一样的(SEC_BASED类型)内存块组织起来
ULONG u;
ULONG StartingSector;
ULONG NumberOfFullSectors;
}SUBSECTION,* PSUBSECTION;
_MMVAD._SUBSECTION结构中包含一个重要的结构_CONTROL_AREA。
struct _SEGMENT
{
struct _CONTROL_AREA* ControlArea;
ULONG TotalNumberOfPtes; //内存块包含的页数
ULONG SegmentFlags;
ULONG NumberOfCommittedPages;
ULONGLONG SizeOfSegment; //对应内存块的大小
union
{
struct _MMEXTEND_INFO* ExtendInfo;
void* BasedAddress; //对应内存块的基地址
};
EX_PUSH_LOCK SegmentLock;
ULONG u1;
ULONG u2;
struct _MMPTE* PrototypePte; //原型PTE
//_MMPTE ThePtes[0x1]; //内存块所有页面对应的PTE(一个大型PTE数组)
};
#pragma pack(push,1)
typedef struct _EX_FAST_REF
{
union
{
PVOID Object;
ULONG_PTR RefCnt : 3;
ULONG_PTR Value;
};
} EX_FAST_REF, * PEX_FAST_REF;
#pragma pack(pop)
typedef struct _CONTROL_AREA
{
struct _SEGMENT* Segment;
struct _LIST_ENTRY DereferenceList;
ULONG NumberOfSectionReferences;
ULONG NumberOfPfnReferences;
ULONG NumberOfMappedViews;
ULONG NumberOfUserReferences;
ULONG u;
ULONG FlushInProgressCount;
struct _EX_FAST_REF FilePointer; //指向_FILE_OBJECT
}CONTROL_AREA,* PCONTROL_AREA;
_CONTROL_AREA结构的FilePointer指向的是内存块对应的FILE_OBJECT对象(后3位需要置0),如果_FILE_OBJECT有效就可以得到对应文件的FileName等信息。
_CONTROL_AREA结构的Segment成员为_SEGMENT 结构,_SEGMENT.BasedAddress为对应内存块的基地址,_SEGMENT.SizeOfSegment为对应内存块的大小。
VAD树遍历#
通过驱动程序获取进程EPROCESS并遍历ActiveProcessLinks链表找到需要处理的进程(通过断此链可以实现进程隐藏),获取到对应进程的EPROCESS后获得其VADRoot根结点并进行遍历VAD树,代码如下:
#include <ntifs.h>
#pragma pack(push,1)
typedef struct _EX_FAST_REF
{
union
{
PVOID Object;
ULONG_PTR RefCnt : 3;
ULONG_PTR Value;
};
} EX_FAST_REF, * PEX_FAST_REF;
#pragma pack(pop)
struct _SEGMENT
{
struct _CONTROL_AREA* ControlArea;
ULONG TotalNumberOfPtes;
ULONG SegmentFlags;
ULONG NumberOfCommittedPages;
ULONGLONG SizeOfSegment;
union
{
struct _MMEXTEND_INFO* ExtendInfo;
void* BasedAddress;
};
EX_PUSH_LOCK SegmentLock;
ULONG u1;
ULONG u2;
struct _MMPTE* PrototypePte;
//_MMPTE ThePtes[0x1];
};
struct _CONTROL_AREA
{
struct _SEGMENT* Segment;
struct _LIST_ENTRY DereferenceList;
ULONG NumberOfSectionReferences;
ULONG NumberOfPfnReferences;
ULONG NumberOfMappedViews;
ULONG NumberOfUserReferences;
ULONG u;
ULONG FlushInProgressCount;
struct _EX_FAST_REF FilePointer;
};
struct _SUBSECTION
{
struct _CONTROL_AREA* ControlArea;
struct _MMPTE* SubsectionBase;
struct _SUBSECTION* NextSubsection;
ULONG PtesInSubsection;
ULONG UnusedPtes;
struct _MM_AVL_TABLE* GlobalPerSessionHead;
ULONG u;
ULONG StartingSector;
ULONG NumberOfFullSectors;
};
typedef struct _MMVAD
{
ULONG u1;
struct _MMVAD* LeftChild;
struct _MMVAD* RightChild;
ULONG StartingVpn;
ULONG EndingVpn;
ULONG u;
EX_PUSH_LOCK PushLock;
ULONG u5;
ULONG u2;
struct _SUBSECTION* Subsection;
struct _MSUBSECTION* MappedSubsection;
struct _MMPTE* FirstPrototypePte;
struct _MMPTE* LastContiguousPte;
struct _LIST_ENTRY ViewLinks;
struct _EPROCESS* VadsProcess;
}MMVAD;
typedef struct _MMADDRESS_NODE {
ULONG u1;
struct _MMADDRESS_NODE* LeftChild;
struct _MMADDRESS_NODE* RightChild;
ULONG StartingVpn;
ULONG EndingVpn;
}MMADDRESS_NODE, * PMMADDRESS_NODE;
typedef struct _MM_AVL_TABLE {
MMADDRESS_NODE BalancedRoot;
ULONG sTruct;
PVOID NodeHint;
PVOID NodeFreeHint;
}MM_AVL_TABLE, * PMM_AVL_TABLE;
VOID Unload(IN PDRIVER_OBJECT pDriverObject) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(pDriverObject);
DbgPrint("Driver UnLoad!");
}
//中序遍历VAD的AVL树
VOID _EnumVAD(PMMADDRESS_NODE pVad) {
if (pVad == NULL) return;
_EnumVAD(pVad->LeftChild);
//处理数据
ULONG uRetLen = 0;
MMVAD* Root = (MMVAD*)pVad;
POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION stFileBuffer = (POBJECT_NAME_INFORMATION)ExAllocatePool(PagedPool, 0x100);
if (MmIsAddressValid(Root->Subsection) && MmIsAddressValid(Root->Subsection->ControlArea) && stFileBuffer!=NULL)
{
if (MmIsAddressValid((PVOID)Root->Subsection->ControlArea->FilePointer.Value))
{
PFILE_OBJECT pFileObject = (PFILE_OBJECT)((Root->Subsection->ControlArea->FilePointer.Value >> 3) << 3);
if (MmIsAddressValid(pFileObject))
{
NTSTATUS Status = ObQueryNameString(pFileObject, stFileBuffer, 0x100, &uRetLen);
if (NT_SUCCESS(Status))
{
KdPrint(("Base:%08X Size:%dKb ", Root->Subsection->ControlArea->Segment->BasedAddress,\
(Root->Subsection->ControlArea->Segment->SizeOfSegment) / 0x1000));
KdPrint(("Name:%ws\n", stFileBuffer->Name.Buffer));
}
}
}
}
if (stFileBuffer)
{
ExFreePool(stFileBuffer);
}
_EnumVAD(pVad->RightChild);
return;
}
NTSTATUS _EnumProcess() {
ULONG VadRoot;
PEPROCESS pEprocess = NULL;
PEPROCESS pFirstEprocess = NULL;
ULONG ProcessName = 0; //指向进程的名称
ANSI_STRING szaTestingProcessName; //待检测进程的名称
ANSI_STRING szaProcessName; //进程的名称
//获得EPROCESS进程内核对象
pEprocess = PsGetCurrentProcess();
if (pEprocess == NULL) {
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
pFirstEprocess = pEprocess;
while (pEprocess) {
//获得进程的名称
ProcessName = (ULONG)pEprocess + 0x16c;
//获得VAD树根结点的地址
VadRoot = ((ULONG)pEprocess + 0x278);
RtlInitAnsiString(&szaProcessName, (PCSTR)ProcessName);
RtlInitAnsiString(&szaTestingProcessName, "test.exe");
if (RtlEqualString(&szaProcessName, &szaTestingProcessName, TRUE)) {
//遍历VAD的AVL树
_EnumVAD(((PMMADDRESS_NODE)VadRoot)->RightChild);
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
//继续遍历ActiveProcessLinks链表
pEprocess = (PEPROCESS)(*(ULONG*)((ULONG)pEprocess + 0x0b8) - 0x0b8);
if (pEprocess == pFirstEprocess) {
break;
}
}
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
NTSTATUS DriverEntry(IN PDRIVER_OBJECT pDriverObject, IN PUNICODE_STRING pRegistryPath) {
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(pRegistryPath);
pDriverObject->DriverUnload = Unload;
_EnumProcess();
return STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
注意_MM_AVL_TABLE.BalancedRoot结构为MMADDRESS_NODE ,其实际是个内嵌结构体不能扩展到_MMVAD结构,其LeftChild未使用,RightChild才为真正的根结点。
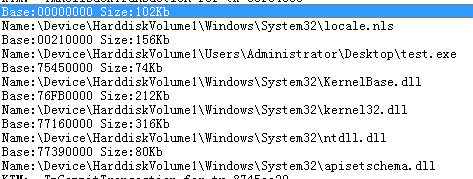
最后DebugView的打印结果为:
VAD隐藏#
_MMVAD.StartingVpn = _MMVAD.EndingVpn#
直接在VAD树遍历的处理代码中加入_MMVAD.StartingVpn = _MMVAD.EndingVpn即可。
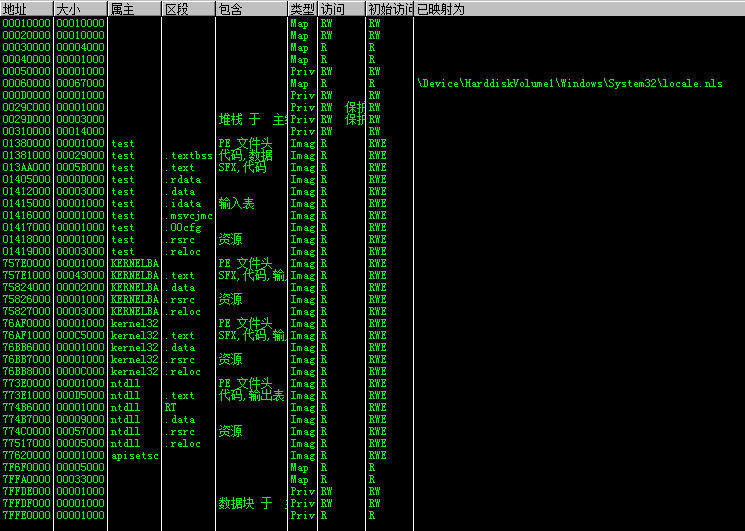
隐藏前OD查看内存为:
隐藏后OD查看内存为
VAD结点融合(宿主_MMVAD.EndingVpn = 待隐藏_MMVAD.StartingVpn)#
通过VAD结点融合,将需要隐藏的内存块的VAD结点合并到其他VAD结点中。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构